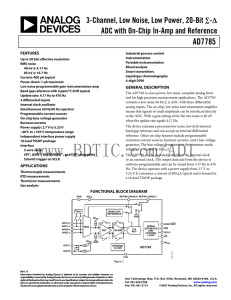
AD7785 3-Channel, Low Noise, Low Power, 20-Bit ∑-Δ
... continuous with all data transmitted in a continuous train of pulses. Alternatively, it can be a noncontinuous clock with the information being transmitted to or from the ADC in smaller batches of data. Clock In/Clock Out. The internal clock can be made available at this pin. Alternatively, the inte ...
... continuous with all data transmitted in a continuous train of pulses. Alternatively, it can be a noncontinuous clock with the information being transmitted to or from the ADC in smaller batches of data. Clock In/Clock Out. The internal clock can be made available at this pin. Alternatively, the inte ...
AD7933 数据手册DataSheet下载
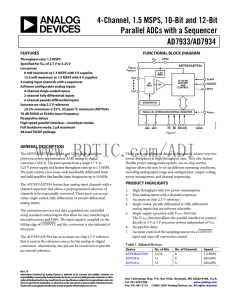
... The AD7933/AD7934 are 10-bit and 12-bit, high speed, low power, successive approximation (SAR) analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). The parts operate from a single 2.7 V to 5.25 V power supply and feature throughput rates up to 1.5 MSPS. The parts contain a low noise, wide bandwidth, differential tr ...
... The AD7933/AD7934 are 10-bit and 12-bit, high speed, low power, successive approximation (SAR) analog-to-digital converters (ADCs). The parts operate from a single 2.7 V to 5.25 V power supply and feature throughput rates up to 1.5 MSPS. The parts contain a low noise, wide bandwidth, differential tr ...
MEASUREMENTS OF ACOUSTIC EMISSION INDUCED BY PARTIAL
... interferences emitted by these tools. Such popularity means a continuous need of their quality enhancement when costs of the used materials and of the assembly process have to be reduced. Both requirements are contradictory and lead to the necessity of a more strict quality monitoring than required ...
... interferences emitted by these tools. Such popularity means a continuous need of their quality enhancement when costs of the used materials and of the assembly process have to be reduced. Both requirements are contradictory and lead to the necessity of a more strict quality monitoring than required ...
New CMOS Realization of Voltage Differencing Buffered Amplifier
... transferred to current at the terminal Z by transconductance gain and the voltage drop at the terminal Z is mirrored in different impedance region, that is, terminal W. However, VDBA provides properties of current mode circuit such as greater bandwidth, lower power consumption, higher slew rate and ...
... transferred to current at the terminal Z by transconductance gain and the voltage drop at the terminal Z is mirrored in different impedance region, that is, terminal W. However, VDBA provides properties of current mode circuit such as greater bandwidth, lower power consumption, higher slew rate and ...
Aalborg Universitet
... % of the DC-link capacitor. applied for a back-to-back converter study Winding case in order capacitance value change K losses W The proposed method requires no additional hardware circuit and can be implemented by using the spare resources of existing digital controllers in most only in the researc ...
... % of the DC-link capacitor. applied for a back-to-back converter study Winding case in order capacitance value change K losses W The proposed method requires no additional hardware circuit and can be implemented by using the spare resources of existing digital controllers in most only in the researc ...
FMS6690 Six Channel, 6 Order, SD/PS/HD Video Filter Driver FM
... The FMS6690 outputs are DC offset from the input by 150mV therefore, VOUT = 2•VIN DC+150mv. This offset is required to obtain optimal performance from the output driver and is held at the minimum value to decrease the standing DC current into the load. Since the FMS6690 has a 2x (6dB) gain, the outp ...
... The FMS6690 outputs are DC offset from the input by 150mV therefore, VOUT = 2•VIN DC+150mv. This offset is required to obtain optimal performance from the output driver and is held at the minimum value to decrease the standing DC current into the load. Since the FMS6690 has a 2x (6dB) gain, the outp ...
PCKV857 70–190 MHz differential 1:10 clock
... 1. This is intended to operate in the SSTL_2 type IV unterminated mode without series resistors on the outputs. 2. All typical values are at respective nominal VDDQ. 3. Differential cross-point voltage is expected to track variations of VDDQ and is the voltage at which the differential signals must ...
