Introduction - Assets - Cambridge
... physical significances. One may seek the total number of each specific kind of atom in the solar system, for example. Today these reside overwhelmingly within the Sun owing to its dominant mass, although complemented to lesser small degrees by the planets. One speaks of this set of abundances as “so ...
... physical significances. One may seek the total number of each specific kind of atom in the solar system, for example. Today these reside overwhelmingly within the Sun owing to its dominant mass, although complemented to lesser small degrees by the planets. One speaks of this set of abundances as “so ...
The Initial Mass Function (IMF) Continued
... • Masses range from ~1000M~ to ~1x106M~ • Metallicity ranges from 0.004 of solar to about solar • Some are very strongly centrally concentrated while others are not • Integrated light has a spectral type ranging from F3 to G5: most of the variation is due to the variation in metallicity {redder = mo ...
... • Masses range from ~1000M~ to ~1x106M~ • Metallicity ranges from 0.004 of solar to about solar • Some are very strongly centrally concentrated while others are not • Integrated light has a spectral type ranging from F3 to G5: most of the variation is due to the variation in metallicity {redder = mo ...
Principles of light guidance
... lines and are reflected back into the jet when they reach its outer surface. Hence the light rays follow the jet of water as it curves towards the ground under gravity. ...
... lines and are reflected back into the jet when they reach its outer surface. Hence the light rays follow the jet of water as it curves towards the ground under gravity. ...
Where stars are born: Javier Blasco-Herrera
... Fabry-Perot interferometry . . . . . The etalon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Data acquisition . . . . . . . . . . . ...
... Fabry-Perot interferometry . . . . . The etalon . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Data acquisition . . . . . . . . . . . ...
Slide 1
... We produce immersion gratings by a process of photolithography and chemical micromachining. ...
... We produce immersion gratings by a process of photolithography and chemical micromachining. ...
SPITZER/MIPS 24 µm OBSERVATIONS OF GALAXY CLUSTERS
... at 0.02 ≤ z ≤ 0.83 that have a total of 1315 spectroscopically confirmed members. The core of our sample is composed of five clusters spanning the entire redshift range with large spectroscopic membership, uniform multifilter optical photometry and deep SST/MIPS imaging1 . For the part of the analys ...
... at 0.02 ≤ z ≤ 0.83 that have a total of 1315 spectroscopically confirmed members. The core of our sample is composed of five clusters spanning the entire redshift range with large spectroscopic membership, uniform multifilter optical photometry and deep SST/MIPS imaging1 . For the part of the analys ...
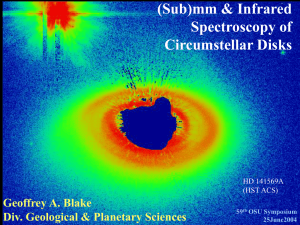
25June2004 - Division of Geological and Planetary Sciences
... •Objects thought to be ~face on have the narrowest line widths, highly inclined systems the largest. •As the excitation energy increases, so does the line width (small effect). •Consistent with disk emission, radii range from 0.5-5 AU at high J. •Low J lines also resonantly scatter 5 mm photons to m ...
... •Objects thought to be ~face on have the narrowest line widths, highly inclined systems the largest. •As the excitation energy increases, so does the line width (small effect). •Consistent with disk emission, radii range from 0.5-5 AU at high J. •Low J lines also resonantly scatter 5 mm photons to m ...
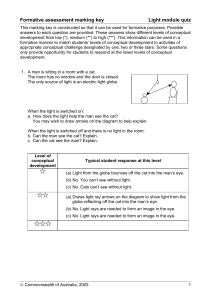
Formative assessment marking key: Light Module Quiz
... b. Explain why light rays bend when they pass from one medium to another (eg from air to glass), striking the boundary between the two media at an angle. c. When white light passes through the corner of an aquarium or through a glass prism a spectrum of colours may be formed. Why does white light br ...
... b. Explain why light rays bend when they pass from one medium to another (eg from air to glass), striking the boundary between the two media at an angle. c. When white light passes through the corner of an aquarium or through a glass prism a spectrum of colours may be formed. Why does white light br ...
Expected Coalescence Rates of NS/NS Binaries for Ground Based
... P( ): probability for a newly formed NS/NS to coalesce in a timescale 0 : minimum coalescence time * : mean timescale required for the newly formed massive system to evolve into two NSs ...
... P( ): probability for a newly formed NS/NS to coalesce in a timescale 0 : minimum coalescence time * : mean timescale required for the newly formed massive system to evolve into two NSs ...
LAB, A2 Color, Polarized Light
... 1. Take one polarizer. As you look through it, observe the effects. Try rotating the polarizer and see if it makes a difference. Answer question 4(a). What happens when you look through a single polarizer and rotate it? ________________________________________________________________________________ ...
... 1. Take one polarizer. As you look through it, observe the effects. Try rotating the polarizer and see if it makes a difference. Answer question 4(a). What happens when you look through a single polarizer and rotate it? ________________________________________________________________________________ ...
