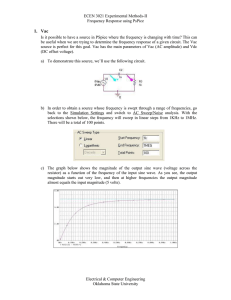
Lab 6
... as 59.2 (or 60) mV/pH unit. Both the constant and the slope of the response are expected to depend on temperature. Clearly, pH measurement requires calibration, as do most instrumental measurements. There are good descriptions of the glass electrode and the associated reference electrodes in most an ...
... as 59.2 (or 60) mV/pH unit. Both the constant and the slope of the response are expected to depend on temperature. Clearly, pH measurement requires calibration, as do most instrumental measurements. There are good descriptions of the glass electrode and the associated reference electrodes in most an ...
Document
... After noise is added, the original amplitudes of a digital signal can be determined. This is not true for an analog signal. ...
... After noise is added, the original amplitudes of a digital signal can be determined. This is not true for an analog signal. ...
5B39 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... without disturbing field wiring or power. The isolated input modules provide 0 to +5V or +5V outputs and accept J, K, T, E, R, S, N, or B type thermocouples. These modules feature complete signal conditioning functions including 240 V rms input protection, filtering, chopper stabilized low drift +1 ...
... without disturbing field wiring or power. The isolated input modules provide 0 to +5V or +5V outputs and accept J, K, T, E, R, S, N, or B type thermocouples. These modules feature complete signal conditioning functions including 240 V rms input protection, filtering, chopper stabilized low drift +1 ...
Floating Signal Inputs
... often must use different instruments because of the various ranges needed. Standard ranges of +/‐10V may handle some applications, but not others, to the required resolution and accuracy. With isolation per channel, combinations of channels can be used to measure higher voltage ranges. Figure 6 ...
... often must use different instruments because of the various ranges needed. Standard ranges of +/‐10V may handle some applications, but not others, to the required resolution and accuracy. With isolation per channel, combinations of channels can be used to measure higher voltage ranges. Figure 6 ...
11.3.4 worksheet - Digilent Learn site
... 2. Signal Conditioning Circuit (50 points total) 1. Provide below a schematic showing your signal conditioning circuit. Include desired resistance and capacitance values (3 pts) ...
... 2. Signal Conditioning Circuit (50 points total) 1. Provide below a schematic showing your signal conditioning circuit. Include desired resistance and capacitance values (3 pts) ...
Presentation 3 File
... Digital multimeters (DMMs) are used to measure voltage, current, and resistance and to indicate measured value on a digital display rather than using a moving pointer as analog meters. Compared to analog multimeters, DMMs provide higher accuracy at lower cost. In addition, digital processing allows ...
... Digital multimeters (DMMs) are used to measure voltage, current, and resistance and to indicate measured value on a digital display rather than using a moving pointer as analog meters. Compared to analog multimeters, DMMs provide higher accuracy at lower cost. In addition, digital processing allows ...
Question 3 [instrument specifications]
... Proper measurement of a particular measurement signal requires its signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) to be better than a factor of 100. It appears that the signal consists of two sinewave components: a measurement signal with frequency 2 Hz and amplitude 50 mV, and an interference signal with frequency 10 ...
... Proper measurement of a particular measurement signal requires its signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) to be better than a factor of 100. It appears that the signal consists of two sinewave components: a measurement signal with frequency 2 Hz and amplitude 50 mV, and an interference signal with frequency 10 ...
How to make Frequency plots with Pspice
... When a sine wave source is applied to a linear circuit, all currents and voltages in the circuit will be sine waves of the same frequency. The only differences between the source sine wave and a response sine wave will be the magnitude difference and the phase shift. Bode plots are graphs that show ...
... When a sine wave source is applied to a linear circuit, all currents and voltages in the circuit will be sine waves of the same frequency. The only differences between the source sine wave and a response sine wave will be the magnitude difference and the phase shift. Bode plots are graphs that show ...
a 8-Bit, 50 MSPS/80 MSPS/100 MSPS 3 V A/D Converter AD9283
... Hand-Held Scopemeters Low Cost Digital Oscilloscopes ...
... Hand-Held Scopemeters Low Cost Digital Oscilloscopes ...
AN-1137 APPLICATION NOTE
... when a large number of samples is averaged. This averaging is carried out in the second part of the ADC, the digital low-pass filter. By averaging a large number of bits from the modulator, the low-pass filter can produce 24-bit data-words that are proportional to the input signal level. The Σ-Δ con ...
... when a large number of samples is averaged. This averaging is carried out in the second part of the ADC, the digital low-pass filter. By averaging a large number of bits from the modulator, the low-pass filter can produce 24-bit data-words that are proportional to the input signal level. The Σ-Δ con ...
Assignment 4: Photocell Bargraph
... The voltage divider generates an output voltage that is a function of the ratio of the two resistances in the legs of the converter. In this instance, the photocell is in the upper leg. Its resistance decreases with increasing light, causing a higher voltage result in this case. Sample Code The file ...
... The voltage divider generates an output voltage that is a function of the ratio of the two resistances in the legs of the converter. In this instance, the photocell is in the upper leg. Its resistance decreases with increasing light, causing a higher voltage result in this case. Sample Code The file ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).












![Question 3 [instrument specifications]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/001115092_1-d26316a852471c5d3da9a6a8712585ee-300x300.png)