CW25-TIM NS18-DS 07 26 March 2009
... The CW25-TIM is a small size GPS OEM module that has been optimized for precision timing applications. The CW25-TIM leverages 12,288 correlators in the BB25IC baseband processor for low signal acquisition and tracking, eliminating the need for an outdoor antenna in many applications. Aside from low ...
... The CW25-TIM is a small size GPS OEM module that has been optimized for precision timing applications. The CW25-TIM leverages 12,288 correlators in the BB25IC baseband processor for low signal acquisition and tracking, eliminating the need for an outdoor antenna in many applications. Aside from low ...
VISIPAK V408 Universal Temperature/Pressure/Process Indicator tm
... two digital inputs and one SPDT relay output. Available with a green or red display, it accepts temperature inputs from J, K, T, L, N, R, S, B, C and Platinel II type thermocouples and three-wire Platinum 100 Ohm (Pt100) RTDs. Process variables such as 4-20mA, 1-5V and 010V as well as strain gauge b ...
... two digital inputs and one SPDT relay output. Available with a green or red display, it accepts temperature inputs from J, K, T, L, N, R, S, B, C and Platinel II type thermocouples and three-wire Platinum 100 Ohm (Pt100) RTDs. Process variables such as 4-20mA, 1-5V and 010V as well as strain gauge b ...
MLVDS Standard
... This Standard specifies the electrical characteristics of low-voltage differential signaling interface circuits that may be employed when specified for the interchange of binary signals between equipment sharing a common data interchange circuit. The electrical characteristics of the circuit are spe ...
... This Standard specifies the electrical characteristics of low-voltage differential signaling interface circuits that may be employed when specified for the interchange of binary signals between equipment sharing a common data interchange circuit. The electrical characteristics of the circuit are spe ...
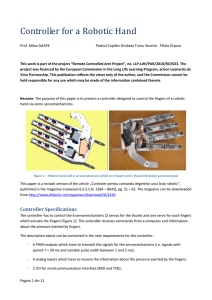
Controller Schematic Design
... little resistance (0.2 Ω). The current through the resistors is the same as the one passing through the corresponding servo. If we measure the voltage across the resistors we have information about the electrical current and therefore about the torque of the servo. Servos supply voltage is V+ and is ...
... little resistance (0.2 Ω). The current through the resistors is the same as the one passing through the corresponding servo. If we measure the voltage across the resistors we have information about the electrical current and therefore about the torque of the servo. Servos supply voltage is V+ and is ...
MT-035 TUTORIAL Op Amp Inputs, Outputs, Single-Supply, and Rail-to-Rail Issues
... input stage, namely: low voltage noise, low offset, and low drift. Additionally, they have low bias current which is fairly stable with temperature. However, their current noise is not very good, and their bias current matching is poor. These latter two undesired side effects result from the externa ...
... input stage, namely: low voltage noise, low offset, and low drift. Additionally, they have low bias current which is fairly stable with temperature. However, their current noise is not very good, and their bias current matching is poor. These latter two undesired side effects result from the externa ...
Coding Schemes Used With Data Converters
... one’s complement of its counterpart BTC, and is also very similar to COB, although this relationship is not immediately obvious. The only difference between COB and CTC is that the MSB has been inverted. With CTC coding, digital “zero” is at an analog voltage which is slightly less (1 LSB) than anal ...
... one’s complement of its counterpart BTC, and is also very similar to COB, although this relationship is not immediately obvious. The only difference between COB and CTC is that the MSB has been inverted. With CTC coding, digital “zero” is at an analog voltage which is slightly less (1 LSB) than anal ...
LT5525 - High Linearity, Low Power Downconverting Mixer.
... balun, RF buffer amplifier, high speed limiting LO buffer and bias/enable circuits. The IC has been optimized for downconverter applications with RF input signals from 0.8GHz to 2.5GHz and LO signals from 500MHz to 3GHz. With proper matching, the IF output can be operated at frequencies from 0.1MHz ...
... balun, RF buffer amplifier, high speed limiting LO buffer and bias/enable circuits. The IC has been optimized for downconverter applications with RF input signals from 0.8GHz to 2.5GHz and LO signals from 500MHz to 3GHz. With proper matching, the IF output can be operated at frequencies from 0.1MHz ...
