Final - Center for Neural Science
... b) occurs when a person who is blind claims that he or she can see. c) occurs when a person can point to the location of a visual stimulus when forced to guess, even though they have brain damage such that they are effectively blind. d) is a scientific hoax. 38) Although there have been many demonst ...
... b) occurs when a person who is blind claims that he or she can see. c) occurs when a person can point to the location of a visual stimulus when forced to guess, even though they have brain damage such that they are effectively blind. d) is a scientific hoax. 38) Although there have been many demonst ...
Revision material
... Draw an annotated diagram explaining how the stretch reflex might operate as part of a servo control system. Describe the somatosensory pathways in the mammalian central nervous system. What are the principal differences between control of eye movements and limb movements? The fly employs a number o ...
... Draw an annotated diagram explaining how the stretch reflex might operate as part of a servo control system. Describe the somatosensory pathways in the mammalian central nervous system. What are the principal differences between control of eye movements and limb movements? The fly employs a number o ...
fahime_sheikhzadeh
... matching and learning processes within the What and Where cortical streams • Laminar Computing: cerebral cortex is organized into layered circuits which undergo characteristic bottom-up, top-down, and horizontal interactions ...
... matching and learning processes within the What and Where cortical streams • Laminar Computing: cerebral cortex is organized into layered circuits which undergo characteristic bottom-up, top-down, and horizontal interactions ...
Are We Paying Attention Yet?
... This data supports the interdependence hypothesis and does not rule out the identity hypothesis This data does NOT support the independence hypothesis ...
... This data supports the interdependence hypothesis and does not rule out the identity hypothesis This data does NOT support the independence hypothesis ...
Exam - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
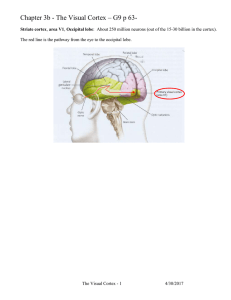
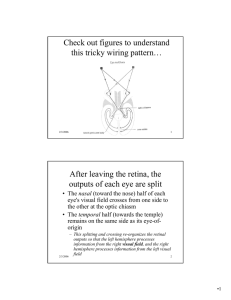
... How is information about light relayed to the brain? • Visual information is relayed to the brain via many pathways. The largest and most studied visual pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the ret ...
... How is information about light relayed to the brain? • Visual information is relayed to the brain via many pathways. The largest and most studied visual pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the ret ...
chapter 4 note sheet
... – Rods: black and white/low light vision – Cones: color and daylight vision • Adaptation: becoming more or less sensitive to light as needed ...
... – Rods: black and white/low light vision – Cones: color and daylight vision • Adaptation: becoming more or less sensitive to light as needed ...
FIGURE LEGENDS FIGURE 22.1 An example of a figure that can
... location and for wavelength. Receptive field 1 is excited by turning on red light (R) at its center and is inhibited by turning on green light (G) in its surround. Receptive field 2 is less common and is antagonistic for wavelength (blue vs. yellow) without being antagonistic for the location of the ...
... location and for wavelength. Receptive field 1 is excited by turning on red light (R) at its center and is inhibited by turning on green light (G) in its surround. Receptive field 2 is less common and is antagonistic for wavelength (blue vs. yellow) without being antagonistic for the location of the ...
Jay_21Mar2013
... • Total cortical surface area: ~100 cm2 • Total surface area of visual cortex: ~ 50 cm2 • ~35 visual areas, ~25 primarily visual • 323 known anatomical pathways; ~33% connectivity • ~75-85% of visual cortical neurons are pyramidal cells * Glutamatergic (thought to be always excitatory) * ~104 synaps ...
... • Total cortical surface area: ~100 cm2 • Total surface area of visual cortex: ~ 50 cm2 • ~35 visual areas, ~25 primarily visual • 323 known anatomical pathways; ~33% connectivity • ~75-85% of visual cortical neurons are pyramidal cells * Glutamatergic (thought to be always excitatory) * ~104 synaps ...
MCB105 QUIZ 5 2016 wA
... owls and why? [1] instructive signal/ visual responses to allow alignment of visual and auditory space - their recordings showed that visual receptive fields of ICX neurons were restricted and quite similar in size to the ones observed in the OT. b) How did they open the 'gate' that prevented these ...
... owls and why? [1] instructive signal/ visual responses to allow alignment of visual and auditory space - their recordings showed that visual receptive fields of ICX neurons were restricted and quite similar in size to the ones observed in the OT. b) How did they open the 'gate' that prevented these ...
Session 4
... Simple cells: Elongated Receptive fields. Orientation selective. Defined regions of excitation and inhibition. Complex cells: Also orientation selective. No well defined regions of excitation and inhibition. Hypercomplex cells: End-stopped. ...
... Simple cells: Elongated Receptive fields. Orientation selective. Defined regions of excitation and inhibition. Complex cells: Also orientation selective. No well defined regions of excitation and inhibition. Hypercomplex cells: End-stopped. ...
New clues to the location of visual consciousness
... “Since this breakdown in binocular vision was discovered, it has been the subject of scientific interest because it involves the switching of visual consciousness without conscious control,” says Randolph Blake, professor of psychology at Vanderbilt. He, Hugh R. Wilson, a mathematician from York Uni ...
