UNIT III - Photochemistry
... i) Fluorescence: When a molecule or atom absorbs radiation of higher frequency (shorter wavelength), it gets excited. Then the excited atom or molecule re-emits the radiation of the same frequency or lower frequency within short time (about 10-8 sec.). This process is called fluorescence, stops as ...
... i) Fluorescence: When a molecule or atom absorbs radiation of higher frequency (shorter wavelength), it gets excited. Then the excited atom or molecule re-emits the radiation of the same frequency or lower frequency within short time (about 10-8 sec.). This process is called fluorescence, stops as ...
11.2 - Partial Refraction and Total Internal Reflection
... Sometimes when you look out a window, you see what is outside as well as your own reflection This is because some light reflects and some light refracts at a surface between two media that have different indices of refraction This phenomenon is called partial reflection and refraction ...
... Sometimes when you look out a window, you see what is outside as well as your own reflection This is because some light reflects and some light refracts at a surface between two media that have different indices of refraction This phenomenon is called partial reflection and refraction ...
How to find ET with infrared light
... then reradiate into space the waste energy, with an infrared radiation profile similar to the planet’s natural heat. Thus, a way to find such an advanced ETC (which would be far more technologically innovative than Earth-based societies) is to look for stars that are invisible or faint at optical wa ...
... then reradiate into space the waste energy, with an infrared radiation profile similar to the planet’s natural heat. Thus, a way to find such an advanced ETC (which would be far more technologically innovative than Earth-based societies) is to look for stars that are invisible or faint at optical wa ...
View/Download-PDF - International Journal of Computer Science
... which are sensitive to electromagnetic radiation [8, 9] like hospitals, airplanes, petrochemical and nuclear power plants, etc. Moreover, the inability of light to propagate through walls offers better level of network security. Signal Modulation in VLC The building block devices in VLC are incohere ...
... which are sensitive to electromagnetic radiation [8, 9] like hospitals, airplanes, petrochemical and nuclear power plants, etc. Moreover, the inability of light to propagate through walls offers better level of network security. Signal Modulation in VLC The building block devices in VLC are incohere ...
The search for extraterrestrial intelligence has mostly revolved
... then reradiate into space the waste energy, with an infrared radiation profile similar to the planet’s natural heat. Thus, a way to find such an advanced ETC (which would be far more technologically innovative than Earth-based societies) is to look for stars that are invisible or faint at optical wa ...
... then reradiate into space the waste energy, with an infrared radiation profile similar to the planet’s natural heat. Thus, a way to find such an advanced ETC (which would be far more technologically innovative than Earth-based societies) is to look for stars that are invisible or faint at optical wa ...
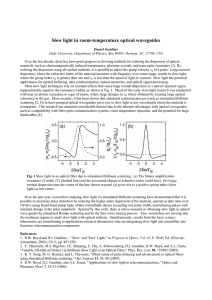
Star Gauging (Star Counting)
... The comet swept past the Sun during the summer of 1862 and made a return appearance in December 1992. By no coincidence, in the early 1990s the Perseids performed spectacularly — displaying a new, additional, much briefer peak with outbursts of up to several hundred meteors per hour in 1991, 1992, a ...
... The comet swept past the Sun during the summer of 1862 and made a return appearance in December 1992. By no coincidence, in the early 1990s the Perseids performed spectacularly — displaying a new, additional, much briefer peak with outbursts of up to several hundred meteors per hour in 1991, 1992, a ...
Chapter 14 Stellar Corpses Stellar Corpses White Dwarfs White
... about that of the Earth • Despite their high surface temperature of about 25,000 K, they are very dim due to their small size • Their light is generated from residual heat (no fusion) in the star’s interior ...
... about that of the Earth • Despite their high surface temperature of about 25,000 K, they are very dim due to their small size • Their light is generated from residual heat (no fusion) in the star’s interior ...
HI in Local Group Dwarf Galaxies
... rgas ~ NHI,core/R ~ 1 x 1020 cm-2/600 pc = 5.4 x10-2 cm-3 v ~ 60 km s-1 (1D velocity dispersion for Local Group dwarf galaxies from Van den Bergh 1999a) ...
... rgas ~ NHI,core/R ~ 1 x 1020 cm-2/600 pc = 5.4 x10-2 cm-3 v ~ 60 km s-1 (1D velocity dispersion for Local Group dwarf galaxies from Van den Bergh 1999a) ...
Sun, Moon, Earth,
... – Neutron Stars: Forms from the remains of the old star. • Very very high density and very very small. – As much as three times the mass of our star in an area the size of a city. – Some give off regular pulses of radio waves and are called pulsars. (these were originally called LGMs). ...
