Krupp (1999) broadly defines the interdisciplinary field
... problems. From Rapa Nui, the constellation happens to pass through the zenith—that is, it can appear directly overhead. There are long intervals of time when it is far from the horizon. Post hoc reasoning yields the following, other unique attributes of Sagittarius: Sagittarius culminates on the zen ...
... problems. From Rapa Nui, the constellation happens to pass through the zenith—that is, it can appear directly overhead. There are long intervals of time when it is far from the horizon. Post hoc reasoning yields the following, other unique attributes of Sagittarius: Sagittarius culminates on the zen ...
The Atmosphere - MIT Haystack Observatory
... • Optimal usable frequency : 13.6 MHz • Most abundant molecules present: Nitrogen in F1 sub layer and Oxygen in F2 sub layer. ...
... • Optimal usable frequency : 13.6 MHz • Most abundant molecules present: Nitrogen in F1 sub layer and Oxygen in F2 sub layer. ...
Mode Identification
... ▸ The stellar flux is determined by the metallicity, the effective temperature, the mass and the radius, or equivalently, by the gravity, of the star. ▸ Parameters are often not well known; their errors propagate into the final selection of the best l value. ...
... ▸ The stellar flux is determined by the metallicity, the effective temperature, the mass and the radius, or equivalently, by the gravity, of the star. ▸ Parameters are often not well known; their errors propagate into the final selection of the best l value. ...
ASTR-1020: Astronomy II Course Lecture Notes - Faculty
... and as such, helium ash gets uniformly mixed throughout the star. No inert He core develops, hence no H-shell burning and no expansion into a red giant. After hydrogen is exhausted, the entire star contracts until the helium becomes degenerate (see the white dwarf section [§VIII.A]) and the star bec ...
... and as such, helium ash gets uniformly mixed throughout the star. No inert He core develops, hence no H-shell burning and no expansion into a red giant. After hydrogen is exhausted, the entire star contracts until the helium becomes degenerate (see the white dwarf section [§VIII.A]) and the star bec ...
Name______________________ Period________
... 65. According to the law of conservation of mass, the total mass of the reacting substances is a. always more than the total mass of the products. b. always less than the total mass of the products. c. sometimes more and sometimes less than the total mass of the products. d. always equal to the tota ...
... 65. According to the law of conservation of mass, the total mass of the reacting substances is a. always more than the total mass of the products. b. always less than the total mass of the products. c. sometimes more and sometimes less than the total mass of the products. d. always equal to the tota ...
light - Churchill High School
... The intensity of light is the amount of energy per second falling on a surface. Most light sources distribute their light equally in all directions, making a spherical pattern. Because light spreads out in a sphere, the intensity decreases the farther you get from the source. ...
... The intensity of light is the amount of energy per second falling on a surface. Most light sources distribute their light equally in all directions, making a spherical pattern. Because light spreads out in a sphere, the intensity decreases the farther you get from the source. ...
Sec 29.3 - Highland High School
... The first nuclear fusion reaction to ignite in a protostar is always the conversion of hydrogen to helium. Once this reaction begins, the star becomes stable because it then has sufficient internal heat to produce the pressure needed to balance gravity. The object is then truly a star. ...
... The first nuclear fusion reaction to ignite in a protostar is always the conversion of hydrogen to helium. Once this reaction begins, the star becomes stable because it then has sufficient internal heat to produce the pressure needed to balance gravity. The object is then truly a star. ...
Exposure Time Calculator for LUCI - USER MANUAL
... The exposure time calculator (ETC) roughly calculates the exposure time of LUCI at the Large Binocular Telescope (LBT). There is a wide choice of different model spectra available (e.g. different main sequence stars). It is also possible to select a blackbody spectrum or a single-line spectrum as an ...
... The exposure time calculator (ETC) roughly calculates the exposure time of LUCI at the Large Binocular Telescope (LBT). There is a wide choice of different model spectra available (e.g. different main sequence stars). It is also possible to select a blackbody spectrum or a single-line spectrum as an ...
Measuring the Complete Transverse Spatial Mode Spectrum
... by optical elements by knowing the effects on the spatial spectral component of generic signals [4]. Recently, an intense research activity on multimode light has burgeoned in quantum information, communication and imaging [5], with successful demonstrations spanning from nanodisplacement measuremen ...
... by optical elements by knowing the effects on the spatial spectral component of generic signals [4]. Recently, an intense research activity on multimode light has burgeoned in quantum information, communication and imaging [5], with successful demonstrations spanning from nanodisplacement measuremen ...
The Stars education kit - Student activities 5-10
... Betelgeuse is a red supergiant star in the constellation of Orion. The surface temperature of Betelgeuse is approximately 3000 degrees Celsius. Its diameter fluctuates in size from about 300 to 400 times the Sun’s diameter. It is estimated to be about 427 light years away. Aldebaran is a red giant s ...
... Betelgeuse is a red supergiant star in the constellation of Orion. The surface temperature of Betelgeuse is approximately 3000 degrees Celsius. Its diameter fluctuates in size from about 300 to 400 times the Sun’s diameter. It is estimated to be about 427 light years away. Aldebaran is a red giant s ...
