What insights can fMRI offer into the structure and function of mid-tier visual areas?
... how strongly fMRI studies must rely on modeling, behavioral measures, and single-unit recordings; fMRI data cannot be interpreted in isolation. What does it mean to discover information in a decoding analysis? While the previous analysis showed that subpopulation responses were indeed accessible beh ...
... how strongly fMRI studies must rely on modeling, behavioral measures, and single-unit recordings; fMRI data cannot be interpreted in isolation. What does it mean to discover information in a decoding analysis? While the previous analysis showed that subpopulation responses were indeed accessible beh ...
Attention induces synchronization-based response gain in steady
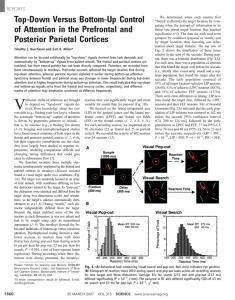
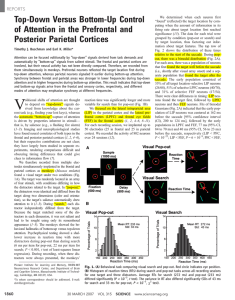
... directly boosts visual responses that are elicited by the attended stimulus (Fig. 1b). Evidence in support of these hypotheses must demonstrate that there is a multiplicative attention effect on population activity that is stimulus selective. Therefore, we recorded frequency-tagged SSVEPs from numer ...
... directly boosts visual responses that are elicited by the attended stimulus (Fig. 1b). Evidence in support of these hypotheses must demonstrate that there is a multiplicative attention effect on population activity that is stimulus selective. Therefore, we recorded frequency-tagged SSVEPs from numer ...
Spindle-Like Thalamocortical Synchronization in a Rat Brain Slice
... Jacques Louvel, René Pumain, and Massimo Avoli. Spindle-like thalamocortical synchronization in a rat brain slice preparation. J Neurophysiol 84: 1093–1097, 2000. We obtained rat brain slices (550 – 650 m) that contained part of the frontoparietal cortex along with a portion of the thalamic ventro ...
... Jacques Louvel, René Pumain, and Massimo Avoli. Spindle-like thalamocortical synchronization in a rat brain slice preparation. J Neurophysiol 84: 1093–1097, 2000. We obtained rat brain slices (550 – 650 m) that contained part of the frontoparietal cortex along with a portion of the thalamic ventro ...
neural mechanisms for detecting and remembering novel events
... which activity during a delayed matching-to-sample task was compared between trials involving novel or familiar stimuli32. Activity is shown for a region in the lateral prefrontal cortex that had a greater delay-period activity during ‘novel’ trials than during ‘familiar’ trials. The coloured gradie ...
... which activity during a delayed matching-to-sample task was compared between trials involving novel or familiar stimuli32. Activity is shown for a region in the lateral prefrontal cortex that had a greater delay-period activity during ‘novel’ trials than during ‘familiar’ trials. The coloured gradie ...
A simultaneous ERP/fMRI investigation of the P300 aging effect
... maximize the benefit of simultaneous acquisition by extracting single-trial information that is common to both modalities and that would otherwise be lost during standard averaging. When a consistent relationship is detected using this method one can infer that the corresponding fMRI activation eith ...
... maximize the benefit of simultaneous acquisition by extracting single-trial information that is common to both modalities and that would otherwise be lost during standard averaging. When a consistent relationship is detected using this method one can infer that the corresponding fMRI activation eith ...
Vision
... David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel 1960’s at Harvard University Discovered that neurons in the visual cortex did not simply respond to light; they selectively responded to specific features of the visual world. ...
... David Hubel and Torsten Wiesel 1960’s at Harvard University Discovered that neurons in the visual cortex did not simply respond to light; they selectively responded to specific features of the visual world. ...
Top-Down Versus Bottom-Up Control of Attention in the Prefrontal
... but their respective contributions are not clear; they have largely been studied in separate experiments, rendering comparisons difficult and obscuring timing differences that could give clues to information flow (7). We therefore recorded from multiple electrodes simultaneously implanted in the fro ...
... but their respective contributions are not clear; they have largely been studied in separate experiments, rendering comparisons difficult and obscuring timing differences that could give clues to information flow (7). We therefore recorded from multiple electrodes simultaneously implanted in the fro ...
Top-Down Versus Bottom-Up Control
... but their respective contributions are not clear; they have largely been studied in separate experiments, rendering comparisons difficult and obscuring timing differences that could give clues to information flow (7). We therefore recorded from multiple electrodes simultaneously implanted in the fro ...