... “Since this breakdown in binocular vision was discovered, it has been the subject of scientific interest because it involves the switching of visual consciousness without conscious control,” says Randolph Blake, professor of psychology at Vanderbilt. He, Hugh R. Wilson, a mathematician from York Uni ...
The effect of visual experience on the development of the mirror
... Neural correlates of mental representation of space in sighted and blind individuals Daniela Bonino Laboratory of Clinical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Pisa Medical School, Pisa, Italy Visual perception and visual imagery share common cortical regions within the parietal lobes. ...
... Neural correlates of mental representation of space in sighted and blind individuals Daniela Bonino Laboratory of Clinical Biochemistry and Molecular Biology, University of Pisa Medical School, Pisa, Italy Visual perception and visual imagery share common cortical regions within the parietal lobes. ...
Moran Furman
... the superior-colliculus and thalamic pulvinar. In higher mammals, this colliculo-pulvinar-cortical pathway is less dominant than the retino-geniculate pathway, but it plays important roles in eye movements, spatial attention, and rapid motion processing. (Source: Reproduced, with permission, from Wa ...
... the superior-colliculus and thalamic pulvinar. In higher mammals, this colliculo-pulvinar-cortical pathway is less dominant than the retino-geniculate pathway, but it plays important roles in eye movements, spatial attention, and rapid motion processing. (Source: Reproduced, with permission, from Wa ...
After leaving the retina, the outputs of each eye are split
... – Architecture: microanatomy can differ widely across brain areas • For example, V1 is also referred to as "striate cortex" because it has a series of stripes that run parallel to the surface; these stripes end abruptly at the end of V1. ...
... – Architecture: microanatomy can differ widely across brain areas • For example, V1 is also referred to as "striate cortex" because it has a series of stripes that run parallel to the surface; these stripes end abruptly at the end of V1. ...
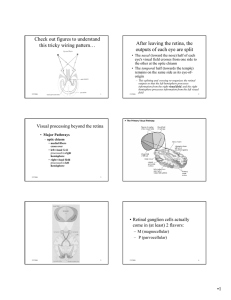
Check out figures to understand this tricky wiring pattern… After
... • Brain areas can be differentiated according to 4 main criteria: – Function: physiology • Neurons in different parts of the brain are responsive to different aspects of the stimulus (= do different things). ...
... • Brain areas can be differentiated according to 4 main criteria: – Function: physiology • Neurons in different parts of the brain are responsive to different aspects of the stimulus (= do different things). ...
Background: Classical fear conditioning is a phenomenon in which
... CS to evoke a fearful reaction even in absence of the US (Pavlov, 1927). In some cases, this fear of the conditioned danger cue (CS+) can also be observed when a subject is presented a stimulus that shares similar characteristics with the CS+. This is known as fear generalization. Although some amou ...
... CS to evoke a fearful reaction even in absence of the US (Pavlov, 1927). In some cases, this fear of the conditioned danger cue (CS+) can also be observed when a subject is presented a stimulus that shares similar characteristics with the CS+. This is known as fear generalization. Although some amou ...
Visual categorization shapes feature selectivity in the primate
... Visual categorization shapes feature selectivity in the primate temporal cortex Interdisciplinary Program in Brain Science Eye Movement & Vision Research LAB Hwang, Jae Won ...
... Visual categorization shapes feature selectivity in the primate temporal cortex Interdisciplinary Program in Brain Science Eye Movement & Vision Research LAB Hwang, Jae Won ...
From Vision to Movement
... Perhaps the most fundamental question in Visual-Motor Neuroscience is when, where, and how visual signals are transformed into motor signals. We will consider more complex aspects of this in the following sessions, but right now we just want to differentiate between visual and motor signals in the b ...
... Perhaps the most fundamental question in Visual-Motor Neuroscience is when, where, and how visual signals are transformed into motor signals. We will consider more complex aspects of this in the following sessions, but right now we just want to differentiate between visual and motor signals in the b ...
primary visual cortex - UBC Psychology`s Research Labs
... pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the retinas “cross over” and ascend to the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) of the thalamus. Thus, each hemisphere receives information from the contralat ...
... pathway is the retina-geniculate-striate pathway. • Within this pathway is the optic chiasm: at this point, axons from the nasal halves of the retinas “cross over” and ascend to the dorsal lateral geniculate nucleus (LGN) of the thalamus. Thus, each hemisphere receives information from the contralat ...
The outer layer of the cerebral cortex is divided into different areas
... stimuli together into a single event (see the figure), the brain, like a good playwright, is likely to ask “when” (time), “where” (space), “what” (identity), and “why” (why does the stimulus matter to the organism). Integration of different but related sensory stimuli does not require the glue of at ...
... stimuli together into a single event (see the figure), the brain, like a good playwright, is likely to ask “when” (time), “where” (space), “what” (identity), and “why” (why does the stimulus matter to the organism). Integration of different but related sensory stimuli does not require the glue of at ...
Slide ()
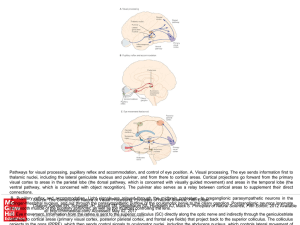
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...
... Pathways for visual processing, pupillary reflex and accommodation, and control of eye position. A. Visual processing. The eye sends information first to thalamic nuclei, including the lateral geniculate nucleus and pulvinar, and from there to cortical areas. Cortical projections go forward from the ...