Galaxies on Sub-Galactic Scales
... many other things a significant number of optically elusive satellite galaxies (Willman et al. 2005a,b; Belokurov et al. 2006a,b, 2007b, 2009, 2010; Sakamoto & Hasegawa 2006; Zucker et al. 2006b; Walsh et al. 2007; Liu et al. 2008; Grillmair 2009) as well as several largescale stellar streams whose ...
... many other things a significant number of optically elusive satellite galaxies (Willman et al. 2005a,b; Belokurov et al. 2006a,b, 2007b, 2009, 2010; Sakamoto & Hasegawa 2006; Zucker et al. 2006b; Walsh et al. 2007; Liu et al. 2008; Grillmair 2009) as well as several largescale stellar streams whose ...
17 April 2013 When Galaxies Collide Professor Carolin Crawford
... The bulge is a yellowy-white colour, revealing that it is an accumulation of older stars, similar to the population found in an elliptical galaxy. The spiral arms within the disc are notably much bluer, as they trace regions where massive star formation is currently active (blue stars are short-liv ...
... The bulge is a yellowy-white colour, revealing that it is an accumulation of older stars, similar to the population found in an elliptical galaxy. The spiral arms within the disc are notably much bluer, as they trace regions where massive star formation is currently active (blue stars are short-liv ...
Copyright 1995 Scientific American, Inc.
... mark the end of a pattern of stellar evolution that now appears to be more likely than astronomers once thought. More than half the stars in the sky belong to binary systems; perhaps one in 100 of the most massive pairs will ultimately become neutron star binaries. Gravitational waves given oÝ by th ...
... mark the end of a pattern of stellar evolution that now appears to be more likely than astronomers once thought. More than half the stars in the sky belong to binary systems; perhaps one in 100 of the most massive pairs will ultimately become neutron star binaries. Gravitational waves given oÝ by th ...
The life cycle of stars
... 9. Using the images you saw, and what you learned from this activity, draw and label a diagram showing the life cycle of a star. ...
... 9. Using the images you saw, and what you learned from this activity, draw and label a diagram showing the life cycle of a star. ...
Introduction to Astronomy
... Observing Tools - 3 • Telescopes – Refracting – Reflecting – Catadioptric ...
... Observing Tools - 3 • Telescopes – Refracting – Reflecting – Catadioptric ...
The extended structure of the dwarf irregular galaxy Sagittarius⋆⋆⋆
... Telescope (HST) programme (Gallart 2008) that performs extremely deep observations in small central fields of a small sample of isolated galaxies, searching for the effects of SN feedback and/or cosmic re-ionisation, since they may be recorded in the star formation history (SFH) of the systems (see, ...
... Telescope (HST) programme (Gallart 2008) that performs extremely deep observations in small central fields of a small sample of isolated galaxies, searching for the effects of SN feedback and/or cosmic re-ionisation, since they may be recorded in the star formation history (SFH) of the systems (see, ...
Power Point
... telescope (nearby this not the case – one has to target individual galaxies in clusters one by one) • around a cluster there are many more galaxies that lie within a single telescope pointing than for a typical field pointing ...
... telescope (nearby this not the case – one has to target individual galaxies in clusters one by one) • around a cluster there are many more galaxies that lie within a single telescope pointing than for a typical field pointing ...
Chapter 10
... Once many stars are plotted on an H–R diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. ...
... Once many stars are plotted on an H–R diagram, a pattern begins to form: These are the 80 closest stars to us; note the dashed lines of constant radius. ...
Patterns in the Night Sky
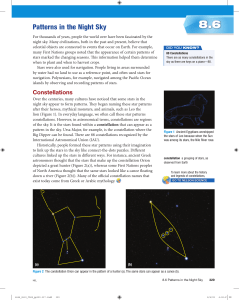
... Although we can mark out the same constellations our ancient ancestors saw thousands of years ago, their component stars are not in exactly the same location as they were then. Precise observations of stars reveal that they move relative to each other in space, but these changes in position occur s ...
... Although we can mark out the same constellations our ancient ancestors saw thousands of years ago, their component stars are not in exactly the same location as they were then. Precise observations of stars reveal that they move relative to each other in space, but these changes in position occur s ...
Quantum Fluctuation in the Inflating Universe
... 7.3. Comparison to other results Figure 35 compares our results from Table 3 (modeling approach) with other measurements from galaxy surveys, but must be interpreted with care. The UZC points may contain excess large-scale power due to selection function effects (Padmanabhan et al. 2000; THX02), and ...
... 7.3. Comparison to other results Figure 35 compares our results from Table 3 (modeling approach) with other measurements from galaxy surveys, but must be interpreted with care. The UZC points may contain excess large-scale power due to selection function effects (Padmanabhan et al. 2000; THX02), and ...
chapter35
... Retroreflection: reflected light travels in parallel but opposite in direction to the incident light. Can be achieved by two plane mirrors with an angle of 90o between them. Applications include ...
... Retroreflection: reflected light travels in parallel but opposite in direction to the incident light. Can be achieved by two plane mirrors with an angle of 90o between them. Applications include ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.