... but their respective contributions are not clear; they have largely been studied in separate experiments, rendering comparisons difficult and obscuring timing differences that could give clues to information flow (7). We therefore recorded from multiple electrodes simultaneously implanted in the fro ...
contextual influences on visual processing
... noninteractively to render the objects of perceptual experience. In the mid–nineteenth century, associationism was embraced by many of the great figures in the emerging field of experimental psychology. Wilhelm Wundt (1902), in particular, pressed further the deconstruction of psychological reality ...
... noninteractively to render the objects of perceptual experience. In the mid–nineteenth century, associationism was embraced by many of the great figures in the emerging field of experimental psychology. Wilhelm Wundt (1902), in particular, pressed further the deconstruction of psychological reality ...
Attention
... Teaching Suggestion: Explain the concepts of shifting attention by asking students to describe examples of using the “spotlight of attention.” 8. Describe how fMRI imaging has been used to study attention to location and PET imaging to study attention to visual features. (Refer to PowerPoint slides ...
... Teaching Suggestion: Explain the concepts of shifting attention by asking students to describe examples of using the “spotlight of attention.” 8. Describe how fMRI imaging has been used to study attention to location and PET imaging to study attention to visual features. (Refer to PowerPoint slides ...
Melting the Iceberg
... (A) The classical model of orientation selectivity. The ON and OFF subregions of the receptive field of a V1 simple cell are obtained by summing appropriately aligned LGN inputs (circles). (B) The orientation selectivity of membrane potential in response to stimuli of 50% contrast (green) and 5% con ...
... (A) The classical model of orientation selectivity. The ON and OFF subregions of the receptive field of a V1 simple cell are obtained by summing appropriately aligned LGN inputs (circles). (B) The orientation selectivity of membrane potential in response to stimuli of 50% contrast (green) and 5% con ...
Review The Neural Basis of Perceptual Learning
... of perceptual learning will aid in the localization of the process of discrimination and the mechanism of learning within the visual system rests on this specificity. Specificity in learning for position in visual space and for the orientation of a stimulus suggests the involvement of early stages i ...
... of perceptual learning will aid in the localization of the process of discrimination and the mechanism of learning within the visual system rests on this specificity. Specificity in learning for position in visual space and for the orientation of a stimulus suggests the involvement of early stages i ...
- Neuro-Optometric Rehabilitation Association
... which a person can select where to place his or her attention and, finally, where to aim and focus his or her eyes. The symptoms of visual and nonvisual system dysfunction following TBI often derive from subcortical or subconscious pathways dysfunctions that can be, by standard central eyesight testi ...
... which a person can select where to place his or her attention and, finally, where to aim and focus his or her eyes. The symptoms of visual and nonvisual system dysfunction following TBI often derive from subcortical or subconscious pathways dysfunctions that can be, by standard central eyesight testi ...
Segregation and convergence of specialised pathways in
... part of each pair shows dorsal V2, which maps the contralateral inferior quadrant within the lunate and parieto-occipital sulci; the lower part of each pair shows ventral V2, which maps the contralateral superior quadrant within the inferior occipital, occipitotemporal and calcarine sulci. To the ri ...
... part of each pair shows dorsal V2, which maps the contralateral inferior quadrant within the lunate and parieto-occipital sulci; the lower part of each pair shows ventral V2, which maps the contralateral superior quadrant within the inferior occipital, occipitotemporal and calcarine sulci. To the ri ...
The Human Expression of Symmetry: Art and - Smith
... has been well studied in the fovea,[Julesz, 1971 #8; Bruce, 1975 #12; Corballis, 1974 #24; Barlow, 1979 #1; Jenkins, 1982 #16] where it can be discriminated from noise for presentations less than 100 msec.[Barlow, 1979 #1; Carmody, 1977 #13; Tyler, 1995 #38] The rapidity of this processing suggests ...
... has been well studied in the fovea,[Julesz, 1971 #8; Bruce, 1975 #12; Corballis, 1974 #24; Barlow, 1979 #1; Jenkins, 1982 #16] where it can be discriminated from noise for presentations less than 100 msec.[Barlow, 1979 #1; Carmody, 1977 #13; Tyler, 1995 #38] The rapidity of this processing suggests ...
Motor and cognitive functions of the ventral premotor cortex
... that an area homologous to monkey F4 exists in humans. Particularly interesting in this respect is a recent functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study [26••]. Bremmer et al. [26••] attempted to localize the multimodal tactile, auditory and visual cortical areas in humans. Tactile stimuli (ap ...
... that an area homologous to monkey F4 exists in humans. Particularly interesting in this respect is a recent functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) study [26••]. Bremmer et al. [26••] attempted to localize the multimodal tactile, auditory and visual cortical areas in humans. Tactile stimuli (ap ...
Neuronal mechanisms for the perception of ambiguous stimuli
... suppressed. Neuronal responses to suppressed stimuli have been studied with a specific paradigm of flash suppression as well as with binocular rivalry. In both paradigms, suppressed stimuli provide one index of whether or not neuronal firing is directly linked with conscious perception of objects. I ...
