* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download In this method cross correlation is used to find the impedance of the
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Negative feedback wikipedia , lookup
Ground loop (electricity) wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Transmission line loudspeaker wikipedia , lookup
Multidimensional empirical mode decomposition wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Nominal impedance wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Regenerative circuit wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Wien bridge oscillator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Zobel network wikipedia , lookup
Analog-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
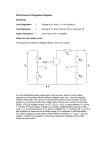
Omar Nasr Weekly Report In this method cross correlation is used to find the impedance of the crystal, reducing much of the complications thought of before, and also minimizing the error percentage. Using white noise as an input signal will drown out interfering signals coming from surrounding obstacles that can affect results. The white noise signal will be stimulated by the computer using a software program, which will then be sent to a D/A converter. The signal coming out from the D/A converter will stimulate the crystal to oscillate via an Op-amp. Using the Op-amp here will be beneficial in allowing low output impedance, and flat frequency response. The crystal’s output signal will then be fed into an Op-amp of the same type as the input. The signal will then be converted back to digital using an A/D converter, which will then be sent to the computer for data analysis. Using this data the impedance can be measured and by finding the impedance components the viscosity can ultimately be found. In the process a TTL signal is also taken into consideration as it will keep the system coordinated together, which will be used to mark the beginning of each stimulus while collecting data. To apply white noise input using a stimulator the design would require a ‘pseudo random binary noise source’ which would be complex in design. Figure 1 shows a general view of the design components. Figure 1 1 Omar Nasr Components to be used: Analog Devices Catalog AD 8033 Op-Amp is a voltage feedback amplifier which has a small signal bandwith of 80 MHz AD 7656 Converter operates with an input bandwidth of 50 KHz. AD 7273 Converter operates with an input bandwidth of 1 MHz. AD 5660 16-Bit nanoDAC converter. Using another approach a voltage controlled oscillator (VCO) generates an AC control voltage signal which is sent to the crystal by an Op-amp having it oscillate at a defined input. Using the Op-amp here will also be beneficial in allowing low output impedance, and flat frequency response. The output from the crystal will then be sent to another Op-amp of the same type as the input Op-amp. The output from this Op-amp will then be fed into a comparator which will identify between the high and low voltages. This will also be performed for the input signal going into the crystal. From this point the data is sent to a phase detector which output the phase difference signal. The output from the phase detector will then be sent to the computer for analysis. The impedance components 2 Omar Nasr of electrical resonant resistance and resonant frequency shift can then be found to solve for viscosity, and visco-elasticity. The resonant resistance and the resonant frequency are proportional to the viscosity of the fluid, and thus the viscosity can be determined. Figure 2 shows a general overview of the design layout. Figure 2 Components that will be used: Max 08 Voltage Controlled Oscillator LUCDA4044 Phase Frequency Detector LM339 Comparator Communicator to send information to computer 3