ONET4291T 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... Figure 15 shows an application circuit for an ONET4291T being used in a typical fiber-optic receiver. The ONET4291T converts the electrical current generated by the PIN photodiode into a differential output voltage. The FILTER input provides a dc bias voltage for the PIN that is low-pass filtered by ...
... Figure 15 shows an application circuit for an ONET4291T being used in a typical fiber-optic receiver. The ONET4291T converts the electrical current generated by the PIN photodiode into a differential output voltage. The FILTER input provides a dc bias voltage for the PIN that is low-pass filtered by ...
Relative material
... feedback results when the signal being feed back is in phase with the input signal. Negative feedback occurs when the signal being feed back is 180 degrees out of phase with the input signal. In a common emitter or common collector amplifier, feedback is introduced into the base of the first stage t ...
... feedback results when the signal being feed back is in phase with the input signal. Negative feedback occurs when the signal being feed back is 180 degrees out of phase with the input signal. In a common emitter or common collector amplifier, feedback is introduced into the base of the first stage t ...
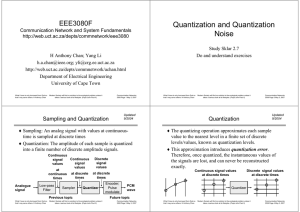
Quantization and Quantization Noise
... ♦ A remedy is to use nonuniform quantization levels. This can be achieved by using a nonuniform quantizer: level 7 level 6 level 5 level 4 level 3 level 2 ...
... ♦ A remedy is to use nonuniform quantization levels. This can be achieved by using a nonuniform quantizer: level 7 level 6 level 5 level 4 level 3 level 2 ...
Voltage Divider Design Considerations - Saint
... to ground. (For high rate applications, other dynodes may be bypassed also, i.g., D7 and D8 in Figure 1.) In our application, a pulse of light generated in the NaI(Tl) crystal strikes the photocathode and causes a pulse of photoelectrons to be emitted. This electron pulse is amplified as it travels ...
... to ground. (For high rate applications, other dynodes may be bypassed also, i.g., D7 and D8 in Figure 1.) In our application, a pulse of light generated in the NaI(Tl) crystal strikes the photocathode and causes a pulse of photoelectrons to be emitted. This electron pulse is amplified as it travels ...
signal processing - ifm
... dependence. Fig. 2 (right) shows the noise waveform superimposed on a small signal. As can be seen, the noise level determines the minimum signal whose presence can be discerned. In an optimized system, the time scale of the fluctuations is comparable to that of the signal, so the peak amplitude flu ...
... dependence. Fig. 2 (right) shows the noise waveform superimposed on a small signal. As can be seen, the noise level determines the minimum signal whose presence can be discerned. In an optimized system, the time scale of the fluctuations is comparable to that of the signal, so the peak amplitude flu ...
Fulltext - Brunel University Research Archive
... incremental evolution and development”. Among these methods only “divide-and-conquer” ([1],[12]) were distinctly utilized in analog domain, however, as it can be seen from Table 1, the targeted circuits there were not complex enough to fully exploit the potential of the proposed techniques. The expe ...
... incremental evolution and development”. Among these methods only “divide-and-conquer” ([1],[12]) were distinctly utilized in analog domain, however, as it can be seen from Table 1, the targeted circuits there were not complex enough to fully exploit the potential of the proposed techniques. The expe ...
DG535/536
... GND pin. If this condition is possible (e.g. transients in the signal), then a diode or Zener clamp may be used to prevent breakdown. The overvoltage conditions described may exist if the supplies are collapsed while a signal is present on the inputs. If this condition is unavoidable, then the neces ...
... GND pin. If this condition is possible (e.g. transients in the signal), then a diode or Zener clamp may be used to prevent breakdown. The overvoltage conditions described may exist if the supplies are collapsed while a signal is present on the inputs. If this condition is unavoidable, then the neces ...
AN ALTERNATIVE CONFIGURATION FOR DIGITALLY CONTROLLED PARALLEL CONNECTED DC–DC POWER CONVERTERS
... to the research or development of digitally controlled parallel connected DC–DC power converters. In fact, the authors have found only few works [3], [4], reporting in their attempts to run digitally controlled DC–DC power converters in parallel. Even so, the controller used is a centralized digital ...
