interface with analog world
... The motor seed, 0-1000rpm, goes from 0 to full-scale. Each step in DAC output produce a step in motor speed. We want the step size not greater than 5 rpm. Thus, at least we need 200 steps (1000/5). Number of steps: 2N – 1 ≥ 200 or 2N ≥ 201, since 28=256, therefore 8 bits. Using 8 bits, how close to ...
... The motor seed, 0-1000rpm, goes from 0 to full-scale. Each step in DAC output produce a step in motor speed. We want the step size not greater than 5 rpm. Thus, at least we need 200 steps (1000/5). Number of steps: 2N – 1 ≥ 200 or 2N ≥ 201, since 28=256, therefore 8 bits. Using 8 bits, how close to ...
Chapter 4
... □ Good voice reproduction □ PCM - 128 levels (7 bit) □ Voice bandwidth 4khz □ Should be 8000 x 7 = 56kbps for PCM □ Data compression can improve on this □ e.g. Interframe coding techniques for video ...
... □ Good voice reproduction □ PCM - 128 levels (7 bit) □ Voice bandwidth 4khz □ Should be 8000 x 7 = 56kbps for PCM □ Data compression can improve on this □ e.g. Interframe coding techniques for video ...
vlsi design of low power high speed adc
... pulses which was counted to generate the binary output at a sample rate of 6 kS/s. Following this, the successive approximation ADC was developed in 1948 by Black, Edson and Goodall to digitize voice to 5‐bits at 8 kS/s .Also in 1948, a 96 kS/s, 7‐bit ADC was developed and it was implemented using a ...
... pulses which was counted to generate the binary output at a sample rate of 6 kS/s. Following this, the successive approximation ADC was developed in 1948 by Black, Edson and Goodall to digitize voice to 5‐bits at 8 kS/s .Also in 1948, a 96 kS/s, 7‐bit ADC was developed and it was implemented using a ...
6. Pulse code modulation with
... In this section the binary codes produced by the ADC TL5501 corresponding to different analog input voltages will be determined. 1. Set the following parameters in the bottom function generator (FG2): Amplitude=2.3 V, Offset=1.2 V, Waveform: square, Frequency=10 kHz. The top function generator (FG1) ...
... In this section the binary codes produced by the ADC TL5501 corresponding to different analog input voltages will be determined. 1. Set the following parameters in the bottom function generator (FG2): Amplitude=2.3 V, Offset=1.2 V, Waveform: square, Frequency=10 kHz. The top function generator (FG1) ...
In this method cross correlation is used to find the impedance of the
... In this method cross correlation is used to find the impedance of the crystal, reducing much of the complications thought of before, and also minimizing the error percentage. Using white noise as an input signal will drown out interfering signals coming from surrounding obstacles that can affect res ...
... In this method cross correlation is used to find the impedance of the crystal, reducing much of the complications thought of before, and also minimizing the error percentage. Using white noise as an input signal will drown out interfering signals coming from surrounding obstacles that can affect res ...
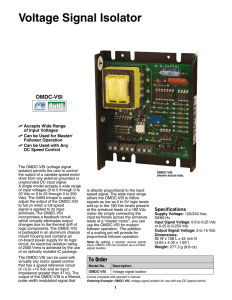
Voltage Signal Isolator
... isolator) permits the user to control the output of a variable speed motor drive from any external grounded or ungrounded DC input signal. A single model accepts a wide range of input voltages (0 to 5 through 0 to 25 Vdc or 0 to 25 through 0 to 250 Vdc). The GAIN trimpot is used to adjust the output ...
... isolator) permits the user to control the output of a variable speed motor drive from any external grounded or ungrounded DC input signal. A single model accepts a wide range of input voltages (0 to 5 through 0 to 25 Vdc or 0 to 25 through 0 to 250 Vdc). The GAIN trimpot is used to adjust the output ...
Lecture Circuits
... bank feeds a logic circuit that generates a code for each voltage range. Direct conversion is very fast, but usually has only 8 bits of resolution (255 comparators - since the number of comparators required is 2n - 1) or fewer, as it needs a large, expensive circuit. A successive-approximation ADC u ...
... bank feeds a logic circuit that generates a code for each voltage range. Direct conversion is very fast, but usually has only 8 bits of resolution (255 comparators - since the number of comparators required is 2n - 1) or fewer, as it needs a large, expensive circuit. A successive-approximation ADC u ...
Slide 1
... bank feeds a logic circuit that generates a code for each voltage range. Direct conversion is very fast, but usually has only 8 bits of resolution (255 comparators - since the number of comparators required is 2n - 1) or fewer, as it needs a large, expensive circuit. A successive-approximation ADC u ...
... bank feeds a logic circuit that generates a code for each voltage range. Direct conversion is very fast, but usually has only 8 bits of resolution (255 comparators - since the number of comparators required is 2n - 1) or fewer, as it needs a large, expensive circuit. A successive-approximation ADC u ...
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... input voltage. For the AD7625, the common-mode voltage is one-half the internal reference voltage, REF/2, where REF = 4.096 V. ...
... input voltage. For the AD7625, the common-mode voltage is one-half the internal reference voltage, REF/2, where REF = 4.096 V. ...
Presentation
... • Analog signals can produce an infinite amount of signal resolution. However, in case of digital signals this is not possible. • Processing of analog signals is simpler & more straight forward. Eg: Reading an analog signal is easy as measuring a voltage. • Processing of digital signals it is more c ...
... • Analog signals can produce an infinite amount of signal resolution. However, in case of digital signals this is not possible. • Processing of analog signals is simpler & more straight forward. Eg: Reading an analog signal is easy as measuring a voltage. • Processing of digital signals it is more c ...
Digital Examination - Philadelphia University Jordan
... 9- Unused inputs of NOR gates should be connected to the: Power supply. Used input. Left floating. 10- The job of top transistor (T3) in totem pole output is to provide a path for the output ; High impedance. Low impedance.. None of the above 11- In order to increase the switching speed ...
... 9- Unused inputs of NOR gates should be connected to the: Power supply. Used input. Left floating. 10- The job of top transistor (T3) in totem pole output is to provide a path for the output ; High impedance. Low impedance.. None of the above 11- In order to increase the switching speed ...
DAC
... Source of error: step size of the internal DAC. Quantization error: difference between the actual (analog) quantity and the digital values assigned to it. Accuracy is dependent on the accuracy of the circuit components. Example 10-14. ...
... Source of error: step size of the internal DAC. Quantization error: difference between the actual (analog) quantity and the digital values assigned to it. Accuracy is dependent on the accuracy of the circuit components. Example 10-14. ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).