* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download a-d conversion
Mathematics of radio engineering wikipedia , lookup
Electrical substation wikipedia , lookup
Spark-gap transmitter wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
History of electric power transmission wikipedia , lookup
Current source wikipedia , lookup
Three-phase electric power wikipedia , lookup
Electrical ballast wikipedia , lookup
Chirp spectrum wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Television standards conversion wikipedia , lookup
Integrating ADC wikipedia , lookup
Power MOSFET wikipedia , lookup
Distribution management system wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope types wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Variable-frequency drive wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Utility frequency wikipedia , lookup
Surge protector wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Voltage regulator wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Stray voltage wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Alternating current wikipedia , lookup
Voltage optimisation wikipedia , lookup
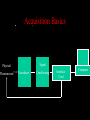
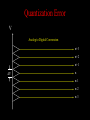
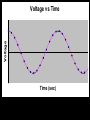
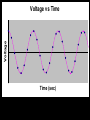
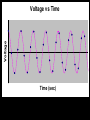
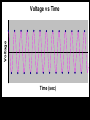
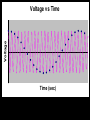
Computer Based Data Acquisition Basics Outline • Basics of data acquisition • Analog to Digital Conversion – Quantization – Aliasing Acquisition Basics Signal Physical Phenomenon Transducer Conditioning Interface Card Computer Analog to Digital Conversion • In this process, we convert an analog voltage into a number • Computers store numbers in “bits” • Typically use a 12 bit converter - converts each input voltage into some number between 0 and 4095 (212-1) • Maximum sample rate - if 100 kHz – takes 10 sec to perform the conversion Sources of Error • The fact that we are using a converter which has a finite number of bits introduces an error called “quantization error” • The fact that it takes a finite (non-zero) amount of time to perform the conversion introduces the possibility of an error called “aliasing” Quantization Error V Analog to Digital Conversion n+3 n+2 n+1 V n n-1 n-2 n-3 Quantization Error • For example, if we have a – 10 volt input range – n ranges from 0-4095 10 V V 2.44mV 4096 • Uncertainty of 1.22 mV Aliasing • Aliasing can lead to incorrect frequency information • Sampling Theorem - Maximum frequency component that can be correctly identified is that frequency which is 1/2 the sample frequency. This maximum frequency is called the Nyquist frequency. Voltage Voltage vs Time Time (sec) Voltage Voltage vs Time Time (sec) Voltage Voltage vs Time Time (sec) Voltage Voltage vs Time Time (sec) Voltage Voltage vs Time Time (sec) Aliasing • Once the observed frequency exceeds 1/2 half the sampling frequency, trouble starts 0.6 0.4 nal fmeasured /fsig Relation between Measured Frequency, Sampling Frequency and Signal Frequency 0.2 0 0 0.5 1 1.5 2 fsignal /fsample 2.5 3