Test Procedure for the NIS5132-35GEVB Evaluation Board
... 1. Basic operation. With no load, apply 12 volts at the 12V INPUT and Gnd pins of the board. Measure the voltage at the 12V OUTPUT terminal to Gnd. It should be equal to the input voltage. 2. Enable pin. With the input power still applied, ground the upper pad of the J-E12 jumper. The output should ...
... 1. Basic operation. With no load, apply 12 volts at the 12V INPUT and Gnd pins of the board. Measure the voltage at the 12V OUTPUT terminal to Gnd. It should be equal to the input voltage. 2. Enable pin. With the input power still applied, ground the upper pad of the J-E12 jumper. The output should ...
P13323_Technical_Paperx
... infrared sensors that are temporarily affixed to a guitar and that reproduce string tones through an analog or digital filter set. This is a completely optical system for each string so that each note is filtered and reproduced individually, thereby minimizing the influences of mechanical and electr ...
... infrared sensors that are temporarily affixed to a guitar and that reproduce string tones through an analog or digital filter set. This is a completely optical system for each string so that each note is filtered and reproduced individually, thereby minimizing the influences of mechanical and electr ...
DTMF decoder
... The HT9170 series tone decoders consist of three band pass filters and two digital decode circuits to convert a tone (DTMF) signal into digital code output. The pre-filter is a band rejection filter which reduces the dialing tone from 350Hz to 400Hz. The low group filter filters low group frequency ...
... The HT9170 series tone decoders consist of three band pass filters and two digital decode circuits to convert a tone (DTMF) signal into digital code output. The pre-filter is a band rejection filter which reduces the dialing tone from 350Hz to 400Hz. The low group filter filters low group frequency ...
Frequency Meter - Erasmus DWSPIT Polkowice
... A Q meter is a piece of equipment used in the testing of radio frequency circuits. It has been largely replaced in professional laboratories by other types of impedance measuring device, though it is still in use among radio amateurs. It was developed at Boonton Radio Corporation in Boonton, New Jer ...
... A Q meter is a piece of equipment used in the testing of radio frequency circuits. It has been largely replaced in professional laboratories by other types of impedance measuring device, though it is still in use among radio amateurs. It was developed at Boonton Radio Corporation in Boonton, New Jer ...
The Field Effect Transistor
... Redo the circuit replacing the computer-generated voltages with a power supply for VDD and a signal generator for the variable input voltages as shown in Figure 3. Choose a value of Rs to give the following circuit a good operating point. For a good operating point, the drain voltage is between 3 an ...
... Redo the circuit replacing the computer-generated voltages with a power supply for VDD and a signal generator for the variable input voltages as shown in Figure 3. Choose a value of Rs to give the following circuit a good operating point. For a good operating point, the drain voltage is between 3 an ...
altmann
... AMM reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein to improve reliability, function or design. ...
... AMM reserves the right to make changes without further notice to any products herein to improve reliability, function or design. ...
212k
... (1) Resistance type meter: the longitudinal 1-16 row of the socket is respectively as the 1-16 lines of three-line system resistance sensor input terminals and connect with each end of the resistance individually; the intermediate and bottom lines’ terminals connect the two outlet wires of another e ...
... (1) Resistance type meter: the longitudinal 1-16 row of the socket is respectively as the 1-16 lines of three-line system resistance sensor input terminals and connect with each end of the resistance individually; the intermediate and bottom lines’ terminals connect the two outlet wires of another e ...
WAVE SHAPING AND MULTIVIBRATOR CIRCUITS
... sufficient to snap Q1 on. Q1 quickly goes into saturation. The change in voltage from -VCC to 0Vcauses C1 to discharge. This voltage is coupled to the base of Q2 Placing / holding Q2 in cutoff. C1 begins to charge and will snap Q2 on when a sufficient voltage value is reached. In Summary, whenever a ...
... sufficient to snap Q1 on. Q1 quickly goes into saturation. The change in voltage from -VCC to 0Vcauses C1 to discharge. This voltage is coupled to the base of Q2 Placing / holding Q2 in cutoff. C1 begins to charge and will snap Q2 on when a sufficient voltage value is reached. In Summary, whenever a ...
An ultralow-energy adc for smart dust - Solid
... CMOS process. An annotated die micrograph of the standalone ADC chip (active area only) is shown in Fig. 8. The core circuitry as shown measures 0.053 mm , which is dominated by the capacitor array. To illustrate the relative size of the ADC in relation to the other components in Smart Dust, Fig. 9 ...