... 1. This is intended to operate in the SSTL_2 type IV unterminated mode without series resistors on the outputs. 2. All typical values are at respective nominal VDDQ. 3. Differential cross-point voltage is expected to track variations of VDDQ and is the voltage at which the differential signals must ...
LT5519 - 0.7GHz to 1.4GHz High Linearity
... The LT®5519 mixer is designed to meet the high linearity requirements of wireless and cable infrastructure transmission systems. A high speed, internally 50Ω matched, LO amplifier drives a double-balanced mixer core, allowing the use of a low power, single-ended LO source. An RF output transformer i ...
... The LT®5519 mixer is designed to meet the high linearity requirements of wireless and cable infrastructure transmission systems. A high speed, internally 50Ω matched, LO amplifier drives a double-balanced mixer core, allowing the use of a low power, single-ended LO source. An RF output transformer i ...
Evaluate: MAX1286/MAX1288/MAX1086/MAX1088 MAX1286 Evaluation Kit and Evaluation System General Description
... The MAX1286EVC16 EV system operates from a usersupplied 8V to 20V DC power supply. Windows 95/98 software interfaces to the EV system board through the PC’s standard serial port. See the Quick Start section for setup and operating instructions. ...
... The MAX1286EVC16 EV system operates from a usersupplied 8V to 20V DC power supply. Windows 95/98 software interfaces to the EV system board through the PC’s standard serial port. See the Quick Start section for setup and operating instructions. ...
315MHz/433MHz ASK Superheterodyne Receiver with Extended Dynamic Range General Description Features
... frequency range. Its signal range is from -114dBm to 0dBm. With few external components and a low-current power-down mode, it is ideal for cost- and power-sensitive applications typical in the automotive and consumer markets. The chip consists of a low-noise amplifier (LNA), a fully differential ima ...
... frequency range. Its signal range is from -114dBm to 0dBm. With few external components and a low-current power-down mode, it is ideal for cost- and power-sensitive applications typical in the automotive and consumer markets. The chip consists of a low-noise amplifier (LNA), a fully differential ima ...
Example: Diode Circuit Transfer Function
... In other words, we have determined that the ideal diode will be reverse biased when vS < 0.7 V , and that the output voltage will ...
... In other words, we have determined that the ideal diode will be reverse biased when vS < 0.7 V , and that the output voltage will ...
MAX8215/MAX8216 ±5V, ±12V (±15V) Dedicated Microprocessor Voltage Monitors _______________General Description
... Pull-up resistors are required at the outputs of each comparator. Resistor values should not be less than 2.7kΩ if the outputs are pulled up to VDD. In general, save power by using higher values, e.g., ≥100kΩ. Use of higher-value resistors also minimizes the possibility of oscillations due to a spur ...
... Pull-up resistors are required at the outputs of each comparator. Resistor values should not be less than 2.7kΩ if the outputs are pulled up to VDD. In general, save power by using higher values, e.g., ≥100kΩ. Use of higher-value resistors also minimizes the possibility of oscillations due to a spur ...
14-Bit, 500 kSPS PulSAR ADC in MSOP AD7946
... the middle of each code to the true straight line (Figure 24). ...
... the middle of each code to the true straight line (Figure 24). ...
LF2418891896
... The multiplier used in PD is a very important part of PLL system since it compares the input reference and the VCO signals simultaneously. If both inputs to the multiplier are sinusoidal then the mixing operation is true analog multiplication and the output is a function of input signal amplitudes, ...
... The multiplier used in PD is a very important part of PLL system since it compares the input reference and the VCO signals simultaneously. If both inputs to the multiplier are sinusoidal then the mixing operation is true analog multiplication and the output is a function of input signal amplitudes, ...
DM7446A, DM7447A BCD to 7-Segment Decoders/Drivers
... Note 1: BI/RBO is a wire-AND logic serving as blanking input (BI) and/or ripple-blanking output (RBO). Note 2: The blanking input (BI) must be OPEN or held at a HIGH logic level when output functions 0 through 15 are desired. The ripple-blanking input (RBI) must be OPEN or HIGH if blanking of a deci ...
... Note 1: BI/RBO is a wire-AND logic serving as blanking input (BI) and/or ripple-blanking output (RBO). Note 2: The blanking input (BI) must be OPEN or held at a HIGH logic level when output functions 0 through 15 are desired. The ripple-blanking input (RBI) must be OPEN or HIGH if blanking of a deci ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).