No Slide Title
... and goddesses ruled the world and the afterlife Amon-Re: sun god Osiris: god of the underworld and of the Nile • The pharaoh was believed to be a god as well as a ruler Falcon Headed Sun God ...
... and goddesses ruled the world and the afterlife Amon-Re: sun god Osiris: god of the underworld and of the Nile • The pharaoh was believed to be a god as well as a ruler Falcon Headed Sun God ...
The Old kingdom
... felt about the pharaohs by building them pyramids • Pyramid – large Egyptian tombs • B/c the sun set in the west, they were built on the west bank of the Nile • They were designed to protect the Pharaoh’s bodies from floods, animals, and robbers ...
... felt about the pharaohs by building them pyramids • Pyramid – large Egyptian tombs • B/c the sun set in the west, they were built on the west bank of the Nile • They were designed to protect the Pharaoh’s bodies from floods, animals, and robbers ...
Mummy - a body that has been embalmed and wrapped in linen
... Mummy - a body that has been embalmed and wrapped in linen Deity - god or goddess Pharaohs - all powerful king in ancient Egypt Pyramid - huge stone structure built by the ancient Egyptians To serve as a tomb Embalming process developed by the ancient Egyptians of preserving a persons body after dea ...
... Mummy - a body that has been embalmed and wrapped in linen Deity - god or goddess Pharaohs - all powerful king in ancient Egypt Pyramid - huge stone structure built by the ancient Egyptians To serve as a tomb Embalming process developed by the ancient Egyptians of preserving a persons body after dea ...
What we want to find out about egypt
... • 6.When a body had been treated in this way it was called a mummy. • 7.The mummy was put in a coffin. The coffin was the same shape as the body, and had a calved, painted face on it. • 8.A funeral was held by the priest In the temple. • 9.Now the coffin was then taken to pharaohs tomb. • 10.The pha ...
... • 6.When a body had been treated in this way it was called a mummy. • 7.The mummy was put in a coffin. The coffin was the same shape as the body, and had a calved, painted face on it. • 8.A funeral was held by the priest In the temple. • 9.Now the coffin was then taken to pharaohs tomb. • 10.The pha ...
Name Period Date Chapter 5: Egypt Review Packet Lesson 1 ____
... 3. Because Egyptians believed that the pharaoh was a child of the ____________________, hard times were a sign that the pharaoh was not ____________________ them properly. 4. The step pyramid is the oldest-known large ____________________ structure in the world. 5. The Great Pyramid took nearly ____ ...
... 3. Because Egyptians believed that the pharaoh was a child of the ____________________, hard times were a sign that the pharaoh was not ____________________ them properly. 4. The step pyramid is the oldest-known large ____________________ structure in the world. 5. The Great Pyramid took nearly ____ ...
Ancient Egypt
... families of kings and queen. If a king or queen died then their son would become king. Pharaohs made the laws in the land and decided what to do in a time of crisis. ...
... families of kings and queen. If a king or queen died then their son would become king. Pharaohs made the laws in the land and decided what to do in a time of crisis. ...
Chapter 4 Scavenger Hunt
... 21. Temples were not only houses of ______________ but also were ___________________________. ...
... 21. Temples were not only houses of ______________ but also were ___________________________. ...
Social Studies Review Chapter 4 (pgs. 86
... The ka is the person’s life force; after a person died the ka left the body to become a spirit The ka was linked to the body and could not leave the burial site and had the same needs as the person when he/she was living The ba travelled between the tomb and the outside world Rich burial = mummifica ...
... The ka is the person’s life force; after a person died the ka left the body to become a spirit The ka was linked to the body and could not leave the burial site and had the same needs as the person when he/she was living The ba travelled between the tomb and the outside world Rich burial = mummifica ...
Unit Test on Ancient Egypt Study Guide Answers
... • 3. peasant – a farmer or unskilled worker; person who is on the bottom of the social pyramid • 4. sarcophagus – stone coffin • 5. artisans – craftspeople • 6. treaty – an agreement to end a war • 7. social classes – different levels of jobs and statuses in society • 8. afterlife – belief in life ...
... • 3. peasant – a farmer or unskilled worker; person who is on the bottom of the social pyramid • 4. sarcophagus – stone coffin • 5. artisans – craftspeople • 6. treaty – an agreement to end a war • 7. social classes – different levels of jobs and statuses in society • 8. afterlife – belief in life ...
Ancient Egypt PPT
... People wore linen robes Women wore make-up and jewelry People shaved their heads and wore wigs for special occasions. ...
... People wore linen robes Women wore make-up and jewelry People shaved their heads and wore wigs for special occasions. ...
Ancient_Egypt_PPT[1]
... People wore linen robes Women wore make-up and jewelry People shaved their heads and wore wigs for special occasions. ...
