Second-Order Patterns in Human Visual Cortex`` on ``Orientation
... with previous physiological studies, their findings show orientation selective adaptation for both first-order and second-order stimuli in primary and extrastriate areas, suggesting that the processing of second-order textures is distributed across visual areas rather than specialized within a singl ...
... with previous physiological studies, their findings show orientation selective adaptation for both first-order and second-order stimuli in primary and extrastriate areas, suggesting that the processing of second-order textures is distributed across visual areas rather than specialized within a singl ...
Artificial Eye.pdf - 123SeminarsOnly.com
... The Visual System The human visual system is remarkable instrument. It features two mobile acquisition units each has formidable preprocessing circuitry placed at a remote location from the central processing system (brain). Its primary task include transmitting images with a viewing angle of at le ...
... The Visual System The human visual system is remarkable instrument. It features two mobile acquisition units each has formidable preprocessing circuitry placed at a remote location from the central processing system (brain). Its primary task include transmitting images with a viewing angle of at le ...
Powerpoint template for scientific posters (Swarthmore
... 3Kennedy Center for Research on Human Development, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN ...
... 3Kennedy Center for Research on Human Development, Vanderbilt University, Nashville, TN ...
Textures of Natural Images in the Human Brain. Focus on
... with previous physiological studies, their findings show orientation selective adaptation for both first-order and second-order stimuli in primary and extrastriate areas, suggesting that the processing of second-order textures is distributed across visual areas rather than specialized within a singl ...
... with previous physiological studies, their findings show orientation selective adaptation for both first-order and second-order stimuli in primary and extrastriate areas, suggesting that the processing of second-order textures is distributed across visual areas rather than specialized within a singl ...
Final answers - Center for Neural Science
... b) occurs when a person who is blind claims that he or she can see. c) occurs when a person can point to the location of a visual stimulus when forced to guess, even though they have brain damage such that they are effectively blind. d) is a scientific hoax. 37) Although there have been many demonst ...
... b) occurs when a person who is blind claims that he or she can see. c) occurs when a person can point to the location of a visual stimulus when forced to guess, even though they have brain damage such that they are effectively blind. d) is a scientific hoax. 37) Although there have been many demonst ...
Slides from Discussion section VI 11/15/2004 (Elissa
... This study supports the notion that perception of visual category information is processed in the Inferior Temporal cortex ...
... This study supports the notion that perception of visual category information is processed in the Inferior Temporal cortex ...
THE VISUAL SYSTEM
... BRAIN • Optic chiasm: pt at which the optic nerves from the inside half of each eye cross over and then project to the opposite half of the brain • Optic fibers then diverge along 2 paths • Main path projects into thalamus; retinal axons synapse in the Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) • Then to the ...
... BRAIN • Optic chiasm: pt at which the optic nerves from the inside half of each eye cross over and then project to the opposite half of the brain • Optic fibers then diverge along 2 paths • Main path projects into thalamus; retinal axons synapse in the Lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) • Then to the ...
Chapter Summary Chapter 5: Sensation and Perception • Sensation
... several principles by which we recognize stimuli even when visual inputs are limited. We use binocular and monocular cues for depth perception. Perceptual constancies, based on learning from previous experiences, help us to see things as stable despite constant shifts in our visual inputs. These top ...
... several principles by which we recognize stimuli even when visual inputs are limited. We use binocular and monocular cues for depth perception. Perceptual constancies, based on learning from previous experiences, help us to see things as stable despite constant shifts in our visual inputs. These top ...
Visual Brain
... What and How Pathways - Further Evidence • Rod and frame illusion – Observers perform two tasks: matching and grasping • Matching task involves ventral (what) pathway • Grasping task involves dorsal (how) pathway – Results show that the frame orientation affects the matching task but not the ...
... What and How Pathways - Further Evidence • Rod and frame illusion – Observers perform two tasks: matching and grasping • Matching task involves ventral (what) pathway • Grasping task involves dorsal (how) pathway – Results show that the frame orientation affects the matching task but not the ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 46.1 Lateral viewof a human brain
... and performed an object discrimination task, a distributed frontoparietal network was activated, including the SEF, the FEF, and the SPL. (C) The same network of frontal and parietal areas was activated when the subject directed attention to the peripheral target location in the expectation of the s ...
... and performed an object discrimination task, a distributed frontoparietal network was activated, including the SEF, the FEF, and the SPL. (C) The same network of frontal and parietal areas was activated when the subject directed attention to the peripheral target location in the expectation of the s ...
669790507205MyersMod_LG_12
... Acuity, or sharpness of vision, can be affected by small distortions in the shape of the eye. In nearsightedness, nearby objects are seen more clearly than distant objects because the lens focuses the image of distant objects in front of the retina. In farsightedness, faraway objects are seen more c ...
... Acuity, or sharpness of vision, can be affected by small distortions in the shape of the eye. In nearsightedness, nearby objects are seen more clearly than distant objects because the lens focuses the image of distant objects in front of the retina. In farsightedness, faraway objects are seen more c ...
Click here to a word document of this Fact
... Those experiencing homonymous hemianopia may not be aware that their vision has been altered. Without being aware of a problem they cannot correct for it. Going into crowded stores may become difficult, because people seem to suddenly appear in front of them. Anxiety leaving the home can occur and s ...
... Those experiencing homonymous hemianopia may not be aware that their vision has been altered. Without being aware of a problem they cannot correct for it. Going into crowded stores may become difficult, because people seem to suddenly appear in front of them. Anxiety leaving the home can occur and s ...