The nature of the faint galaxies in the Hubble Deep Field
... the PISA software in the Starlink environment. These were further confirmed using the FOCAS/IRAF source identification package. Aperture photometry was then carried out with PHOTOM on all the identified galaxies, using an aperture size of O.5-arcsec radius. For 0.5 < z < 3, this corresponds to a lin ...
... the PISA software in the Starlink environment. These were further confirmed using the FOCAS/IRAF source identification package. Aperture photometry was then carried out with PHOTOM on all the identified galaxies, using an aperture size of O.5-arcsec radius. For 0.5 < z < 3, this corresponds to a lin ...
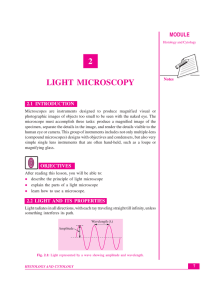
Lesson-2 Light Microscopy
... photographic images of objects too small to be seen with the naked eye. The microscope must accomplish three tasks: produce a magnified image of the specimen, separate the details in the image, and render the details visible to the human eye or camera. This group of instruments includes not only mul ...
... photographic images of objects too small to be seen with the naked eye. The microscope must accomplish three tasks: produce a magnified image of the specimen, separate the details in the image, and render the details visible to the human eye or camera. This group of instruments includes not only mul ...
REVIEWS The formation of the first stars and galaxies Volker Bromm
... matter interacts with the baryons only via gravity. However, dark matter can indirectly affect the dynamics of a pre-stellar gas. A popular candidate for CDM is the neutralino, for which the self-annihilation cross-section is large. Neutralino dark matter is thus expected to pairannihilate in very d ...
... matter interacts with the baryons only via gravity. However, dark matter can indirectly affect the dynamics of a pre-stellar gas. A popular candidate for CDM is the neutralino, for which the self-annihilation cross-section is large. Neutralino dark matter is thus expected to pairannihilate in very d ...
The Life Cycles of Stars
... mass of a star, in addition, decides the temperature of a star’s core each time it goes into a period of flexion. Depending on the stage in a star’s development, various elements are formed within the core of the star, with the heaviest sustainable material being iron, when a massive star forms an i ...
... mass of a star, in addition, decides the temperature of a star’s core each time it goes into a period of flexion. Depending on the stage in a star’s development, various elements are formed within the core of the star, with the heaviest sustainable material being iron, when a massive star forms an i ...
Document
... hits a spot in the surface that is at a slightly different angle, causing the rays to go in many different directions. • Diffuse reflection is the reflection of light rays from a rough surface. ...
... hits a spot in the surface that is at a slightly different angle, causing the rays to go in many different directions. • Diffuse reflection is the reflection of light rays from a rough surface. ...
The Sun - MrsAllisonMagee
... • Nuclear Fusion: the process by which nuclei of small atoms combine to form a new, more massive nucleus, which results in large amounts of energy being released. • Nuclear fusion produces the sun’s energy. • In our sun hydrogen fuses into helium. ...
... • Nuclear Fusion: the process by which nuclei of small atoms combine to form a new, more massive nucleus, which results in large amounts of energy being released. • Nuclear fusion produces the sun’s energy. • In our sun hydrogen fuses into helium. ...
Intro
... Our visual system is most sensitive when the photopigments have not absorbed any light for about 30 minutes. Under these conditions we say that the photopigments are fully regenerated. When the rod photopigments are exposed to light they undergo a process called bleaching. It is called bleaching bec ...
... Our visual system is most sensitive when the photopigments have not absorbed any light for about 30 minutes. Under these conditions we say that the photopigments are fully regenerated. When the rod photopigments are exposed to light they undergo a process called bleaching. It is called bleaching bec ...
Booklet 5 – Stellar Processes and Evolution
... Stars with a mass of between 8 and 20 solar masses have a more complex evolution. Initially, they evolve in the same way as low mass stars, turning into red giants and undergoing a core helium burning phase. In medium mass stars, however, the burning of helium into carbon is no longer the end phase ...
... Stars with a mass of between 8 and 20 solar masses have a more complex evolution. Initially, they evolve in the same way as low mass stars, turning into red giants and undergoing a core helium burning phase. In medium mass stars, however, the burning of helium into carbon is no longer the end phase ...
Document
... • Drop matter from a high “potential” • About 10% efficient when falling onto massive bodies with very small radii. ...
... • Drop matter from a high “potential” • About 10% efficient when falling onto massive bodies with very small radii. ...
Krupp (1999) broadly defines the interdisciplinary field
... problems. From Rapa Nui, the constellation happens to pass through the zenith—that is, it can appear directly overhead. There are long intervals of time when it is far from the horizon. Post hoc reasoning yields the following, other unique attributes of Sagittarius: Sagittarius culminates on the zen ...
... problems. From Rapa Nui, the constellation happens to pass through the zenith—that is, it can appear directly overhead. There are long intervals of time when it is far from the horizon. Post hoc reasoning yields the following, other unique attributes of Sagittarius: Sagittarius culminates on the zen ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.