... People wore linen robes Women wore make-up and jewelry People shaved their heads and wore wigs for special occasions. ...
1 - inetTeacher
... 18. Sesostris III super forts can or cannot be visited? 19. Egyptian obelisks were moved by roads or during the yearly floods of the Nile? 20. How did ancient Egyptians move obelisks? We don’t know for sure or ...
... 18. Sesostris III super forts can or cannot be visited? 19. Egyptian obelisks were moved by roads or during the yearly floods of the Nile? 20. How did ancient Egyptians move obelisks? We don’t know for sure or ...
EGYPT
... – Body was packed with various materials to help keep its shape – Salts were placed on the body to dry it out – Finally the body was wrapped in strips of linen ...
... – Body was packed with various materials to help keep its shape – Salts were placed on the body to dry it out – Finally the body was wrapped in strips of linen ...
New Kingdom
... 1. Ahmose drove out Hyksos beginning the New Kingdom: 1550 BC-1080 BC 2. Pharaohs made empire building a priority 3. Egypt reached the height of its glory 4. Hatshepsut, the first Egyptian female pharaoh, increased trade 5. Thutmose’s armies expanded Egypt’s borders(more territory than ever before) ...
... 1. Ahmose drove out Hyksos beginning the New Kingdom: 1550 BC-1080 BC 2. Pharaohs made empire building a priority 3. Egypt reached the height of its glory 4. Hatshepsut, the first Egyptian female pharaoh, increased trade 5. Thutmose’s armies expanded Egypt’s borders(more territory than ever before) ...
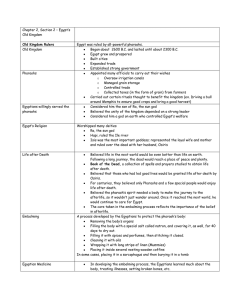
Chapter 2, Section 2 – Egypt`s Old Kingdom Old Kingdom Rulers
... Following a long journey, the dead would reach a place of peace and plenty. Book of the Dead, a collection of spells and prayers studied to obtain life after death. Believed that those who had led good lives would be granted life after death by Osiris. For centuries, they believed only Pharaohs and ...
... Following a long journey, the dead would reach a place of peace and plenty. Book of the Dead, a collection of spells and prayers studied to obtain life after death. Believed that those who had led good lives would be granted life after death by Osiris. For centuries, they believed only Pharaohs and ...
Egyptian Pyramids - Pearson Canada School Division
... to move and position the large blocks of stone they used in their constructions. Even with these tools, the builders would have needed thousands of workers to complete the pyramids. ...
... to move and position the large blocks of stone they used in their constructions. Even with these tools, the builders would have needed thousands of workers to complete the pyramids. ...
Egypt`s Early Rulers - Mater Academy Lakes High School
... social status, or position in society. • The king or pharaoh and his family held the highest social position in Egypt, followed by a small upper class of army commanders, nobles, and priests. • A larger group of traders, artisans, and scribes made up the middle class. • Lowest but largest groups in ...
... social status, or position in society. • The king or pharaoh and his family held the highest social position in Egypt, followed by a small upper class of army commanders, nobles, and priests. • A larger group of traders, artisans, and scribes made up the middle class. • Lowest but largest groups in ...
Notes- Chapter 5
... • Thoth was the god of learning. He could take human or animal form—or both—as did most gods and goddesses. ...
... • Thoth was the god of learning. He could take human or animal form—or both—as did most gods and goddesses. ...
Ancient Egypt jeopardy 2
... One of the greatest rulers of The New Kingdom. He studied plants and led his ...
... One of the greatest rulers of The New Kingdom. He studied plants and led his ...
Tombs During the Old Kingdom, mastabas and pyramids were built
... The ancient Egyptians had an elaborate set of burial customs that they believed were necessary to ensure their immortality after death. The building of tomb structures such as mastabas and pyramids were intended to preserve the corpse of the deceased, under the belief that this would in turn preser ...
... The ancient Egyptians had an elaborate set of burial customs that they believed were necessary to ensure their immortality after death. The building of tomb structures such as mastabas and pyramids were intended to preserve the corpse of the deceased, under the belief that this would in turn preser ...
Ancient Egyptian funerary practices

The ancient Egyptians had an elaborate set of funerary practices that they believed were necessary to ensure their immortality after death (the after life). These rituals and protocols included mummifying the body, casting of magic spells, and burial with specific grave goods thought to be needed in the Egyptian afterlife.The burial process used by the ancient Egyptians evolved throughout time as old customs were discarded and new ones adopted, but several important elements of the process persisted. Although specific details changed over time, the preparation of the body, the magic rituals involved, and the grave goods provided were all essential parts of a proper Egyptian funeral.













![Ancient_Egypt_PPT[1]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/003961717_1-e60e333be34cd6eff9a295b52d154e89-300x300.png)