* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Current-Switched R-2R DAC
Linear time-invariant theory wikipedia , lookup
PID controller wikipedia , lookup
Power inverter wikipedia , lookup
Solar micro-inverter wikipedia , lookup
Dynamic range compression wikipedia , lookup
Quantization (signal processing) wikipedia , lookup
Immunity-aware programming wikipedia , lookup
Resistive opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
Control system wikipedia , lookup
Buck converter wikipedia , lookup
Power electronics wikipedia , lookup
Flip-flop (electronics) wikipedia , lookup
Oscilloscope history wikipedia , lookup
Switched-mode power supply wikipedia , lookup
Schmitt trigger wikipedia , lookup
Pulse-width modulation wikipedia , lookup
Time-to-digital converter wikipedia , lookup
Opto-isolator wikipedia , lookup
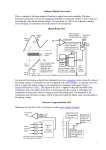
Current-Switched R-2R DAC Voltage-Switched R-2R DAC DAC Non-Linearities Differential & Integral Non-Linearities Ideal Actual 7 Output (Voltage) Value 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 Digital Input Value 5 6 7 DAC Gain & Offset Errors Gain and Offset Errors Ideal Gain Error Example Offset Error Example Output (Voltage) Value 7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0 0 1 2 3 4 Digital Input Value 5 6 7 Direct (Flash) ADC Successive Approximation ADC n-bit conversion in n clock cycles (n+1) bit conversion if comparator output used Comparator Analogue Input Logic DAC Digital Output 100(1) Clock Successive Approximation ADC 110(0) 101(1) Integrating ADCs There is a whole family of these circuits: o single-slope •o dual-slope •o multi-slope •o charge balance, PWM •o sigma-delta (-) (order 1 to m) • None need a T(S)/H, (but may be useful) • All integrate the input signal for a fixed time and then digitize it [conversion time up to 2 x 2n = 2n+1 clock periods] • However, the last 2 types integrate continuously • All allow increased resolution but are slower than the - type Dual-Slope ADC Integrator Output Waveforms VC 2n clock periods (2nT) m clock periods (mT) Time V -VREFt/R -VINt/R V = (2nT)VIN/R = mTVREF/R VIN/VREF = m/2n Dual-Slope Multi-Slope (n-bit conversion) Integrator Output Voltage Waveforms Multi-Slope ADC • To increase resolution, the comparator threshold becomes the limiting factor • Multi-slope uses smaller and smaller reference values to progressively approach the comparator zero at a slower rate • Each reference period ‘de-integrates’ the remaining error • Very much more complex circuit and costly • Much faster than Dual-Slope for the same resolution - used in some DVMs • May also be used with Charge-Balance Charge-Balance ADC Integrator Output Waveforms T mT Clock -(VIN/R)t/C Integrator Output Comparator Output D-Type (Q) Output -[(VIN/R) + I0]t/C V Charge Balance Performance Integrates signal and ‘reference’ signals continuously I0 = VREF/R then VIN = VREF.Count/CountMax Reduces integrator capacitor error of DualSlope Capable of 10-8 (26-bit) performance, if you can wait - speed v resolution DVM type ADC [PWM variants] Sigma-Delta ADC (1) • • • • • • • Recent variant of Delta modulator and Charge-Balance concepts Originally used for audio only, now used from dc to rf Very high resolution up to 22bits and very fast … 1000x faster than dual-slope Very complex internal operation but quite simple analog circuitry Uses a special (decimating) digital filter Can be integrated with µCs etc Minimal chip cost but support circuits still expensive for ultra-high performance Sigma-Delta ADC (2) Functional Diagram of 3rd order Sigma-Delta ADC LTC2440