Chapter 8: Data Communication Fundamentals
... of Analog Data Primarily used in retransmission devices The sampling theorem: If a signal is sampled at regular intervals of time and at a rate higher than twice the significant signal frequency, the samples contain all the information of the original signal. 8000 samples/sec sufficient for 4000h ...
... of Analog Data Primarily used in retransmission devices The sampling theorem: If a signal is sampled at regular intervals of time and at a rate higher than twice the significant signal frequency, the samples contain all the information of the original signal. 8000 samples/sec sufficient for 4000h ...
display
... Test the power amplifier circuit with input connected to sweep signal generator from 0 ~ 20V pp sine wave and also sweep frequencies between 100 Hz to 100 kHz in 100 Hz increments, record the output data. Calculate the frequency response of the output voltage. Combine current limiting circuit and re ...
... Test the power amplifier circuit with input connected to sweep signal generator from 0 ~ 20V pp sine wave and also sweep frequencies between 100 Hz to 100 kHz in 100 Hz increments, record the output data. Calculate the frequency response of the output voltage. Combine current limiting circuit and re ...
3B30 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Output modules accept 0 to +10V (or +10V) single-ended signals and provide an isolated 4-20 mA (or 0-20 mA) process signal. All modules feature a universal pin-out and may be readily hot-swapped under full power and interchanged without disrupting field wiring. The Analog Devices 3B Series Signal Co ...
... Output modules accept 0 to +10V (or +10V) single-ended signals and provide an isolated 4-20 mA (or 0-20 mA) process signal. All modules feature a universal pin-out and may be readily hot-swapped under full power and interchanged without disrupting field wiring. The Analog Devices 3B Series Signal Co ...
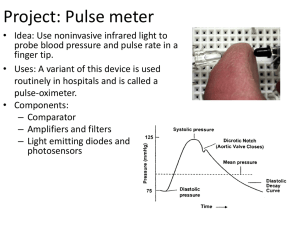
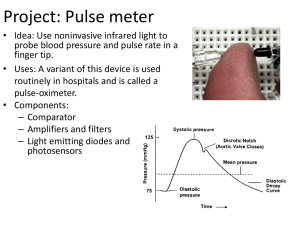
Pulse_meter_project_brl4
... – Build a noninverting amplifier with a gain of 11. A high pass filter at 1 radian/sec and low pass at 100 radians/sec. Use power supply voltages of +5 and -5 volts. – Test it by connecting the input to the waveform generator and the output to the scope as shown below. – Set up the waveform generato ...
... – Build a noninverting amplifier with a gain of 11. A high pass filter at 1 radian/sec and low pass at 100 radians/sec. Use power supply voltages of +5 and -5 volts. – Test it by connecting the input to the waveform generator and the output to the scope as shown below. – Set up the waveform generato ...
IF Alignment - Canadian Vintage Radio Society
... • Very few commercial units available… so, why not build one yourself? The example here is from ’Radio Bygones’ magazine, April/May, 2003. It is combined in one box with a DFM kit from Norcal ...
... • Very few commercial units available… so, why not build one yourself? The example here is from ’Radio Bygones’ magazine, April/May, 2003. It is combined in one box with a DFM kit from Norcal ...
View File - UET Taxila
... Whenever the bandwidth of a medium linking two devices is greater than the bandwidth needs of the devices, the link can be shared. Multiplexing is the set of techniques that allows the simultaneous transmission of multiple signals across a single data link. As data and telecommunications use increas ...
... Whenever the bandwidth of a medium linking two devices is greater than the bandwidth needs of the devices, the link can be shared. Multiplexing is the set of techniques that allows the simultaneous transmission of multiple signals across a single data link. As data and telecommunications use increas ...
3B40 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... Output modules accept 0 to +10V (or +10V) single-ended signals and provide an isolated 4-20 mA (or 0-20 mA) process signal. All modules feature a universal pin-out and may be readily hot-swapped under full power and interchanged without disrupting field wiring. The Analog Devices 3B Series Signal Co ...
... Output modules accept 0 to +10V (or +10V) single-ended signals and provide an isolated 4-20 mA (or 0-20 mA) process signal. All modules feature a universal pin-out and may be readily hot-swapped under full power and interchanged without disrupting field wiring. The Analog Devices 3B Series Signal Co ...
EVALUATION AND DESIGN SUPPORT
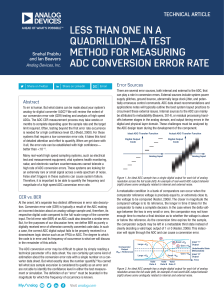
... The ADC full-scale voltage is equal to 2.3 V. The maximum detector output voltage (when operating in its linear input range) is approximately 3.5 V (see ADL5902 data sheet figures 6, 7, 8, 12, 13, and 14) and must, therefore, be scaled down by a factor of 0.657 before driving the AD7466. This scalin ...
... The ADC full-scale voltage is equal to 2.3 V. The maximum detector output voltage (when operating in its linear input range) is approximately 3.5 V (see ADL5902 data sheet figures 6, 7, 8, 12, 13, and 14) and must, therefore, be scaled down by a factor of 0.657 before driving the AD7466. This scalin ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).