... suppressed. Neuronal responses to suppressed stimuli have been studied with a specific paradigm of flash suppression as well as with binocular rivalry. In both paradigms, suppressed stimuli provide one index of whether or not neuronal firing is directly linked with conscious perception of objects. I ...
primary visual cortex and visual awareness
... processing of attended stimuli and suppress the processing of irrelevant stimuli. Behavioural studies indicate that attention is necessary but not sufficient for visual awareness — even during sustained attention, awareness can fluctuate (as during binocular rivalry61) or fail to isolate the target ...
... processing of attended stimuli and suppress the processing of irrelevant stimuli. Behavioural studies indicate that attention is necessary but not sufficient for visual awareness — even during sustained attention, awareness can fluctuate (as during binocular rivalry61) or fail to isolate the target ...
Joint maps for orientation, eye, and direction preference in a self
... maps, spatiotemporal receptive fields, and lateral connections synergetically self-organize from moving stimuli. The model predicts that long-range lateral connections in V1 will be found to connect neurons with similar direction preference as well as orientation preference, as suggested in prelimin ...
... maps, spatiotemporal receptive fields, and lateral connections synergetically self-organize from moving stimuli. The model predicts that long-range lateral connections in V1 will be found to connect neurons with similar direction preference as well as orientation preference, as suggested in prelimin ...
Hemispheric Asymmetry in Visual Perception Arises from Differential Encoding
... Figure 1(a)). She referred to the two levels of the stimulus as having differential spatial frequency contents: low frequency for the global pattern and high frequency for the local pattern. In her experiment, she used four letters to compose the hierarchical letter patterns: "H" and "L" were design ...
... Figure 1(a)). She referred to the two levels of the stimulus as having differential spatial frequency contents: low frequency for the global pattern and high frequency for the local pattern. In her experiment, she used four letters to compose the hierarchical letter patterns: "H" and "L" were design ...
Large-Field Visual Motion Directly Induces an Involuntary Rapid
... Recent neuroscience studies have been concerned with how aimed movements are generated on the basis of target localization. However, visual information from the surroundings as well as from the target can influence arm motor control, in a manner similar to known effects in postural and ocular motor ...
... Recent neuroscience studies have been concerned with how aimed movements are generated on the basis of target localization. However, visual information from the surroundings as well as from the target can influence arm motor control, in a manner similar to known effects in postural and ocular motor ...
The effect of learning on the face selective responses of neurons in
... temporal sulcus and the inferior temporal gyrus of macaque monkeys respond to faces. These neurons provided a consistently identifiable substrate with which studies of the storage of visual information were performed. To determine whether face responsive neurons change how much they respond to diffe ...
... temporal sulcus and the inferior temporal gyrus of macaque monkeys respond to faces. These neurons provided a consistently identifiable substrate with which studies of the storage of visual information were performed. To determine whether face responsive neurons change how much they respond to diffe ...
pdf - Olin Neuropsychiatry Research Center
... increased relative to the Go stimulus. Similarly, interpretation of the findings of Braver et al (2001), who also employed a task in which Go and NoGo trials were equally probable, is complicated by the inclusion of multiple Go stimulus variants (i.e., any letter that was not an ‘X’) versus only a s ...
... increased relative to the Go stimulus. Similarly, interpretation of the findings of Braver et al (2001), who also employed a task in which Go and NoGo trials were equally probable, is complicated by the inclusion of multiple Go stimulus variants (i.e., any letter that was not an ‘X’) versus only a s ...
Hayrunnisa Bolay, Turkey
... dependent on full conscious experience as highly vulnerable to anesthetics. Blockade of TRN activation by valproate, triptans and CGRP antagonists implicated its relation to nociception. CSD selectively activated visual sector of TRN, though other six TRN sectors of auditory, gustatory, visceral, so ...
... dependent on full conscious experience as highly vulnerable to anesthetics. Blockade of TRN activation by valproate, triptans and CGRP antagonists implicated its relation to nociception. CSD selectively activated visual sector of TRN, though other six TRN sectors of auditory, gustatory, visceral, so ...
Auditory Cortex (1)
... 1. Woolsey CN and Walzl EM. Topical projection of nerve fibers from local regions of the cochlea to the cerebral cortex of the cat. Bulletin of the Johns Hopkins Hospital 71: 315-344, 1942. 2. Evans EF, Ross HF and Whitfield IC. The spatial distribution of unit characteristic frequency in the primar ...
... 1. Woolsey CN and Walzl EM. Topical projection of nerve fibers from local regions of the cochlea to the cerebral cortex of the cat. Bulletin of the Johns Hopkins Hospital 71: 315-344, 1942. 2. Evans EF, Ross HF and Whitfield IC. The spatial distribution of unit characteristic frequency in the primar ...