* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download The Sun - MrsAllisonMagee
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
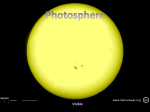
The Sun Chapter 29 Composition of the Sun • 75% of the sun’s mass is hydrogen. • 99% of the sun’s mass is hydrogen and helium. • A stars spectrum determines the amounts of elements that are present in a star. Nuclear Fusion • Nuclear Fusion: the process by which nuclei of small atoms combine to form a new, more massive nucleus, which results in large amounts of energy being released. • Nuclear fusion produces the sun’s energy. • In our sun hydrogen fuses into helium. Nuclear Fusion •In our sun hydrogen fuses into helium. •The mass that is lost during fusion becomes energy, we measure this energy using Einstein’s equation E = mc2 . The Sun’s Interior • The Core: the center of the sun where it is extremely hot and under high amounts of pressure. (15,000,000 C) The Sun’s Interior • Radiative Zone: the zone of the sun’s interior that is between the core and the convective zone and in which energy moves by radiation. The Sun’s Interior • Convective Zone: the region of the sun’s interior that is between the radiative zone and the photosphere and in which energy is carried upward by convection. The Sun’s Atmosphere • Photosphere: the innermost layer of the solar atmosphere and is the visible surface of the sun from which we see light. The Sun’s Atmosphere • Chromosphere: the thin layer of the sun that is just above the photosphere and that glows a reddish color during eclipses. The Sun’s Atmosphere • Corona: the outermost layer of the sun’s atmosphere made of gas. Sunspots • Sunspot: a dark area of the photosphere of the sun that is cooler than the surrounding areas and that has a strong magnetic field. Solar Ejections • Prominence: a loop of relatively cool, incandescent gas that extends above the photosphere. Solar Ejections • Solar Flare: an explosive release of energy that comes from the sun and that is associated with magnetic disturbances on the sun’s surface. Solar Ejections • Coronal Mass Ejection: a part of coronal gas that is thrown into space from the sun. Auroras • Aurora: colored light produced by charged particles from the solar wind and from the magnetosphere that react with and excite the oxygen and nitrogen of Earth’s upper atmosphere; usually seen in the sky near Earth’s magnetic poles.