Ch. 20
... The Hyades cluster, shown here, is also rather young; its main-sequence turnoff indicates an age of about 600 million years. ...
... The Hyades cluster, shown here, is also rather young; its main-sequence turnoff indicates an age of about 600 million years. ...
Document
... 2 tests: public cluster (30 – 35 machines LXPLUS) and dedicated cluster (15 machines LXSHARE) ...
... 2 tests: public cluster (30 – 35 machines LXPLUS) and dedicated cluster (15 machines LXSHARE) ...
Project 2. CCD Photometry
... Rather than just have one apparent magnitude, measured across the entire visible spectrum we can use a filter to restrict the incoming light to a narrow waveband. If, for instance, we use a filter that only allows light in the blue part of the spectrum, we can measure a star's blue ...
... Rather than just have one apparent magnitude, measured across the entire visible spectrum we can use a filter to restrict the incoming light to a narrow waveband. If, for instance, we use a filter that only allows light in the blue part of the spectrum, we can measure a star's blue ...
Wide-eyed Telescope Finds its First Transiting
... Search for Planets) programme. Using wide-angle camera lenses, backed by topquality CCD cameras, the SuperWASP team have been repeatedly surveying several million stars over vast swathes of the sky, looking for the tiny dips in the starlight caused when a planet passes in front of its star. This is ...
... Search for Planets) programme. Using wide-angle camera lenses, backed by topquality CCD cameras, the SuperWASP team have been repeatedly surveying several million stars over vast swathes of the sky, looking for the tiny dips in the starlight caused when a planet passes in front of its star. This is ...
Wide-eyed Telescope Finds its First Transiting
... Search for Planets) programme. Using wide-angle camera lenses, backed by topquality CCD cameras, the SuperWASP team have been repeatedly surveying several million stars over vast swathes of the sky, looking for the tiny dips in the starlight caused when a planet passes in front of its star. This is ...
... Search for Planets) programme. Using wide-angle camera lenses, backed by topquality CCD cameras, the SuperWASP team have been repeatedly surveying several million stars over vast swathes of the sky, looking for the tiny dips in the starlight caused when a planet passes in front of its star. This is ...
Electrons In Atoms - Norwell Public Schools
... o How are the frequencies of light given off by an atom related to changes in electron energies? • Light ________ ______ by an electron moving from a _________ to a ________ energy level has a ____________ directly _______________ to the _________ _________ of the electron. o Each ___________ pro ...
... o How are the frequencies of light given off by an atom related to changes in electron energies? • Light ________ ______ by an electron moving from a _________ to a ________ energy level has a ____________ directly _______________ to the _________ _________ of the electron. o Each ___________ pro ...
IND 6 - 1 Stars and Stellar Evolution In order to better understand
... A low mass star (less than 8 times the mass of our Sun ( < 8 Msun)) eventually ejects its outer layers to produce a planetary nebula. The now naked stellar core remaining is called a white dwarf (because it is very hot but dim). In contrast, a high-mass star, more than 8 times the mass of our Su ...
... A low mass star (less than 8 times the mass of our Sun ( < 8 Msun)) eventually ejects its outer layers to produce a planetary nebula. The now naked stellar core remaining is called a white dwarf (because it is very hot but dim). In contrast, a high-mass star, more than 8 times the mass of our Su ...
Vast Spaces Of The Universe
... But Gamma is estimated by astronomers to be very much larger than the others, judging from its luminosity and taking into account its enormous distance. Recent revised calculations show it to be so far away that its light takes 95 years to get here, and that it is, therefore, some 6,200,000 times as ...
... But Gamma is estimated by astronomers to be very much larger than the others, judging from its luminosity and taking into account its enormous distance. Recent revised calculations show it to be so far away that its light takes 95 years to get here, and that it is, therefore, some 6,200,000 times as ...
Tuneability of amplified spontaneous emission through control of the waveguide-mode... in conjugated polymer films
... the ASE taken from Fig. 2 共circles兲. We find that for the five thinnest films, the zero-order TE mode is the only mode guided in the film whereas for the thickest film 共156 nm兲 light below 590 nm can also be guided in the zero-order TM mode. The figure also shows clearly that for thick films 共154–76 ...
... the ASE taken from Fig. 2 共circles兲. We find that for the five thinnest films, the zero-order TE mode is the only mode guided in the film whereas for the thickest film 共156 nm兲 light below 590 nm can also be guided in the zero-order TM mode. The figure also shows clearly that for thick films 共154–76 ...
Answers to Coursebook questions – Chapter E4
... be seen or easily detected. This is divided between WIMPS and MACHOS. WIMPS (massive weakly interacting particles) may include neutrinos and exotic particles predicted by models of particle physics e.g. supersymmetric particles. These have masses similar to those of atomic nuclei and interact via th ...
