Objectives 31
... 3. – Receptive fields of lateral geniculate neurons are similar to those of ganglion cells: input from one eye, center-surround antagonism, some receptive fields are for color and others are for black/white contrast, lot of representation of small foveal receptive fields, LGN neurons project to stri ...
... 3. – Receptive fields of lateral geniculate neurons are similar to those of ganglion cells: input from one eye, center-surround antagonism, some receptive fields are for color and others are for black/white contrast, lot of representation of small foveal receptive fields, LGN neurons project to stri ...
PY460: Physiological Psychology
... can explain color constancy only works when entire view has been tinted ...
... can explain color constancy only works when entire view has been tinted ...
PowerPoint Slides Chapter 6
... Striate modules show: – Ocular dominance: cells in each half of the module respond to only one eye – Orientation columns: orientationsensitive ...
... Striate modules show: – Ocular dominance: cells in each half of the module respond to only one eye – Orientation columns: orientationsensitive ...
Development of a paradigm to investigate mechanisms of divided
... serial reaction time task evaluates sustained but not other attention types. We decided to profit from a recent finding that Alzheimer’s patients have an impaired ability to detect objects approaching on a collision course in tests for selective and divided visual attention [1,2]. Collision detectio ...
... serial reaction time task evaluates sustained but not other attention types. We decided to profit from a recent finding that Alzheimer’s patients have an impaired ability to detect objects approaching on a collision course in tests for selective and divided visual attention [1,2]. Collision detectio ...
primary visual cortex
... Comprise all layers of the primary visual cortex, except lower layer IV. Characterized by rectangular receptive fields. These fields are comprised of excitatory areas and inhibitory areas separated by straight lines. ...
... Comprise all layers of the primary visual cortex, except lower layer IV. Characterized by rectangular receptive fields. These fields are comprised of excitatory areas and inhibitory areas separated by straight lines. ...
mspn12a
... Output layers: sends projections to the LGN and other areas of the brain, contain primarily stellate (interneuron)/pyramidal cells that make local/far-reaching projections (circle one). Circle pyramidal and ...
... Output layers: sends projections to the LGN and other areas of the brain, contain primarily stellate (interneuron)/pyramidal cells that make local/far-reaching projections (circle one). Circle pyramidal and ...
Cortex
... presented with a sample cue, followed by a memory delay during which that sample has to be remembered. Then one or more choice stimuli are presented and the animal is required to respond depending on whether the choice cue is the same as the sample (a match) or not (a nonmatch). ...
... presented with a sample cue, followed by a memory delay during which that sample has to be remembered. Then one or more choice stimuli are presented and the animal is required to respond depending on whether the choice cue is the same as the sample (a match) or not (a nonmatch). ...
Perception - U
... to association cortex in the posterior parietal region • Ventral Stream: info flows from primary visual cortex through the ventral prestriate secondary cortex to association cortex in the inferotemporal region ...
... to association cortex in the posterior parietal region • Ventral Stream: info flows from primary visual cortex through the ventral prestriate secondary cortex to association cortex in the inferotemporal region ...
Pattern recognition and visual word forms
... ntative model of functional anatomical pathways involved in visual perception of words. Letter strings are first processed in ventral occipital regions (V1 to lateral to the stimuli, building up increasingly abstract visual representations (right). For stimuli in the left visual field, information i ...
... ntative model of functional anatomical pathways involved in visual perception of words. Letter strings are first processed in ventral occipital regions (V1 to lateral to the stimuli, building up increasingly abstract visual representations (right). For stimuli in the left visual field, information i ...
Science - Princeton University
... visual receptive fielcls which were very large (greclter than 10 by 10 degrees) and alnzost alwciys iizcluded the fovea. Some extended well into both halves o f the visual fielcl, while others were coizfiized to the ipsilateral or coiztralateral side. These nezrrolis were diflerentially seizsitive t ...
... visual receptive fielcls which were very large (greclter than 10 by 10 degrees) and alnzost alwciys iizcluded the fovea. Some extended well into both halves o f the visual fielcl, while others were coizfiized to the ipsilateral or coiztralateral side. These nezrrolis were diflerentially seizsitive t ...
CHAPTER 15 THE CENTRAL VISUAL PATHWAYS
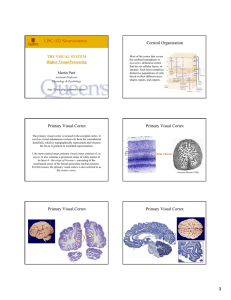
... Although much processing takes place in the retina, even more takes place in the central nervous system. At every level of the visual system, there is one obvious organizational principle. This is the systematic representation of different points in the visual field across a population of neurons. S ...
... Although much processing takes place in the retina, even more takes place in the central nervous system. At every level of the visual system, there is one obvious organizational principle. This is the systematic representation of different points in the visual field across a population of neurons. S ...
The NTVA framework: Linking Cognition and Neuroscience
... single cells, each of which correspond closely with the predictions of NTVA (Bundesen, Habekost, & Kyllingsbæk, 2005). By far the strongest changes of a cell’s firing rate can occur when multiple objects are present in the classical RF. Under these conditions a general finding is that attention to o ...
... single cells, each of which correspond closely with the predictions of NTVA (Bundesen, Habekost, & Kyllingsbæk, 2005). By far the strongest changes of a cell’s firing rate can occur when multiple objects are present in the classical RF. Under these conditions a general finding is that attention to o ...
