Neutron Stars and Black Holes
... a. The protons and electrons, being charged particles, are all ejected during the supernova event by the strong magnetic field. b. The electrons and protons combine to form neutrons and ...
... a. The protons and electrons, being charged particles, are all ejected during the supernova event by the strong magnetic field. b. The electrons and protons combine to form neutrons and ...
Placing Our Solar System in Context
... rare among sun-like stars in the Milky Way galaxy? Primordial Disk Evolution: - disks around lower mass stars are less massive and live longer than their more massive counterparts. - large dispersion in evolutionary times could indicate dispersion in initial conditions. - evolution appears to procee ...
... rare among sun-like stars in the Milky Way galaxy? Primordial Disk Evolution: - disks around lower mass stars are less massive and live longer than their more massive counterparts. - large dispersion in evolutionary times could indicate dispersion in initial conditions. - evolution appears to procee ...
WASP-7: The brightest transiting-exoplanet system in the Southern
... In addition to the spectral analysis, we have also used TYCHO, DENIS and 2MASS magnitudes to estimate the effective temperature using the Infrared Flux Method (Blackwell & Shallis 1977). This gives Teff = 6370 ± 150 K, which is in close agreement with that obtained from the spectroscopic analysis. T ...
... In addition to the spectral analysis, we have also used TYCHO, DENIS and 2MASS magnitudes to estimate the effective temperature using the Infrared Flux Method (Blackwell & Shallis 1977). This gives Teff = 6370 ± 150 K, which is in close agreement with that obtained from the spectroscopic analysis. T ...
Star Constellations
... Ancient Babylonian astronomers created the Zodiac. The Zodiac is a circle that divides the ecliptic into twelve 30-degree zones. Each zone contains a constellation, many of them animals. Horoscopes based on these astrological signs first appeared in Ptolemaic Egypt in around 50 BC. These early peopl ...
... Ancient Babylonian astronomers created the Zodiac. The Zodiac is a circle that divides the ecliptic into twelve 30-degree zones. Each zone contains a constellation, many of them animals. Horoscopes based on these astrological signs first appeared in Ptolemaic Egypt in around 50 BC. These early peopl ...
Current Challenges Facing Planet Transit Surveys
... promising of the remaining extrasolar planet systems. The requisite photometric precision can be achieved with amateur-grade, commercially-available CCD cameras. Amateur telescopes provide more than enough aperture to gather the requisite flux (recall that Charbonneau et al., 2000 used a 10 cm apert ...
... promising of the remaining extrasolar planet systems. The requisite photometric precision can be achieved with amateur-grade, commercially-available CCD cameras. Amateur telescopes provide more than enough aperture to gather the requisite flux (recall that Charbonneau et al., 2000 used a 10 cm apert ...
Telescopes
... • Clouds, rain, and snow don’t interfere • Observations at an entirely different frequency; get totally different information ...
... • Clouds, rain, and snow don’t interfere • Observations at an entirely different frequency; get totally different information ...
Gemini - Sochias
... Contrast at larger radii is limited by array controller issues, read noise, and short exposure times used for these tests (ADI) ...
... Contrast at larger radii is limited by array controller issues, read noise, and short exposure times used for these tests (ADI) ...
Radio to infrared spectra of latetype galaxies
... using the IRAM 30-m telescope; our model fit (based on Planck HFI) predicts ∼2.3 Jy at the same frequency (∼3σ higher). This discrepancy is likely due to the much larger beam size of Planck, which will capture more of the extended emission. We find a best-fitting free–free emission measure of 920 ± ...
... using the IRAM 30-m telescope; our model fit (based on Planck HFI) predicts ∼2.3 Jy at the same frequency (∼3σ higher). This discrepancy is likely due to the much larger beam size of Planck, which will capture more of the extended emission. We find a best-fitting free–free emission measure of 920 ± ...
Spectroscopic methods for biology and medicine
... and frequency domain. The resulting Fourier transformation (FT) methods allow the measurement of spin correlation (→ ”multidimensional spectroscopy”) and therefore the structural characterization of macromolecular systems. The same properties are used for the tomographic imaging of tissue on a macro ...
... and frequency domain. The resulting Fourier transformation (FT) methods allow the measurement of spin correlation (→ ”multidimensional spectroscopy”) and therefore the structural characterization of macromolecular systems. The same properties are used for the tomographic imaging of tissue on a macro ...
Lecture 16: Iron Core Collapse, Neutron Stars
... is halted and turned around, but it is heated to such high temperature that the iron is disintegrated to unbound neutrons and protons. This costs a lot of energy. All burning since the main sequence is undone ...
... is halted and turned around, but it is heated to such high temperature that the iron is disintegrated to unbound neutrons and protons. This costs a lot of energy. All burning since the main sequence is undone ...
Chapter 10
... • Asteroids are small, generally rocky bodies that orbit Sun • Most asteroids (thousands) lie in the asteroid belt, a region between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter • The first asteroid (Ceres) of this asteroid belt swarm was discovered as a result of a search for the “missing planet” of Bode’s law • ...