... CMOS process. An annotated die micrograph of the standalone ADC chip (active area only) is shown in Fig. 8. The core circuitry as shown measures 0.053 mm , which is dominated by the capacitor array. To illustrate the relative size of the ADC in relation to the other components in Smart Dust, Fig. 9 ...
Data and Computer Communications
... Intermodulation noise • produced by nonlinearities in the transmitter, receiver, and/or intervening transmission medium • effect is to produce signals at a frequency that is the sum or difference of the two original frequencies (sosmat.com) ...
... Intermodulation noise • produced by nonlinearities in the transmitter, receiver, and/or intervening transmission medium • effect is to produce signals at a frequency that is the sum or difference of the two original frequencies (sosmat.com) ...
3B47 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Output modules accept 0 to +10V (or +10V) single-ended signals and provide an isolated 4-20 mA (or 0-20 mA) process signal. All modules feature a universal pin-out and may be readily hot-swapped under full power and interchanged without disrupting field wiring. The Analog Devices 3B Series Signal Co ...
... Output modules accept 0 to +10V (or +10V) single-ended signals and provide an isolated 4-20 mA (or 0-20 mA) process signal. All modules feature a universal pin-out and may be readily hot-swapped under full power and interchanged without disrupting field wiring. The Analog Devices 3B Series Signal Co ...
CIRCUIT FUNCTION AND BENEFITS
... CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION This is a precise, fast sample-and-hold circuit. During the sample mode, SW2 is closed, and the output, VOUT, follows the input signal, VIN. In the hold mode, SW2 is opened, and the signal is held by the hold capacitor, CH. Due to switch and capacitor leakage current, the voltage ...
... CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION This is a precise, fast sample-and-hold circuit. During the sample mode, SW2 is closed, and the output, VOUT, follows the input signal, VIN. In the hold mode, SW2 is opened, and the signal is held by the hold capacitor, CH. Due to switch and capacitor leakage current, the voltage ...
7B22 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... other process control signals. The 7B Series modules amplify, linearize, isolate, protect and convert the transducer output signals to standardized analog inputs for high-level analog I/O subsystems. The 7B Series Subsystem consists of 19-inch rackcompatible hardware (model AC 1363), with universal ...
... other process control signals. The 7B Series modules amplify, linearize, isolate, protect and convert the transducer output signals to standardized analog inputs for high-level analog I/O subsystems. The 7B Series Subsystem consists of 19-inch rackcompatible hardware (model AC 1363), with universal ...
Sampling: DAC and ADC conversion
... (2) The quantization error is determined by the number of bits that are later used to encode the signal. If we increase the number of bits, the error will decrease Question: How many bits do we need in the ADC? How fine should the quantization be? (equivalent questions) Answer: the number of bits ch ...
... (2) The quantization error is determined by the number of bits that are later used to encode the signal. If we increase the number of bits, the error will decrease Question: How many bits do we need in the ADC? How fine should the quantization be? (equivalent questions) Answer: the number of bits ch ...
Digital Circuit I (EEI 101)
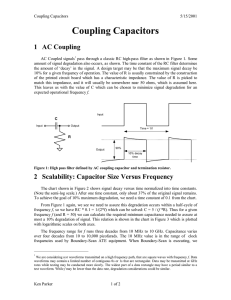
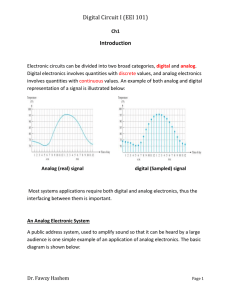
... Most waveforms encountered in digital systems are composed of series of pulses, sometimes called pulse trains, and can be classified as either periodic or nonperiodic. A periodic pulse waveform is one that repeats itself at a fixed interval, called a period (T). The frequency (f) is the rate at whic ...
... Most waveforms encountered in digital systems are composed of series of pulses, sometimes called pulse trains, and can be classified as either periodic or nonperiodic. A periodic pulse waveform is one that repeats itself at a fixed interval, called a period (T). The frequency (f) is the rate at whic ...
EVAL-CN0255-SDPZ Datasheet
... The heart of this circuit is the AD7988-1, a 16-bit, 100 kSPS successive approximation, ADC that operates from a single VDD power supply. It contains a low power, high speed, 16-bit sampling ADC and a versatile serial port interface (SPI). On the CNV rising edge, it samples an analog input, IN+, bet ...
... The heart of this circuit is the AD7988-1, a 16-bit, 100 kSPS successive approximation, ADC that operates from a single VDD power supply. It contains a low power, high speed, 16-bit sampling ADC and a versatile serial port interface (SPI). On the CNV rising edge, it samples an analog input, IN+, bet ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).