... be seen or easily detected. This is divided between WIMPS and MACHOS. WIMPS (massive weakly interacting particles) may include neutrinos and exotic particles predicted by models of particle physics e.g. supersymmetric particles. These have masses similar to those of atomic nuclei and interact via th ...
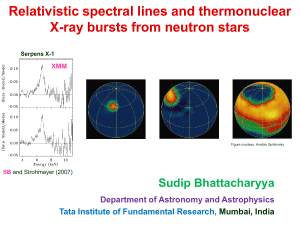
Broad Relativistic Iron Lines from Neutron Star LMXBs
... (4) observer’s inclination angle w.r.t. NS spin axis: i; (5) beaming (due to NS atmosphere) parameter: n [specific intensity as a function of angle (in emitter’s frame) from surface normal is given by I() cosn() ]; (6) background. ...
... (4) observer’s inclination angle w.r.t. NS spin axis: i; (5) beaming (due to NS atmosphere) parameter: n [specific intensity as a function of angle (in emitter’s frame) from surface normal is given by I() cosn() ]; (6) background. ...
Q1. Table 1 shows information about different light bulbs. The bulbs
... The results show a negative correlation: the more hours a mobile phone is used each day, the lower the sperm count. However, the results do not necessarily mean using a mobile phone causes the reduced sperm count. ...
... The results show a negative correlation: the more hours a mobile phone is used each day, the lower the sperm count. However, the results do not necessarily mean using a mobile phone causes the reduced sperm count. ...
lightandeye - Leon County Schools
... Light and the Human Eye (cont.) • The retina is a layer of special light-sensitive cells in the back of the eye. • In the retina, chemical reactions produce nerve signals that the optic nerve sends to your brain. • Rod cells and cone cells are two types of lightsensitive cells in your retina. • Rod ...
... Light and the Human Eye (cont.) • The retina is a layer of special light-sensitive cells in the back of the eye. • In the retina, chemical reactions produce nerve signals that the optic nerve sends to your brain. • Rod cells and cone cells are two types of lightsensitive cells in your retina. • Rod ...
electron orbits atomic spectra the Bohr atom
... More specifically, it is not difficult to show that the angular momentum is quantized in units of h/2, which we call ħ. L = n h / 2 = n ħ . ...
... More specifically, it is not difficult to show that the angular momentum is quantized in units of h/2, which we call ħ. L = n h / 2 = n ħ . ...
Agenda - Relativity Group
... • As the 3 M star evolved into a red giant – tidal forces began to deform the star – the surface got close enough to the other star so that gravity… – pulled matter from it onto the other star ...
... • As the 3 M star evolved into a red giant – tidal forces began to deform the star – the surface got close enough to the other star so that gravity… – pulled matter from it onto the other star ...
The structure and evolution of stars
... there are four basic equations to describe structure. All physical quantities depend on the distance from the centre of the star alone 1) Equation of hydrostatic equilibrium: at each radius, forces due to pressure differences balance gravity 2) Conservation of mass 3) Conservation of energy : at ...
... there are four basic equations to describe structure. All physical quantities depend on the distance from the centre of the star alone 1) Equation of hydrostatic equilibrium: at each radius, forces due to pressure differences balance gravity 2) Conservation of mass 3) Conservation of energy : at ...
What is Radio Astronomy?
... Visible light has wavelengths in the region of 500nm, that is, 5.0x10-7 meters From a physics standpoint, there's no difference between visible light, and microwave/radio-wave “light”. Living things have receptors for only a tiny part of the EM spectrum ...
... Visible light has wavelengths in the region of 500nm, that is, 5.0x10-7 meters From a physics standpoint, there's no difference between visible light, and microwave/radio-wave “light”. Living things have receptors for only a tiny part of the EM spectrum ...
April - Bristol Astronomical Society
... for locating a number of objects scattered across the sky. After finding that most of the objects on their list were a bit too faint, a new list was put together and the test re-started. The GoTo telescope was very accurate and the object being observed was always near the centre of the field of vie ...
... for locating a number of objects scattered across the sky. After finding that most of the objects on their list were a bit too faint, a new list was put together and the test re-started. The GoTo telescope was very accurate and the object being observed was always near the centre of the field of vie ...
Spectroscopy – Lecture 1
... If in a region of the star the opacity changes, then the star can block energy (photons) which can be subsequently released in a later phase of the pulsation. Helium and and Hydrogen ionization zones of the star are normally where this works. Consider the Helium ionization zone in the interior of a ...
... If in a region of the star the opacity changes, then the star can block energy (photons) which can be subsequently released in a later phase of the pulsation. Helium and and Hydrogen ionization zones of the star are normally where this works. Consider the Helium ionization zone in the interior of a ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.