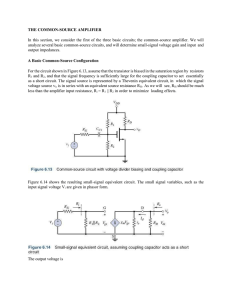
the common-source amplifier
... R1 and R2, and that the signal frequency is sufficiently large for the coupling capacitor to act essentially as a short circuit. The signal source is represented by a Thevenin equivalent circuit, in which the signal voltage source vi, is in series with an equivalent source resistance RSi. As we will ...
... R1 and R2, and that the signal frequency is sufficiently large for the coupling capacitor to act essentially as a short circuit. The signal source is represented by a Thevenin equivalent circuit, in which the signal voltage source vi, is in series with an equivalent source resistance RSi. As we will ...
DC1384 - LTC2452CDDB Evaluation Kit Quick Start Guide
... QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 1384 ...
... QUICK START GUIDE FOR DEMONSTRATION CIRCUIT 1384 ...
ppt
... a) Use new coding scheme, all codes have 4 ones and 4 zeros b) Use a 7-bit gray code with 1 parity bit For full-scale ADC (DAC step size ~16) ...
... a) Use new coding scheme, all codes have 4 ones and 4 zeros b) Use a 7-bit gray code with 1 parity bit For full-scale ADC (DAC step size ~16) ...
Benefits of Sigma-Delta ADCs
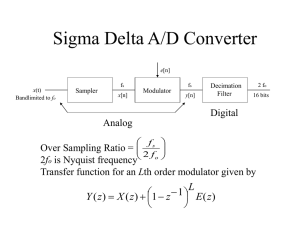
... data rate is achieved by a process called decimation by a factor of M. This process passes every Mth bit to the output, while discarding the remainder. The factor M can be any integer value, provided that the output data rate is greater than twice the signal bandwidth. No loss of information will re ...
... data rate is achieved by a process called decimation by a factor of M. This process passes every Mth bit to the output, while discarding the remainder. The factor M can be any integer value, provided that the output data rate is greater than twice the signal bandwidth. No loss of information will re ...
Electronic signal converters Micropace™ LMI
... Electronic signal converters Micropace™ LMI Micropace™ Range •The Micropace™ line of rugged, low cost control modules provide you with the ability to proportionally adjust the output of any LMI AA7/AA9/B7/B9/C7/C9 metering pump. •Adjustment can be made by multiplying (MP-500-M), dividing (MP-400-D) ...
... Electronic signal converters Micropace™ LMI Micropace™ Range •The Micropace™ line of rugged, low cost control modules provide you with the ability to proportionally adjust the output of any LMI AA7/AA9/B7/B9/C7/C9 metering pump. •Adjustment can be made by multiplying (MP-500-M), dividing (MP-400-D) ...
Chapter 1.2 - Electronic Signal & Switches
... Timing is very important for digital signals. Clock & timing circuits: ...
... Timing is very important for digital signals. Clock & timing circuits: ...
MCE380 handout - Cleveland State University
... Analog-to-Digital Conversion Principles In ADC we take a sample of an analog voltage and represent it using the available number of bits. ADC converters usually require a sample-and-hold (S&H) circuit at their input. The S&H captures the voltage and holds it constant for the converter to carry its ...
... Analog-to-Digital Conversion Principles In ADC we take a sample of an analog voltage and represent it using the available number of bits. ADC converters usually require a sample-and-hold (S&H) circuit at their input. The S&H captures the voltage and holds it constant for the converter to carry its ...
ADC Presentation - James Cockrell, Justin Loveless
... • Resolution = 3.3V / 4096 = 8.05 mV (p. 803) ...
... • Resolution = 3.3V / 4096 = 8.05 mV (p. 803) ...
File
... ARM Cortex M4F • RISC based microprocessor • 80 MHz clock speed • Two 12-bit ADC modules with maximum sample rate of 1 MSPS • 256 KB Flash memory • Four SSI Modules • 105 GPIOs including 24 shared analog input channels • Single-precision Floating Point Unit (FPU) ...
... ARM Cortex M4F • RISC based microprocessor • 80 MHz clock speed • Two 12-bit ADC modules with maximum sample rate of 1 MSPS • 256 KB Flash memory • Four SSI Modules • 105 GPIOs including 24 shared analog input channels • Single-precision Floating Point Unit (FPU) ...
a-d conversion
... Sources of Error • The fact that we are using a converter which has a finite number of bits introduces an error called “quantization error” • The fact that it takes a finite (non-zero) amount of time to perform the conversion introduces the possibility of an error called ...
... Sources of Error • The fact that we are using a converter which has a finite number of bits introduces an error called “quantization error” • The fact that it takes a finite (non-zero) amount of time to perform the conversion introduces the possibility of an error called ...
Analog to Digital Converter
... Scaling - allows the user to divide or multiply the input voltage to more closely match the full scale range of the ADC Sample Rate - The sample rate must be at least twice the frequency the you are measuring, but 5 times is much better Channel Scan Rate - The channel scan rate is the maximum rate t ...
... Scaling - allows the user to divide or multiply the input voltage to more closely match the full scale range of the ADC Sample Rate - The sample rate must be at least twice the frequency the you are measuring, but 5 times is much better Channel Scan Rate - The channel scan rate is the maximum rate t ...
Common PDR Problems
... suitable voltage range by amplification or attenuation and/or level shifting. For highest accuracy the maximum range of the conditioned signal equals the maximum voltage input range of the ADC. Filtering (noise, extraneous signals). Isolation of sensor from computer system. ...
... suitable voltage range by amplification or attenuation and/or level shifting. For highest accuracy the maximum range of the conditioned signal equals the maximum voltage input range of the ADC. Filtering (noise, extraneous signals). Isolation of sensor from computer system. ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).