LT5511 - High Signal Level Upconverting Mixer.
... current drops to about 1µA. Under no conditions should the voltage on this pin exceed VCC + 0.3V, even at power on. ...
... current drops to about 1µA. Under no conditions should the voltage on this pin exceed VCC + 0.3V, even at power on. ...
EUP7907 数据手册DataSheet 下载
... linear regulator with fast transient response and high PSRR. It offers high output accuracy, extremely low dropout voltage, low quiescent current and fast start-up time. It is designed to work with low-ESR ceramic capacitor, reducing the amount of the PCB area. Only a 2.2uF ceramic capacitor can mak ...
... linear regulator with fast transient response and high PSRR. It offers high output accuracy, extremely low dropout voltage, low quiescent current and fast start-up time. It is designed to work with low-ESR ceramic capacitor, reducing the amount of the PCB area. Only a 2.2uF ceramic capacitor can mak ...
AD7785 3-Channel, Low Noise, Low Power, 20-Bit ∑-Δ
... continuous with all data transmitted in a continuous train of pulses. Alternatively, it can be a noncontinuous clock with the information being transmitted to or from the ADC in smaller batches of data. Clock In/Clock Out. The internal clock can be made available at this pin. Alternatively, the inte ...
... continuous with all data transmitted in a continuous train of pulses. Alternatively, it can be a noncontinuous clock with the information being transmitted to or from the ADC in smaller batches of data. Clock In/Clock Out. The internal clock can be made available at this pin. Alternatively, the inte ...
Presentation Slides
... The CPU will do the following things: • Read in a utility (AC) voltage signal • Read in a battery voltage signal • Control the switching of the power source switch • Control the switching of the charging switch • Output a battery life signal to the display ...
... The CPU will do the following things: • Read in a utility (AC) voltage signal • Read in a battery voltage signal • Control the switching of the power source switch • Control the switching of the charging switch • Output a battery life signal to the display ...
Shielding and Noise
... Floating signal sources can be measured with both differential and single-ended measurement systems. In the case of the differential measurement system, however, care should be taken to ensure that the commonmode voltage level of the signal with respect to the measurement system ground remains in th ...
... Floating signal sources can be measured with both differential and single-ended measurement systems. In the case of the differential measurement system, however, care should be taken to ensure that the commonmode voltage level of the signal with respect to the measurement system ground remains in th ...
Difet OPA124 Low Noise Precision OPERATIONAL AMPLIFIER
... Unlike BIFET amplifiers, the Difet OPA124 requires input current limiting resistors only if its input voltage is greater than 6V more negative than –VCC. A 10kΩ series resistor will limit input current to a safe level with up to ±15V input levels, even if both supply voltages are lost (Figure 2). St ...
... Unlike BIFET amplifiers, the Difet OPA124 requires input current limiting resistors only if its input voltage is greater than 6V more negative than –VCC. A 10kΩ series resistor will limit input current to a safe level with up to ±15V input levels, even if both supply voltages are lost (Figure 2). St ...
LT5518 - 1.5GHz - 2.4GHz High Linearity Direct
... GSM, EDGE, TD-SCDMA, CDMA, CDMA2000, W-CDMA and other systems. It may also be configured as an image reject up-converting mixer, by applying 90° phase-shifted signals to the I and Q inputs. The high impedance I/Q baseband inputs consist of voltage-to-current converters that in turn drive double-balan ...
... GSM, EDGE, TD-SCDMA, CDMA, CDMA2000, W-CDMA and other systems. It may also be configured as an image reject up-converting mixer, by applying 90° phase-shifted signals to the I and Q inputs. The high impedance I/Q baseband inputs consist of voltage-to-current converters that in turn drive double-balan ...
HMC851LC3C 数据资料DataSheet下载
... The HMC851LC3C is a XOR/XNOR gate function designed to support data transmission rates of up to 28 Gbps, and clock frequencies as high as 28 GHz. The HMC851LC3C also features an output level control pin, VR, which allows for loss compensation or for signal level optimization. All input signals to th ...
... The HMC851LC3C is a XOR/XNOR gate function designed to support data transmission rates of up to 28 Gbps, and clock frequencies as high as 28 GHz. The HMC851LC3C also features an output level control pin, VR, which allows for loss compensation or for signal level optimization. All input signals to th ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).