Nature Reviews Neuroscience Highlight
... same side of the boundary but were far apart could appear to be dissimilar. This type of sharp boundary is a classic feature of perceptual categorization and allows for the dissociation of physical similarity and category membership. Two monkeys were trained to categorize the stimuli set as either c ...
... same side of the boundary but were far apart could appear to be dissimilar. This type of sharp boundary is a classic feature of perceptual categorization and allows for the dissociation of physical similarity and category membership. Two monkeys were trained to categorize the stimuli set as either c ...
Summary
... suppression of activity evoked by the target curve which was reversed later in time. We conclude that attentional processing differs between the difficulty levels. In the easy and intermediate condition we see the early attentional modulation specific to the positional cue (curve tracing) and in the ...
... suppression of activity evoked by the target curve which was reversed later in time. We conclude that attentional processing differs between the difficulty levels. In the easy and intermediate condition we see the early attentional modulation specific to the positional cue (curve tracing) and in the ...
Accumulative evidence indicates that microglial cells influence the
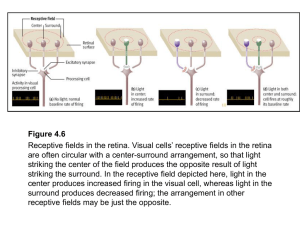
... with electrophysiological recordings. Neurons in the visual cortex have a receptive field like a keyhole through which they look at the scenery in front of the eyes. Visual input from the area surrounding the receptive field fails to induce neuronal firing but can modulate the neuronal responses to ...
... with electrophysiological recordings. Neurons in the visual cortex have a receptive field like a keyhole through which they look at the scenery in front of the eyes. Visual input from the area surrounding the receptive field fails to induce neuronal firing but can modulate the neuronal responses to ...
Slide ()
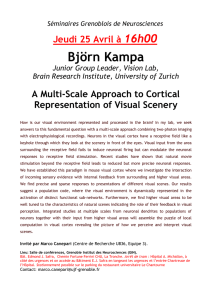
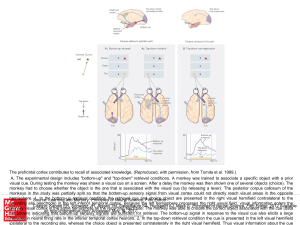
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
Slide ()
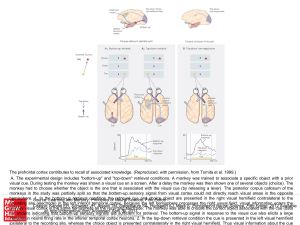
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
... A. The experimental design includes "bottom-up" and "top-down" retrieval conditions. A monkey was trained to associate a specific object with a prior visual cue. During testing the monkey was shown a visual cue on a screen. After a delay the monkey was then shown one of several objects (choice). The ...
Introduction
... (a) Input from the right half of the visual field strikes the left side of each retina and is transmitted to the left hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere (shown in green). The nerve f ...
... (a) Input from the right half of the visual field strikes the left side of each retina and is transmitted to the left hemisphere (shown in red). Input from the left half of the visual field strikes the right side of each retina and is transmitted to the right hemisphere (shown in green). The nerve f ...