... • Asteroids are small, generally rocky bodies that orbit Sun • Most asteroids (thousands) lie in the asteroid belt, a region between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter • The first asteroid (Ceres) of this asteroid belt swarm was discovered as a result of a search for the “missing planet” of Bode’s law • ...
powerpoint
... • The core basically becomes one giant atom (and the electrons fuse with the protons). • The energy to do this (remember it takes energy to break down atoms if they are smaller than iron) comes from the gravitational collapse. ...
... • The core basically becomes one giant atom (and the electrons fuse with the protons). • The energy to do this (remember it takes energy to break down atoms if they are smaller than iron) comes from the gravitational collapse. ...
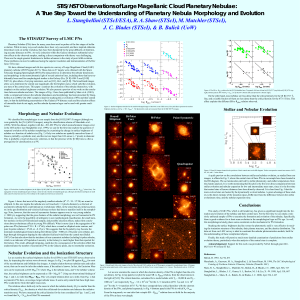
STIS/HST Observations of Large Magellanic Cloud Planetary
... asymmetric nebulae here could indicate an evolutionary effect, in the sense that any initial asymmetry in the gas distribution and velocity field may not have had time to manifest itself in the morphology. Note, however, that the onset of asymmetric features appears even in very young nebulae (< 200 ...
... asymmetric nebulae here could indicate an evolutionary effect, in the sense that any initial asymmetry in the gas distribution and velocity field may not have had time to manifest itself in the morphology. Note, however, that the onset of asymmetric features appears even in very young nebulae (< 200 ...
The Photoelectric Effect
... Millikan. Millikan refused to believe Einstein’s theory because it contradicted the well-established wave theory of light. After a decade of work, however, he was forced to concede that Einstein’s idea was the only explanation that fit his experimental results. Millikan performed a quantitative stud ...
... Millikan. Millikan refused to believe Einstein’s theory because it contradicted the well-established wave theory of light. After a decade of work, however, he was forced to concede that Einstein’s idea was the only explanation that fit his experimental results. Millikan performed a quantitative stud ...
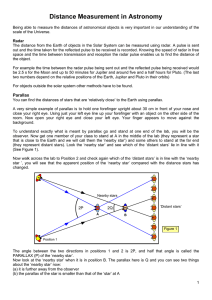
Distance Measurement in Astronomy
... The distance from the Earth of objects in the Solar System can be measured using radar. A pulse is sent out and the time taken for the reflected pulse to be received is recorded. Knowing the speed of radar in free space and the time between transmission and reception the radar pulse enables us to fi ...
... The distance from the Earth of objects in the Solar System can be measured using radar. A pulse is sent out and the time taken for the reflected pulse to be received is recorded. Knowing the speed of radar in free space and the time between transmission and reception the radar pulse enables us to fi ...
Thermonuclear Reactions: The Beginning and the
... thereby temporarily increasing that star's apparent luminosity. As these gravitational microlenses seem to be especially abundant in the halo of our galaxy (and presumably in halos of other galaxies), they — together with neutron stars and black holes — could account for the 90% of "missing dark mat ...
... thereby temporarily increasing that star's apparent luminosity. As these gravitational microlenses seem to be especially abundant in the halo of our galaxy (and presumably in halos of other galaxies), they — together with neutron stars and black holes — could account for the 90% of "missing dark mat ...
Chapter 13 The Stellar Graveyard
... around 1.0 M⊙, its luminosity is very consistent, and can be used as a standard candle for the measurement of distance to distant galaxies (Chapter 15). The amount of energy produced by white dwarf supernovae and massive star supernovae are about the same. But the properties of the light emitted fro ...
... around 1.0 M⊙, its luminosity is very consistent, and can be used as a standard candle for the measurement of distance to distant galaxies (Chapter 15). The amount of energy produced by white dwarf supernovae and massive star supernovae are about the same. But the properties of the light emitted fro ...
A Direct Empirical Proof of the Existence of Dark Matter
... mass within 100 kpc apertures centered on the BCGs and X-ray plasma peaks are shown in Table 2. This aperture size was chosen as smaller apertures had sig nificantly higher kappa measurement errors and larger apertures resulted in significant overlap of the apertures. Plasma masses were computed from ...
... mass within 100 kpc apertures centered on the BCGs and X-ray plasma peaks are shown in Table 2. This aperture size was chosen as smaller apertures had sig nificantly higher kappa measurement errors and larger apertures resulted in significant overlap of the apertures. Plasma masses were computed from ...
Astronomical spectroscopy

Astronomical spectroscopy is the study of astronomy using the techniques of spectroscopy to measure the spectrum of electromagnetic radiation, including visible light, which radiates from stars and other hot celestial objects. Spectroscopy can be used to derive many properties of distant stars and galaxies, such as their chemical composition, temperature, density, mass, distance, luminosity, and relative motion using Doppler shift measurements.