Study Guide 3
... 33. What part of the brain receives the major projection from the lateral geniculate nucleus? 34. Describe three different functional classes of neurons found in primary visual cortex. 35. What is a cortical module? An orientation column? An ocular dominance column? 36. What is the difference betwee ...
... 33. What part of the brain receives the major projection from the lateral geniculate nucleus? 34. Describe three different functional classes of neurons found in primary visual cortex. 35. What is a cortical module? An orientation column? An ocular dominance column? 36. What is the difference betwee ...
Chapter 4: Sensation and Perception
... –Receptors for red, green, blue – color mixing •Opponent Process theory – Hering –3 pairs of antagonistic colors –red/green, blue/yellow, black/white •Current perspective: both theories necessary Perceiving Forms, Patterns, and Objects •Reversible figures •Perceptual sets •Inattentional blindness •F ...
... –Receptors for red, green, blue – color mixing •Opponent Process theory – Hering –3 pairs of antagonistic colors –red/green, blue/yellow, black/white •Current perspective: both theories necessary Perceiving Forms, Patterns, and Objects •Reversible figures •Perceptual sets •Inattentional blindness •F ...
ppt file
... The Retina • Why don’t you notice your blind spot? – Blindspots don’t overlap! – Your brain “fills in” the missing information – The specific information in the blindspot isn’t much more missing than the rest of the periphery! ...
... The Retina • Why don’t you notice your blind spot? – Blindspots don’t overlap! – Your brain “fills in” the missing information – The specific information in the blindspot isn’t much more missing than the rest of the periphery! ...
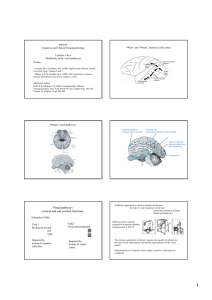
Visual pathways cortical and sub
... e.g. Perrett et al. (1984; 1991) cells in Superior Temporal Sulcus category specific (e.g. faces) ...
... e.g. Perrett et al. (1984; 1991) cells in Superior Temporal Sulcus category specific (e.g. faces) ...
primary visual cortex
... Friday, December 3: 3:30-4:30 Thursday, December 9: 10:00-12:00, 1:00-3:00 Friday, December 10: 10:00-1:00 ...
... Friday, December 3: 3:30-4:30 Thursday, December 9: 10:00-12:00, 1:00-3:00 Friday, December 10: 10:00-1:00 ...
Visual Processing - West Virginia University
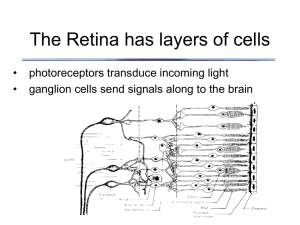
... Pattern of illumination that maximally excites ganglion cell is doughnut shaped Center-surround receptive field Lateral inhibition of receptive fields enhances boundaries ...
... Pattern of illumination that maximally excites ganglion cell is doughnut shaped Center-surround receptive field Lateral inhibition of receptive fields enhances boundaries ...
Memory Capacity of a Hebbian Learning Model with Inhibition
... It has been shown that for a general discrete Hebbian-type learning model, when all parameters governing the stochastic learning process are fixed, the storage capacity of the model to learn a stream of uncorrelated stimuli is as low as O(log N), where N is the number of neurons in the network. If t ...
... It has been shown that for a general discrete Hebbian-type learning model, when all parameters governing the stochastic learning process are fixed, the storage capacity of the model to learn a stream of uncorrelated stimuli is as low as O(log N), where N is the number of neurons in the network. If t ...
File
... The ______________, the Skin, the Eye, the ________________, and the Tongue The Nervous System and Environment The ___________________ is everything outside the body. The sense organs gather information from outside the body, then send the messages to the brain STIMULUS & RESPONSE Stimulus (the ca ...
... The ______________, the Skin, the Eye, the ________________, and the Tongue The Nervous System and Environment The ___________________ is everything outside the body. The sense organs gather information from outside the body, then send the messages to the brain STIMULUS & RESPONSE Stimulus (the ca ...
Theory of Vision: What We Can Easily See
... This poster shows multiple feature channels and visual searches. This duo tone poster has color as the top of the visual hierarchy. The blue and yellow have a pop effect, bold, bright colors on a black and white poster. These color features are also arrows that bring direction and motion to the pos ...
... This poster shows multiple feature channels and visual searches. This duo tone poster has color as the top of the visual hierarchy. The blue and yellow have a pop effect, bold, bright colors on a black and white poster. These color features are also arrows that bring direction and motion to the pos ...
Review 2 - Texas A&M University
... square stimulus creates a square image on the retina. However, this image could also have been created by the other two shapes and many other stimuli. This is why we say that the image on the retina is ambiguous. ...
... square stimulus creates a square image on the retina. However, this image could also have been created by the other two shapes and many other stimuli. This is why we say that the image on the retina is ambiguous. ...
Summary - VU Research Portal
... the animal learned the task. The enhanced activity for the figure correlated with performance on the shape discrimination task. In a task in which the animal attended to a second shape on the opposite side of the screen, we found that figure-ground modulation is weakened for the unattended figure in ...
... the animal learned the task. The enhanced activity for the figure correlated with performance on the shape discrimination task. In a task in which the animal attended to a second shape on the opposite side of the screen, we found that figure-ground modulation is weakened for the unattended figure in ...