
9.1 Introduction 9.2 Static Models
... and the average mass of a particle, hmi = µ mH . µ is the mean molecular weight which we have already encountered several times. Let us consider its value for fully ionised gas (a reasonably good assumption in the interiors of stars, where the most abundant elements, H and He, are fully ionised. How ...
... and the average mass of a particle, hmi = µ mH . µ is the mean molecular weight which we have already encountered several times. Let us consider its value for fully ionised gas (a reasonably good assumption in the interiors of stars, where the most abundant elements, H and He, are fully ionised. How ...
History of Physics
... As proved below, Schrodinger's Equation (SE) creates a mathematical model for an atom that physically does not exist and therefore Schrodinger's Equation does not represent physical reality. 1. SE was originally created to derive the wavelengths of light emitted by excited hydrogen: Four lines in th ...
... As proved below, Schrodinger's Equation (SE) creates a mathematical model for an atom that physically does not exist and therefore Schrodinger's Equation does not represent physical reality. 1. SE was originally created to derive the wavelengths of light emitted by excited hydrogen: Four lines in th ...
Detectable radio flares following gravitational waves from mergers of
... detectable for years at 150 megahertz, as well as at 1.4 gigahertz, from slightly shorter distances. The radio transient RT 19870422 (ref. 11) has the properties predicted by our model, and its most probable origin is the merger of a compact neutron-star/neutron-star binary. The lack of radio detect ...
... detectable for years at 150 megahertz, as well as at 1.4 gigahertz, from slightly shorter distances. The radio transient RT 19870422 (ref. 11) has the properties predicted by our model, and its most probable origin is the merger of a compact neutron-star/neutron-star binary. The lack of radio detect ...
October 2012 - astronomy for beginners
... the Summer Triangle find a dark location away from any lights that will reduce your night vision and look towards the south. Almost overhead is Deneb the brightest star in the constellation of Cygnus (the Swan). Look towards the west (right) about the width of your two clenched fists when held up at ...
... the Summer Triangle find a dark location away from any lights that will reduce your night vision and look towards the south. Almost overhead is Deneb the brightest star in the constellation of Cygnus (the Swan). Look towards the west (right) about the width of your two clenched fists when held up at ...
When will a neutron star collapse to a black hole?
... fascinating objects known to exist in our universe: Such a star has a mass that is up to twice that of the sun but a radius of only a dozen kilometres: hence it has an enormous density, thousands of billions of times that of the densest element on Earth. An important property of neutron stars, disti ...
... fascinating objects known to exist in our universe: Such a star has a mass that is up to twice that of the sun but a radius of only a dozen kilometres: hence it has an enormous density, thousands of billions of times that of the densest element on Earth. An important property of neutron stars, disti ...
EBL - UCSC Physics - University of California, Santa Cruz
... Joel Primack & Alberto Domínguez Data from (non-) attenuation of gamma rays from blazars and gamma ray bursts (GRBs) give upper limits on the EBL from the UV to the mid-IR that are only a little above the lower limits from observed galaxies. New data on attenuation of gamma rays from blazers now lea ...
... Joel Primack & Alberto Domínguez Data from (non-) attenuation of gamma rays from blazars and gamma ray bursts (GRBs) give upper limits on the EBL from the UV to the mid-IR that are only a little above the lower limits from observed galaxies. New data on attenuation of gamma rays from blazers now lea ...
Compiled questions (docx 32 kB)
... Question: Concentrating electromagnetic radiation from the far to the near field. 1. Explain the concepts of quality factor and effective mode volume in order to characterize an optical cavity. For conventional dielectric cavities, what is the lower limit of the mode volume? 2. Describe how nanoscal ...
... Question: Concentrating electromagnetic radiation from the far to the near field. 1. Explain the concepts of quality factor and effective mode volume in order to characterize an optical cavity. For conventional dielectric cavities, what is the lower limit of the mode volume? 2. Describe how nanoscal ...
Slide sem título - Instituto de Física / UFRJ
... black holes, have been proposed. We can obtain an upper limit for the charge a black hole can acquire by demanding that the singularity is not naked. In the Reissner-Nordstrøm spacetime, this requirement sets Q2 M2 and the maximum charge a black hole can have is Qmax ~ 1020(M/M) C. If a black hol ...
... black holes, have been proposed. We can obtain an upper limit for the charge a black hole can acquire by demanding that the singularity is not naked. In the Reissner-Nordstrøm spacetime, this requirement sets Q2 M2 and the maximum charge a black hole can have is Qmax ~ 1020(M/M) C. If a black hol ...
Prof. Kenney C lass 8 September 26, 2016
... basic idea: outer layers of star heat up so much that they expand so much that outer layers are ejected * pressure wins over gravity! * no hydrostatic equilibrium in outer layers ...
... basic idea: outer layers of star heat up so much that they expand so much that outer layers are ejected * pressure wins over gravity! * no hydrostatic equilibrium in outer layers ...
Power Punt on Binary Asteroids
... Lightcurves of asteroids • Asteroids spin (typically in 8 hours) and as they spin, they change brightness as we see more or less reflected sunlight • By measuring lightcurves (brightness vs time) from different viewing angles, can get 3dim shape of asteroid • Binary asteroids show additional “bumps ...
... Lightcurves of asteroids • Asteroids spin (typically in 8 hours) and as they spin, they change brightness as we see more or less reflected sunlight • By measuring lightcurves (brightness vs time) from different viewing angles, can get 3dim shape of asteroid • Binary asteroids show additional “bumps ...
