Data Acquisition
... Definition → Sampling is the process by which the signal is converted to digital values. ...
... Definition → Sampling is the process by which the signal is converted to digital values. ...
Experiment # 9
... often the value of a signal must be measured during a given time interval in order to reconstruct its shape tm correctly. The answer is given by the sampling theorem of time functions (Nyquist Criterion): If the given time function F(t) has a limited bandwidth B and the time interval of measurement ...
... often the value of a signal must be measured during a given time interval in order to reconstruct its shape tm correctly. The answer is given by the sampling theorem of time functions (Nyquist Criterion): If the given time function F(t) has a limited bandwidth B and the time interval of measurement ...
Microprocessor Engineering
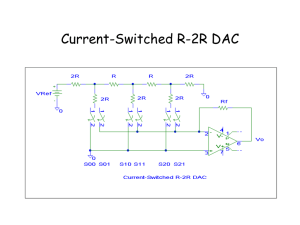
... Resisters need to have a tolerance less than the resolution. E.g. 8-bit resolution = 1:28 = 1/256 = 0.00390625 resolution = 0.390625% Alternative is R-2R ladder arrangement R-2R ...
... Resisters need to have a tolerance less than the resolution. E.g. 8-bit resolution = 1:28 = 1/256 = 0.00390625 resolution = 0.390625% Alternative is R-2R ladder arrangement R-2R ...
EELab2_Exp8_AD_Converter
... usually continuous voltages or currents, to digital words used in computing, data transmission, information processing and storage, and control systems. We do this conversion because digital signals are eas to store, debug, and are almost free from noise. ...
... usually continuous voltages or currents, to digital words used in computing, data transmission, information processing and storage, and control systems. We do this conversion because digital signals are eas to store, debug, and are almost free from noise. ...
(ADC) and Digital to analog converter (DAC)
... 2. A bipolar DAC hat 10 bits and a reference of 5v.what outputs will result from input of 04FH and 2A4H.What digital input gives a zero output voltage? 3. Determine how many bits a D/A converter must have to provide output increments of 0.04 volts or less. The reference is 10 volts. 4. A control val ...
... 2. A bipolar DAC hat 10 bits and a reference of 5v.what outputs will result from input of 04FH and 2A4H.What digital input gives a zero output voltage? 3. Determine how many bits a D/A converter must have to provide output increments of 0.04 volts or less. The reference is 10 volts. 4. A control val ...
Lecture 7
... different voltage levels, with each level corresponding to a different binary number. This process is called quantization Converted to the closest binary value provided in the digitizing system At each sampling interval, the analog amplitude is quantized into the closest available quantization level ...
... different voltage levels, with each level corresponding to a different binary number. This process is called quantization Converted to the closest binary value provided in the digitizing system At each sampling interval, the analog amplitude is quantized into the closest available quantization level ...
Figure 1–1 Communication system.
... • Quantizing noise (during A/D conversion) • Environment noise (e.g., EM interference) • Filtering noise (low pass filtering at decoder) Types of Quantization Noise • Overload noise (input too large) • Random noise (input too small) • Granular noise (non uniform error jump) • Hunting noise (too long ...
... • Quantizing noise (during A/D conversion) • Environment noise (e.g., EM interference) • Filtering noise (low pass filtering at decoder) Types of Quantization Noise • Overload noise (input too large) • Random noise (input too small) • Granular noise (non uniform error jump) • Hunting noise (too long ...
1 - Electrical Engineering and Computer Science
... – Those filters typically have a cut-off frequency just above ½ their maximum sampling rate. • Which is great if you are using the maximum sampling rate, less useful if you are sampling at a slower rate. ...
... – Those filters typically have a cut-off frequency just above ½ their maximum sampling rate. • Which is great if you are using the maximum sampling rate, less useful if you are sampling at a slower rate. ...
Trabalho 1
... with fsignal close to fcut-off needed to build a Bode plot of the filter (amplitude & phase transfer function). Acquire both signals at the input and output of the filter. Note: you must use ADC Simultaneous Sampling Mode. 7) Introduce an artificial “jitter” on the Timer, by changing the PRx (period ...
... with fsignal close to fcut-off needed to build a Bode plot of the filter (amplitude & phase transfer function). Acquire both signals at the input and output of the filter. Note: you must use ADC Simultaneous Sampling Mode. 7) Introduce an artificial “jitter” on the Timer, by changing the PRx (period ...
IC Applications. Successive Approximation A/D converter
... One method of addressing the digital ramp ADC's shortcomings is the so-called successive-approximation ADC. The only change in this design is a very special counter circuit known as a successive-approximation register. Instead of counting up in binary sequence, this register counts by trying all val ...
... One method of addressing the digital ramp ADC's shortcomings is the so-called successive-approximation ADC. The only change in this design is a very special counter circuit known as a successive-approximation register. Instead of counting up in binary sequence, this register counts by trying all val ...
Sheet 5
... 1. To sketch the following circuits and explain the operation of each: 1. Digital to Analog. 2. Analog to Digital. 2. To analyze and design circuits of the type listed in item I above. 3. To trouble shoot and analyze faults in the circuits. 1.2 PRE LAB QUESTIONS 1. A comparator may be thought of as ...
... 1. To sketch the following circuits and explain the operation of each: 1. Digital to Analog. 2. Analog to Digital. 2. To analyze and design circuits of the type listed in item I above. 3. To trouble shoot and analyze faults in the circuits. 1.2 PRE LAB QUESTIONS 1. A comparator may be thought of as ...
***** 1
... Minimal load impact. A gain-transfer characteristic of an active filter is practically independent of the load the filter works for and a source that controls the filter. Non-inductive filters. To design an active filter only resistors and capacitors are required, inductance is not required. This fe ...
... Minimal load impact. A gain-transfer characteristic of an active filter is practically independent of the load the filter works for and a source that controls the filter. Non-inductive filters. To design an active filter only resistors and capacitors are required, inductance is not required. This fe ...
Slide 1
... MC_HI(STANBY); MC_LO(LEFT0); MC_LO(LEFT1); MC_LO(RIGHT0); MC_LO(RIGHT1); int speed = 1000; ...
... MC_HI(STANBY); MC_LO(LEFT0); MC_LO(LEFT1); MC_LO(RIGHT0); MC_LO(RIGHT1); int speed = 1000; ...
Preliminary Project in Preparation for the Mid
... another sample. It may do this several times a second. An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The inverse operation (Digital to Analog) is performed by a ...
... another sample. It may do this several times a second. An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The inverse operation (Digital to Analog) is performed by a ...
Electronics Analog-to
... In practice, the resolution of the converter is limited by the signal-to-noise ratio of the signal in question. If there is too much noise present in the analog input, it will be impossible to accurately resolve beyond a certain number of bits of resolution, the "effective number of bits" (ENOB). Wh ...
... In practice, the resolution of the converter is limited by the signal-to-noise ratio of the signal in question. If there is too much noise present in the analog input, it will be impossible to accurately resolve beyond a certain number of bits of resolution, the "effective number of bits" (ENOB). Wh ...
Analog-to-Digital Conversion
... Illustrated is a 3-bit flash ADC with resolution 1 volt (after Tocci). The resistor net and comparators provide an input to the combinational logic circuit, so the conversion time is just the propagation delay through the network - it is not limited by the clock rate or some convergence sequence. It ...
... Illustrated is a 3-bit flash ADC with resolution 1 volt (after Tocci). The resistor net and comparators provide an input to the combinational logic circuit, so the conversion time is just the propagation delay through the network - it is not limited by the clock rate or some convergence sequence. It ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).