... – Neutron Stars: Forms from the remains of the old star. • Very very high density and very very small. – As much as three times the mass of our star in an area the size of a city. – Some give off regular pulses of radio waves and are called pulsars. (these were originally called LGMs). ...
Our Island in Space
... Light from distant galaxies appeared ““red red shifted.” shifted.” In 1929, Hubble recognized this as a Doppler shift. He concluded that galaxies were moving away rapidly. No galaxies were found to be moving toward Earth. ...
... Light from distant galaxies appeared ““red red shifted.” shifted.” In 1929, Hubble recognized this as a Doppler shift. He concluded that galaxies were moving away rapidly. No galaxies were found to be moving toward Earth. ...
The Photoelectric Effect
... The photoelectric effect was discovered by Heinrich Hertz in the 1880's when he observed that under the right conditions, when light is shined on a metal, electrons are ejected from the surface of the metal. This process was called photoemission. In 1880 light was believed to be completely wavelike ...
... The photoelectric effect was discovered by Heinrich Hertz in the 1880's when he observed that under the right conditions, when light is shined on a metal, electrons are ejected from the surface of the metal. This process was called photoemission. In 1880 light was believed to be completely wavelike ...
–1– 28. HIGH-MASS STAR FORMATION: THEORY 28.1. The Effects
... mass range, however, which suggests that competitive accretion does not determine the IMF at lower masses either. Second, competitive accretion is effective only if the virial parameter is much less than observed, as discussed in Lecture 24. The most radical and imaginative model for the formation o ...
... mass range, however, which suggests that competitive accretion does not determine the IMF at lower masses either. Second, competitive accretion is effective only if the virial parameter is much less than observed, as discussed in Lecture 24. The most radical and imaginative model for the formation o ...
FantasticTrip - Cooper Church of Christ
... the little Sun star is very small How Long is a Light-Year? The light-year is a measure of distance, not time. It is the distance that a beam of light, moving in a straight line, travels in one year. To obtain an idea of the size of a light-year, take the circumference of the earth (24,900 miles), l ...
... the little Sun star is very small How Long is a Light-Year? The light-year is a measure of distance, not time. It is the distance that a beam of light, moving in a straight line, travels in one year. To obtain an idea of the size of a light-year, take the circumference of the earth (24,900 miles), l ...
The abundance of 26Al-rich planetary systems in the Galaxy
... Al at the solar abundance, the invoked SN needs to be at a small (<2 pc), fine-tuned, distance from the nascent solar system whose exact value depends on the SN mass (Looney et al. 2006). The Orion Nebula has often been presented as the paradigm of such a situation (Hester et al. 2004). However, the ...
... Al at the solar abundance, the invoked SN needs to be at a small (<2 pc), fine-tuned, distance from the nascent solar system whose exact value depends on the SN mass (Looney et al. 2006). The Orion Nebula has often been presented as the paradigm of such a situation (Hester et al. 2004). However, the ...
Astronomy Assignment #1
... 12. A star with the same color as the Sun is found to produce a luminosity 81 times larger. What is its radius, compared to the Sun’s? The following three problems all use the Stefan-Boltzmann Law L 4R 2 T 4 . We can avoid painful and error prone calculations, by using a ratio technique as ill ...
... 12. A star with the same color as the Sun is found to produce a luminosity 81 times larger. What is its radius, compared to the Sun’s? The following three problems all use the Stefan-Boltzmann Law L 4R 2 T 4 . We can avoid painful and error prone calculations, by using a ratio technique as ill ...
Understanding Large Numbers 1/15
... 1. Find a way to make your number more real. The key is to find a value that we understand and then to convert your number into something more understandable. You should find an unrelated example that still uses the number and property you’ve been assigned (for example, if you are given a measuremen ...
... 1. Find a way to make your number more real. The key is to find a value that we understand and then to convert your number into something more understandable. You should find an unrelated example that still uses the number and property you’ve been assigned (for example, if you are given a measuremen ...
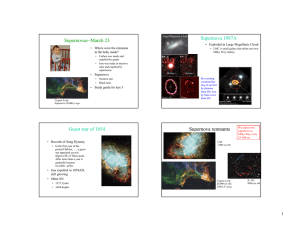
Supernovae March 23 − Supernova 1987A
... ring lit up first by photons from SN, now by blast wave from SN. ...
... ring lit up first by photons from SN, now by blast wave from SN. ...
Slow light in room-temperature optical waveguides
... dispersion, where the refractive index of the material increases with frequency over some range, results in slow light, where the group index ng is greater than one and υg is less than the speed of light in vacuum. Slow light has potential applications for optical buffering, data synchronization, op ...
... dispersion, where the refractive index of the material increases with frequency over some range, results in slow light, where the group index ng is greater than one and υg is less than the speed of light in vacuum. Slow light has potential applications for optical buffering, data synchronization, op ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.