... to the research or development of digitally controlled parallel connected DC–DC power converters. In fact, the authors have found only few works [3], [4], reporting in their attempts to run digitally controlled DC–DC power converters in parallel. Even so, the controller used is a centralized digital ...
T L E 4 9 9 8 P 3 C
... applications. Two capacitors are integrated on the lead frame, making this sensor especially suitable for applications with demanding EMC requirements. The sensor provides a digital PWM signal, which is ideally suited for direct decoding by any unit measuring a duty cycle of a rectangular signal (us ...
... applications. Two capacitors are integrated on the lead frame, making this sensor especially suitable for applications with demanding EMC requirements. The sensor provides a digital PWM signal, which is ideally suited for direct decoding by any unit measuring a duty cycle of a rectangular signal (us ...
LT1993-4
... Amplifier/ADC driver for use in applications from DC to 900MHz. The LT1993-4 has been designed for ease of use, with minimal support circuitry required. Exceptionally low input-referred noise and low distortion products (with either single-ended or differential inputs) make the LT1993-4 an excellent ...
... Amplifier/ADC driver for use in applications from DC to 900MHz. The LT1993-4 has been designed for ease of use, with minimal support circuitry required. Exceptionally low input-referred noise and low distortion products (with either single-ended or differential inputs) make the LT1993-4 an excellent ...
AD8610/AD8620 Precision, Very Low Noise, Low Input Bias Current
... XFCB is fully dielectrically isolated (DI) and used in conjunction with N-channel JFET technology and trimmable thin-film resistors to create the world’s most precise JFET input amplifier. Dielectrically isolated NPN and PNP transistors fabricated on XFCB have FT greater than 3 GHz. Low TC thin film ...
... XFCB is fully dielectrically isolated (DI) and used in conjunction with N-channel JFET technology and trimmable thin-film resistors to create the world’s most precise JFET input amplifier. Dielectrically isolated NPN and PNP transistors fabricated on XFCB have FT greater than 3 GHz. Low TC thin film ...
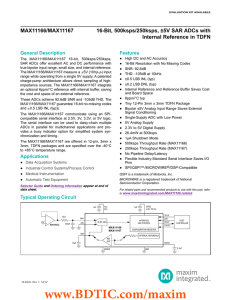
MAX11166/MAX11167 16-Bit, 500ksps/250ksps, ±5V SAR ADCs with Internal Reference in TDFN General Description
... The MAX11166/MAX11167 measure a Q5V (10VP-P) input range while operating from a single 5V supply. A patented charge-pump architecture allows direct sampling of highimpedance sources. The MAX11166/MAX11167 integrate an optional 6ppm/NC reference with internal buffer, saving the cost and space of an e ...
... The MAX11166/MAX11167 measure a Q5V (10VP-P) input range while operating from a single 5V supply. A patented charge-pump architecture allows direct sampling of highimpedance sources. The MAX11166/MAX11167 integrate an optional 6ppm/NC reference with internal buffer, saving the cost and space of an e ...
LF353-N 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant ...
... Texas Instruments Incorporated and its subsidiaries (TI) reserve the right to make corrections, modifications, enhancements, improvements, and other changes to its products and services at any time and to discontinue any product or service without notice. Customers should obtain the latest relevant ...
MAX5874 14-Bit, 200Msps, High-Dynamic-Performance, Dual DAC with CMOS Inputs General Description
... digital-to-analog converter (DAC). This DAC meets the demanding performance requirements of signal synthesis applications found in wireless base stations and other communications applications. Operating from 3.3V and 1.8V supplies, this dual DAC offers exceptional dynamic performance such as 78dBc s ...
... digital-to-analog converter (DAC). This DAC meets the demanding performance requirements of signal synthesis applications found in wireless base stations and other communications applications. Operating from 3.3V and 1.8V supplies, this dual DAC offers exceptional dynamic performance such as 78dBc s ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).