“Conscious” Dorsal Stream
... were observed in ocular saccades, pursuit and optokinetik nistagmus. Tactile stimuli applied to the contralesional side of the face also failed to elicit orienting responses. Single neurons studies showed that most F4 neurons discharge in association with monkey’s active movements (Gentilucci et al. ...
... were observed in ocular saccades, pursuit and optokinetik nistagmus. Tactile stimuli applied to the contralesional side of the face also failed to elicit orienting responses. Single neurons studies showed that most F4 neurons discharge in association with monkey’s active movements (Gentilucci et al. ...
Receptive Field Properties of Single Neurons in Rat Primary Visual
... cells could be divided in two populations: complex-like (43%; F1/F0 , 1), responding mainly with unmodulated elevation in discharge, and simple-like (57%; F1/F0 . 1), having their frequency of discharges mainly modulated at the fundamental stimulus frequency. This distribution of cells according to ...
... cells could be divided in two populations: complex-like (43%; F1/F0 , 1), responding mainly with unmodulated elevation in discharge, and simple-like (57%; F1/F0 . 1), having their frequency of discharges mainly modulated at the fundamental stimulus frequency. This distribution of cells according to ...
Jennifer S. Lund
... the first year as his technician I became a Ph.D. student since I was intrigued to develop new experimental paradigms rather than carry out the routine histology he had hired me to do. I developed a truly baroque thesis project involving teaching split-brain monkeys to adapt their reaching behavior ...
... the first year as his technician I became a Ph.D. student since I was intrigued to develop new experimental paradigms rather than carry out the routine histology he had hired me to do. I developed a truly baroque thesis project involving teaching split-brain monkeys to adapt their reaching behavior ...
Limitations of Neural Map Topography for Decoding Spatial
... requires estimation only of the one-dimensional distribution of ri for each stimulus. We therefore computed the conditional probability that each cell i had response ri given that stimulus sj was presented, P&ri " sj '. Nc $ Ns histograms were computed (Nc: number of cells, and Ns: number of stimuli ...
... requires estimation only of the one-dimensional distribution of ri for each stimulus. We therefore computed the conditional probability that each cell i had response ri given that stimulus sj was presented, P&ri " sj '. Nc $ Ns histograms were computed (Nc: number of cells, and Ns: number of stimuli ...
Functional Properties of Parietal Visual Neurons: Mechanisms of
... and in-field properties are determined by the behavioral state of the animal at the time of study (Mountcastle et al., 1981); they also vary with the parameters of the stimuli used to establish them. We define the relations between the frequency of discharge of PVNs and stimulus speed and emphasize ...
... and in-field properties are determined by the behavioral state of the animal at the time of study (Mountcastle et al., 1981); they also vary with the parameters of the stimuli used to establish them. We define the relations between the frequency of discharge of PVNs and stimulus speed and emphasize ...
Sensory uncertainty decoded from visual cortex
... thought to arise, in part, from internal neural noise affecting the fidelity of cortical orientation representations. We asked whether this trial-bytrial variability in the fidelity of internal knowledge was reflected in fMRI activation patterns. We addressed this question using a modelbased decodin ...
... thought to arise, in part, from internal neural noise affecting the fidelity of cortical orientation representations. We asked whether this trial-bytrial variability in the fidelity of internal knowledge was reflected in fMRI activation patterns. We addressed this question using a modelbased decodin ...
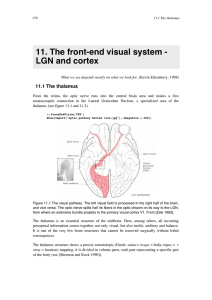
11. The front-end visual system - LGN and cortex
... One speculative option is that they may be modeled as processing some (polynomial?) function of the neighboring derivative cells, and thus be involved in complex differential features (see also [Alonso1998a]). As Ohzawa states: "Complex cell receptive fields are not that interesting when measured wi ...
... One speculative option is that they may be modeled as processing some (polynomial?) function of the neighboring derivative cells, and thus be involved in complex differential features (see also [Alonso1998a]). As Ohzawa states: "Complex cell receptive fields are not that interesting when measured wi ...
Transcripts/2_4 1
... g. We presume that all of this circuitry is helping to modulate or regulate alertness or awareness of visual space. But it doesn’t seem to have very big effects; it must be the case that small subtle shadings of the response patterns of these cells must have behaviorally big consequences. XX. In pri ...
... g. We presume that all of this circuitry is helping to modulate or regulate alertness or awareness of visual space. But it doesn’t seem to have very big effects; it must be the case that small subtle shadings of the response patterns of these cells must have behaviorally big consequences. XX. In pri ...