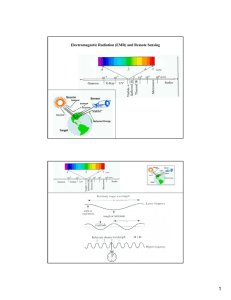
Electromagnetic Radiation (EMR) and Remote Sensing
... materials and which portion of the EMR is being measured. The nature of this reflected component over a range of wavelengths is called spectral response patterns. Spectral patterns are descriptions of the degree to which energy is reflected in different regions of the spectrum. ...
... materials and which portion of the EMR is being measured. The nature of this reflected component over a range of wavelengths is called spectral response patterns. Spectral patterns are descriptions of the degree to which energy is reflected in different regions of the spectrum. ...
The impact of rotation on the line profiles of Wolf
... in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), also made use of fluxconvolution with rotation profiles of very large rotational velocities for a few of them. Sander et al. (2012) used the same technique for two WO stars. So far, at least ten WR stars have been identified to exhibit round and broad line profil ...
... in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), also made use of fluxconvolution with rotation profiles of very large rotational velocities for a few of them. Sander et al. (2012) used the same technique for two WO stars. So far, at least ten WR stars have been identified to exhibit round and broad line profil ...
Document
... gets transmitted (albeit at low levels) into this zone maintaining some transport there. • Accretion rate is not constant in the dead zone long term steady state is not possible ...
... gets transmitted (albeit at low levels) into this zone maintaining some transport there. • Accretion rate is not constant in the dead zone long term steady state is not possible ...
A crash course in optics
... The eye and the brain has the tendency not to see what’s actually there but what it thinks is there – this makes judging color, brightness and ...
... The eye and the brain has the tendency not to see what’s actually there but what it thinks is there – this makes judging color, brightness and ...
An improved classification of B[e]-type stars
... and Ciatti et al. (1974). The stars were sometimes indicated as ”BQ[ ] stars”, were the ”Q” indicates abnormal spectra with forbidden lines. Most authors noticed that the stars also show strong permitted lines, such as the Balmer lines, and a strong infrared excess in the near and mid-IR at λ > 5 µm ...
... and Ciatti et al. (1974). The stars were sometimes indicated as ”BQ[ ] stars”, were the ”Q” indicates abnormal spectra with forbidden lines. Most authors noticed that the stars also show strong permitted lines, such as the Balmer lines, and a strong infrared excess in the near and mid-IR at λ > 5 µm ...
Origin of close binary systems
... Hoogerwerf, R.; de Bruijne, J. H. J.; de Zeeuw, P. T. 2001, A&A 365, 49 ...
... Hoogerwerf, R.; de Bruijne, J. H. J.; de Zeeuw, P. T. 2001, A&A 365, 49 ...
Apr 2017 - Bays Mountain Park
... plenty to choose from. There are about 9 galaxies the lie within this constellation. Some of the more notable ones are M81 and M82, which are sometimes referred to as Bode’s Galaxy and the Cigar Galaxy. Another well-known galaxy is M101, which is known as the Pinwheel Galaxy. Finally, there is also ...
... plenty to choose from. There are about 9 galaxies the lie within this constellation. Some of the more notable ones are M81 and M82, which are sometimes referred to as Bode’s Galaxy and the Cigar Galaxy. Another well-known galaxy is M101, which is known as the Pinwheel Galaxy. Finally, there is also ...
- EPJ Web of Conferences
... 95% of the initial HATNet transit detections turn out to be false positives; see for example Latham et al. 2009). These false positives typically involve multiple star systems which produce light curves derived from wide-field survey images that are consistent with a planet transiting a single star. ...
... 95% of the initial HATNet transit detections turn out to be false positives; see for example Latham et al. 2009). These false positives typically involve multiple star systems which produce light curves derived from wide-field survey images that are consistent with a planet transiting a single star. ...
Physical Science Performance Level Descriptors
... Given data, determine values for various atomic properties (e.g., atomic number, mass number); Distinguish between the isotopes and ions of an element and describe properties of elements based on their position in the periodic table; Determine the chemical names of simple compounds given their formu ...
... Given data, determine values for various atomic properties (e.g., atomic number, mass number); Distinguish between the isotopes and ions of an element and describe properties of elements based on their position in the periodic table; Determine the chemical names of simple compounds given their formu ...
22. Dark Matter and the Fate of the Universe
... • the neutrino…detected coming from the Sun • their masses are so low & speeds so high, they will escape the gravitational pull of a galaxy…they can not account for all of the dark matter observed ...
... • the neutrino…detected coming from the Sun • their masses are so low & speeds so high, they will escape the gravitational pull of a galaxy…they can not account for all of the dark matter observed ...
幻灯片 1
... Times of Maximum Light • 47 times of maximum light in total (13 from our work) • Time span ~ 60 years • New ephemeris formular - HJDmax = 2432144.4377 + 0.267041135 x E - ΔT0 = 0.003 day, ΔP = 0.000000045 day ...
... Times of Maximum Light • 47 times of maximum light in total (13 from our work) • Time span ~ 60 years • New ephemeris formular - HJDmax = 2432144.4377 + 0.267041135 x E - ΔT0 = 0.003 day, ΔP = 0.000000045 day ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.














![An improved classification of B[e]-type stars](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/015293756_1-5784ffaa4d7d33ad2633e3151daf904c-300x300.png)






