MAX12559 Dual, 96Msps, 14-Bit, IF/Baseband ADC General Description Features
... The MAX12559 is a dual, 3.3V, 14-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC) featuring fully differential wideband track-and-hold (T/H) inputs, driving internal quantizers. The MAX12559 is optimized for low power, small size, and high dynamic performance in intermediate frequency (IF) and baseband samplin ...
... The MAX12559 is a dual, 3.3V, 14-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC) featuring fully differential wideband track-and-hold (T/H) inputs, driving internal quantizers. The MAX12559 is optimized for low power, small size, and high dynamic performance in intermediate frequency (IF) and baseband samplin ...
MAX192 Low-Power, 8-Channel, Serial 10-Bit ADC ________________General Description
... of the comparator. The capacitive DAC adjusts during the remainder of the conversion cycle to restore its node ZERO to 0V within the limits of its resolution. This action is equivalent to transferring a charge of 16pF x (VIN+ - VIN-) from CHOLD to the binary-weighted capacitive DAC, which in turn fo ...
... of the comparator. The capacitive DAC adjusts during the remainder of the conversion cycle to restore its node ZERO to 0V within the limits of its resolution. This action is equivalent to transferring a charge of 16pF x (VIN+ - VIN-) from CHOLD to the binary-weighted capacitive DAC, which in turn fo ...
MAX12557 Dual, 65Msps, 14-Bit, IF/Baseband ADC General Description Features
... with the ADC’s internal duty-cycle equalizer (DCE). The MAX12557 features two parallel, 14-bit-wide, CMOS-compatible outputs. The digital output format is pin-selectable to be either two’s complement or Gray code. A separate power-supply input for the digital outputs accepts a 1.7V to 3.6V voltage f ...
... with the ADC’s internal duty-cycle equalizer (DCE). The MAX12557 features two parallel, 14-bit-wide, CMOS-compatible outputs. The digital output format is pin-selectable to be either two’s complement or Gray code. A separate power-supply input for the digital outputs accepts a 1.7V to 3.6V voltage f ...
Oct-1968 - HP Labs
... the reservoir to a metal pen tip and the paper on which the recording is made. Ink is pumped through the tubing to the pen tip prior to starting a record. After this initial 'priming' the ink continues to feed itself to the pen tip on demand by capillary action. The surface tension and vis cosity of ...
... the reservoir to a metal pen tip and the paper on which the recording is made. Ink is pumped through the tubing to the pen tip prior to starting a record. After this initial 'priming' the ink continues to feed itself to the pen tip on demand by capillary action. The surface tension and vis cosity of ...
H E W L E T T - P A... C D J ~ L Â · l
... The product designs described in this issue represent the present state of the art in three of HP's oldest product lines — frequency counters, micro wave instrumentation, and voltmeters. On the cover is a photomicrograph of a gallium arsenide sampler chip, the keystone of the designs of the HP 535 ...
... The product designs described in this issue represent the present state of the art in three of HP's oldest product lines — frequency counters, micro wave instrumentation, and voltmeters. On the cover is a photomicrograph of a gallium arsenide sampler chip, the keystone of the designs of the HP 535 ...
Rail-to-Rail, Very Fast, 2.5 V to 5.5 V, Single-Supply TTL/CMOS Comparator ADCMP603
... input offset voltage) to the 50% point of an output low-to-high transition. Propagation delay measured from the time the input signal crosses the reference (± the input offset voltage) to the 50% point of an output high-to-low transition. Propagation delay measured from the 50% point of the latch en ...
... input offset voltage) to the 50% point of an output low-to-high transition. Propagation delay measured from the time the input signal crosses the reference (± the input offset voltage) to the 50% point of an output high-to-low transition. Propagation delay measured from the 50% point of the latch en ...
MAX3983 Quad Copper-Cable Signal Conditioner General Description Features
... connector or equivalent. All other channels are quiet. Residual deterministic jitter is the difference between the source jitter and the output jitter at the load. The deterministic jitter (DJ) at the output of the transmission line must be from mediainduced loss and not from clock-source modulation ...
... connector or equivalent. All other channels are quiet. Residual deterministic jitter is the difference between the source jitter and the output jitter at the load. The deterministic jitter (DJ) at the output of the transmission line must be from mediainduced loss and not from clock-source modulation ...
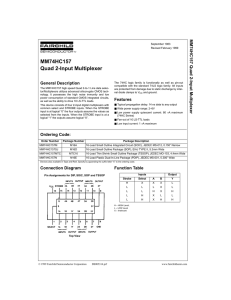
74HC157 pdf
... 2. A critical component in any component of a life support 1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems device or system whose failure to perform can be reawhich, (a) are intended for surgical implant into the sonably expected to cause the failure of the life support body, or (b) suppor ...
... 2. A critical component in any component of a life support 1. Life support devices or systems are devices or systems device or system whose failure to perform can be reawhich, (a) are intended for surgical implant into the sonably expected to cause the failure of the life support body, or (b) suppor ...
High-Speed, Precision Difference Amplifiers
... The INA133 and INA2133 can accurately measure differential signals that are above and below the supply rails. Linear common-mode range extends from 2 • (V+)–3V to 2 • (V–) +3V (nearly twice the supplies). See the typical performance curve, “Input Common-Mode Voltage vs Output Voltage.” OFFSET VOLTAG ...
... The INA133 and INA2133 can accurately measure differential signals that are above and below the supply rails. Linear common-mode range extends from 2 • (V+)–3V to 2 • (V–) +3V (nearly twice the supplies). See the typical performance curve, “Input Common-Mode Voltage vs Output Voltage.” OFFSET VOLTAG ...
Low Distortion Differential ADC Driver AD8138
... performance ADCs, preserving the low frequency and dc information. The common-mode level of the differential output is adjustable by a voltage on the VOCM pin, easily level-shifting the input signals for driving single-supply ADCs. Fast overload recovery preserves sampling accuracy. The AD8138 disto ...
... performance ADCs, preserving the low frequency and dc information. The common-mode level of the differential output is adjustable by a voltage on the VOCM pin, easily level-shifting the input signals for driving single-supply ADCs. Fast overload recovery preserves sampling accuracy. The AD8138 disto ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).