Visual Response Properties of Neurons in Four Extrastriate Visual
... and background responses. Progressions of receptive fields from the upper visual quadrant to the lower quadrant and reversals of progressions at the vertical and horizontal meridians were used to locate the extrastriate areas and their boundaries by comparison with the known organization of owl monk ...
... and background responses. Progressions of receptive fields from the upper visual quadrant to the lower quadrant and reversals of progressions at the vertical and horizontal meridians were used to locate the extrastriate areas and their boundaries by comparison with the known organization of owl monk ...
A Dynamic Field Theory of Visual Recognition in Infant Looking... Gregor Schöner Sammy Perone () and John P. Spencer ()
... category membership or recognized the novel exemplar as belonging to the familiar category. Infants are said to have learned an exclusive category if they increase their looking to an out-of-category exemplar, but they are said to have learned an inclusive category if they look at low levels to both ...
... category membership or recognized the novel exemplar as belonging to the familiar category. Infants are said to have learned an exclusive category if they increase their looking to an out-of-category exemplar, but they are said to have learned an inclusive category if they look at low levels to both ...
The Constructive Nature of Visual Processing
... temporal hemiretinas carrying input from one hemifield join in the optic tract, which extends to the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus. The lateral geniculate nucleus in primates consists of six layers, each of which receives input from either the ipsilateral or the contralateral eye. Becau ...
... temporal hemiretinas carrying input from one hemifield join in the optic tract, which extends to the lateral geniculate nucleus of the thalamus. The lateral geniculate nucleus in primates consists of six layers, each of which receives input from either the ipsilateral or the contralateral eye. Becau ...
Evidence of Basal Temporo-occipital Cortex
... right occipital epilepsy who referred complex partial seizures with visual aura was scheduled for surgery in order to study her epileptic seizures and evaluate possible further surgical treatment. For this, subdural electrode arrays covering the mesial occipital (MO, 8 3 1 electrodes), lateral occip ...
... right occipital epilepsy who referred complex partial seizures with visual aura was scheduled for surgery in order to study her epileptic seizures and evaluate possible further surgical treatment. For this, subdural electrode arrays covering the mesial occipital (MO, 8 3 1 electrodes), lateral occip ...
Williams Syndrome Neuronal Size and Neuronal-Packing Density in Primary Visual Cortex
... of the magnocellular system, and would be more striking in the right hemisphere. The anterior calcarine cortex was sampled and, in fact, the findings were nearly the opposite. Specifically, although the peripheral visual cortex was found to be abnormal in WMS-affected brains, parvocellular sublayers ...
... of the magnocellular system, and would be more striking in the right hemisphere. The anterior calcarine cortex was sampled and, in fact, the findings were nearly the opposite. Specifically, although the peripheral visual cortex was found to be abnormal in WMS-affected brains, parvocellular sublayers ...
reviews - Center for Complex Systems and Brain Sciences
... detectors that respond best to those features that are present at the locations visited by observers while freeviewing images50,51. For instance, Zetzsche et al.50,52 showed using an eye-tracking device how the eyes preferentially fixate regions with multiple superimposed orientations such as corner ...
... detectors that respond best to those features that are present at the locations visited by observers while freeviewing images50,51. For instance, Zetzsche et al.50,52 showed using an eye-tracking device how the eyes preferentially fixate regions with multiple superimposed orientations such as corner ...
Decoding visual consciousness from human
... Despite many years of research on the neural correlates of consciousness (NCCs), it is still unclear how the detailed contents of consciousness are represented in the human brain. It is often assumed that specific contents of consciousness are encoded in dedicated core NCCs – one for each different ...
... Despite many years of research on the neural correlates of consciousness (NCCs), it is still unclear how the detailed contents of consciousness are represented in the human brain. It is often assumed that specific contents of consciousness are encoded in dedicated core NCCs – one for each different ...
Rose F. Kennedy Intellectual and Developmental Disabilities
... York, USA Abstract: Multisensory interactions have been widely reported in primary auditory, visual and somatosensory cortices. How do these interactions operate? Several lines of evidence indicate that these effects predominantly reflect an interaction of a driving input (i.e., one that causes loca ...
... York, USA Abstract: Multisensory interactions have been widely reported in primary auditory, visual and somatosensory cortices. How do these interactions operate? Several lines of evidence indicate that these effects predominantly reflect an interaction of a driving input (i.e., one that causes loca ...
Cross-Modal Transfer of Information between the Tactile
... The psychophysical testing showed that there is a linear relationship between presented and chosen stimulus, regardless of the modalities, as shown by the linear regression curves. The direction of cross-modal information transfer (i.e., tactile to visual vs visual to tactile) had no influence on th ...
... The psychophysical testing showed that there is a linear relationship between presented and chosen stimulus, regardless of the modalities, as shown by the linear regression curves. The direction of cross-modal information transfer (i.e., tactile to visual vs visual to tactile) had no influence on th ...