Background Presentation
... Visual Attention • Attention is the ability to select objects of interest from the surrounding environment • A reliable measure of attention is eye movement during object (target) selection • Early studies show that there are specific brain regions that are involved in the process of target selecti ...
... Visual Attention • Attention is the ability to select objects of interest from the surrounding environment • A reliable measure of attention is eye movement during object (target) selection • Early studies show that there are specific brain regions that are involved in the process of target selecti ...
Area MST has been thought be involved in heading perception not
... single-cue conditions. In the Combined condition, psychophysical thresholds were significantly lower than in the single-cue conditions and very close to predictions of optimal cue integration theories. According to whether the visual and vestibular heading preferences were well matched or nearly opp ...
... single-cue conditions. In the Combined condition, psychophysical thresholds were significantly lower than in the single-cue conditions and very close to predictions of optimal cue integration theories. According to whether the visual and vestibular heading preferences were well matched or nearly opp ...
October 29
... Reddish green, bluish yellow. Red and green mix to form yellow; yellow and blue mix to form white. ...
... Reddish green, bluish yellow. Red and green mix to form yellow; yellow and blue mix to form white. ...
Document
... Aqueous humor - clear watery fluid found in the anterior chamber of the eye; maintains pressure and nourishes the cornea and lens Vitreous humor - clear, jelly-like fluid found in the back portion of the eye: maintains shape of the eye and attaches to the retina Blind spot - small area of the retina ...
... Aqueous humor - clear watery fluid found in the anterior chamber of the eye; maintains pressure and nourishes the cornea and lens Vitreous humor - clear, jelly-like fluid found in the back portion of the eye: maintains shape of the eye and attaches to the retina Blind spot - small area of the retina ...
Visual Field Defects - Northwestern Medical Review
... centers for visual information from the retina. Each LGN receives information from one half of the visual field. For example, the left LGN receives information from ganglion cells of the temporal retina of the left eye plus information from the nasal retina of contralateral (right) eye. The nerves t ...
... centers for visual information from the retina. Each LGN receives information from one half of the visual field. For example, the left LGN receives information from ganglion cells of the temporal retina of the left eye plus information from the nasal retina of contralateral (right) eye. The nerves t ...
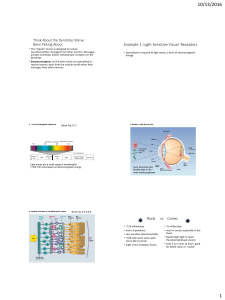
Think About the Dendrites We`ve Been Talking About
... 2 Theories of Color Vision Proposed in 1800’s Trichromatic Theory – 3 different types of color receptors work together to represent all colors of the spectrum. Opponent Process Theory – cells in the visual pathway receive input about pairs of colors (R-G or B-Y). One color makes them fire faster, ...
... 2 Theories of Color Vision Proposed in 1800’s Trichromatic Theory – 3 different types of color receptors work together to represent all colors of the spectrum. Opponent Process Theory – cells in the visual pathway receive input about pairs of colors (R-G or B-Y). One color makes them fire faster, ...
Chapter 13
... Many studies of STM involve a delayed matching-to-sample task (a task that requires the subject to indicate which stimulus has just been perceived) ...
... Many studies of STM involve a delayed matching-to-sample task (a task that requires the subject to indicate which stimulus has just been perceived) ...
Percept
... • Bottom-up processing – Analysis that emphasizes characteristics of the stimulus, rather than internal concepts (stimulus-driven processing). • Top-down processing – Emphasizes perceiver's expectations, memories, and other cognitive factors (conceptually-driven processing). ...
... • Bottom-up processing – Analysis that emphasizes characteristics of the stimulus, rather than internal concepts (stimulus-driven processing). • Top-down processing – Emphasizes perceiver's expectations, memories, and other cognitive factors (conceptually-driven processing). ...
PSY105 Neural Networks 2/5
... Hebb Rule governs changes in weights [+ other additional assumptions which are always needed when you try and make a computational recipe] • Mechanism: At least one response neuron, one unconditioned stimulus neuron and one neuron for each conditioned stimulus ...
... Hebb Rule governs changes in weights [+ other additional assumptions which are always needed when you try and make a computational recipe] • Mechanism: At least one response neuron, one unconditioned stimulus neuron and one neuron for each conditioned stimulus ...
Coding of Visual Information in the Retina Coding of Light d D k and
... Problem: how does one cell code for yp of information? two types A neuron can only vary its frequency of action potentials. If the cone’s response indicates brightness then it cannot signal for brightness, color. ...
... Problem: how does one cell code for yp of information? two types A neuron can only vary its frequency of action potentials. If the cone’s response indicates brightness then it cannot signal for brightness, color. ...
Adaptive, behaviorally gated, persistent encoding of task
... neurons occupy in the bi-directional sensory-to–decision-making hierarchy. In frontal cortex neurons, target modulation latencies ranged from early to late (from 20 ms to over 1,500 ms). • The lasting imprint of attention in A1 and frontal cortex :Frontal cortex neurons exhibited adaptive responses ...
... neurons occupy in the bi-directional sensory-to–decision-making hierarchy. In frontal cortex neurons, target modulation latencies ranged from early to late (from 20 ms to over 1,500 ms). • The lasting imprint of attention in A1 and frontal cortex :Frontal cortex neurons exhibited adaptive responses ...