Supplementary Figure Legends - Word file
... Supplementary Figure 1: Example responses to pure tones and harmonic complex tones from a pitchselective neuron (a, d) (Unit M36n-514) and a non-pitch-selective neuron (b, e) (Unit M2p-140). a. Pure tone frequency response from a pitch-selective neuron. b. Pure tone frequency response from a non-pit ...
... Supplementary Figure 1: Example responses to pure tones and harmonic complex tones from a pitchselective neuron (a, d) (Unit M36n-514) and a non-pitch-selective neuron (b, e) (Unit M2p-140). a. Pure tone frequency response from a pitch-selective neuron. b. Pure tone frequency response from a non-pit ...
Simulating the Fröhlich Effect of Motion Misperception as a Result... Attentional Modulation in the Visual System
... 2001). The Fröhlich effect results because the feedback loop is initially triggered by the actual onset position but meets later stimulus representations during the feedback process. We restricted the model to horizontal motion because one-dimensional motion is sufficient for simulating the Fröhlich ...
... 2001). The Fröhlich effect results because the feedback loop is initially triggered by the actual onset position but meets later stimulus representations during the feedback process. We restricted the model to horizontal motion because one-dimensional motion is sufficient for simulating the Fröhlich ...
Impact on Perception, Attention, and Memory
... awareness. Emotion’s facilitation of awareness also extends to the perception of nonemotional stimuli in the vicinity of emotional stimuli. This was demonstrated using an attentional cuing paradigm (Posner, 1980) in which fearful or neutral faces were used to cue the location of a subsequent target ...
... awareness. Emotion’s facilitation of awareness also extends to the perception of nonemotional stimuli in the vicinity of emotional stimuli. This was demonstrated using an attentional cuing paradigm (Posner, 1980) in which fearful or neutral faces were used to cue the location of a subsequent target ...
Uncomfortable images produce non-sparse responses in a model of
... including headaches, eye-strain and illusions of shape, colour and motion, when viewed, which is referred to as ‘visual discomfort’ [16]. Such images have excessively high amplitude at midrange spatial frequencies in comparison with natural images. In particular, striped gratings (see figure 1a for ...
... including headaches, eye-strain and illusions of shape, colour and motion, when viewed, which is referred to as ‘visual discomfort’ [16]. Such images have excessively high amplitude at midrange spatial frequencies in comparison with natural images. In particular, striped gratings (see figure 1a for ...
Representation of the Visual Field in the Human Occipital Cortex
... To assess the accuracy of the Holmes map4 and a revised map,6 the location of the lesion in each patient was predicted using the 2 maps based on the patient’s visual field defect. We then compared the predicted location of the lesion with its actual location on MRI to assess the compatibility betwee ...
... To assess the accuracy of the Holmes map4 and a revised map,6 the location of the lesion in each patient was predicted using the 2 maps based on the patient’s visual field defect. We then compared the predicted location of the lesion with its actual location on MRI to assess the compatibility betwee ...
Brain Research, 178 (1979) 363-380 363 © Elsevier/North
... of IT (see Fig. 1C and D). Within this area 67 ~ of the 56 receptive fields were larger than 60 ° × 60 °. The second region with larger receptive fields was the dorsal part of IT, specifically, the floor of the superior temporal sulcus and the adjacent 2 mm of the bottom of the ventral bank of the s ...
... of IT (see Fig. 1C and D). Within this area 67 ~ of the 56 receptive fields were larger than 60 ° × 60 °. The second region with larger receptive fields was the dorsal part of IT, specifically, the floor of the superior temporal sulcus and the adjacent 2 mm of the bottom of the ventral bank of the s ...
Making Sense of Internal Logic: Theory and a Case Study
... In order to formulate an e ective interface, we have searched a suÆciently simple yet meaningful cognitive experiment. As one candidate for such an experiment, we considered the type recently carried out by Sakagami and Niki [4] and Sakagami and Tsutsui [5]. They performed a set of experiments inves ...
... In order to formulate an e ective interface, we have searched a suÆciently simple yet meaningful cognitive experiment. As one candidate for such an experiment, we considered the type recently carried out by Sakagami and Niki [4] and Sakagami and Tsutsui [5]. They performed a set of experiments inves ...
The role of early visual cortex in visual integration: a neural model of
... mechanism that can be implemented by the early retinotopic visual areas. On the other hand, when both target and distractors are composed of similar elementary features, the amount of time required to distinguish between them increases linearly with the number of distractors. This is said to suggest ...
... mechanism that can be implemented by the early retinotopic visual areas. On the other hand, when both target and distractors are composed of similar elementary features, the amount of time required to distinguish between them increases linearly with the number of distractors. This is said to suggest ...