LF2418891896
... The multiplier used in PD is a very important part of PLL system since it compares the input reference and the VCO signals simultaneously. If both inputs to the multiplier are sinusoidal then the mixing operation is true analog multiplication and the output is a function of input signal amplitudes, ...
... The multiplier used in PD is a very important part of PLL system since it compares the input reference and the VCO signals simultaneously. If both inputs to the multiplier are sinusoidal then the mixing operation is true analog multiplication and the output is a function of input signal amplitudes, ...
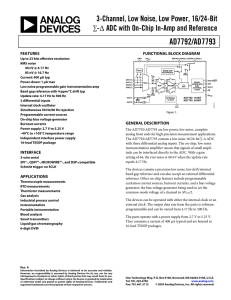
Quad, 8-Bit, 100 MSPS Serial LVDS 1.8 V A/D Converter AD9287
... specified over the industrial temperature range of −40°C to +85°C. ...
... specified over the industrial temperature range of −40°C to +85°C. ...
M74HCT132 - STMicroelectronics
... Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implicatio ...
... Information furnished is believed to be accurate and reliable. However, STMicroelectronics assumes no responsibility for the consequences of use of such information nor for any infringement of patents or other rights of third parties which may result from its use. No license is granted by implicatio ...
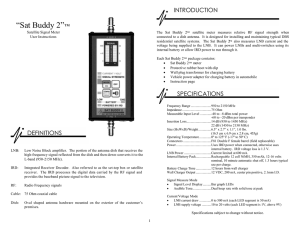
Sat Buddy 2 - Applied Instruments
... products are based upon tests believed to be reliable, but Applied Instruments makes no warranty of the results to be obtained. This warranty is in lieu of all other warranties, expressed or implied, and no representative or person is authorized to represent or assume for Applied Instruments, any li ...
... products are based upon tests believed to be reliable, but Applied Instruments makes no warranty of the results to be obtained. This warranty is in lieu of all other warranties, expressed or implied, and no representative or person is authorized to represent or assume for Applied Instruments, any li ...
INA121 数据资料 dataSheet 下载
... The INA121’s FET input allows use of an R/C input filter without creating large offsets due to input bias current. Figure 5 shows proper implementation of this input filter to preserve the INA121’s excellent high frequency commonmode rejection. Mismatch of the common-mode input time constant (R1C1 a ...
... The INA121’s FET input allows use of an R/C input filter without creating large offsets due to input bias current. Figure 5 shows proper implementation of this input filter to preserve the INA121’s excellent high frequency commonmode rejection. Mismatch of the common-mode input time constant (R1C1 a ...
LT5520 - 1.3GHz to 2.3GHz High Linearity Upconverting Mixer.
... The LT®5520 mixer is designed to meet the high linearity requirements of wireless and cable infrastructure transmission applications. A high-speed, internally matched, LO amplifier drives a double-balanced mixer core, allowing the use of a low power, single-ended LO source. An RF output transformer ...
... The LT®5520 mixer is designed to meet the high linearity requirements of wireless and cable infrastructure transmission applications. A high-speed, internally matched, LO amplifier drives a double-balanced mixer core, allowing the use of a low power, single-ended LO source. An RF output transformer ...
B. Sc.-II Electronics Syllabus
... from each unit. A student is required to attempt one question from each unit. iv.All questions carry equal marks. ...
... from each unit. A student is required to attempt one question from each unit. iv.All questions carry equal marks. ...
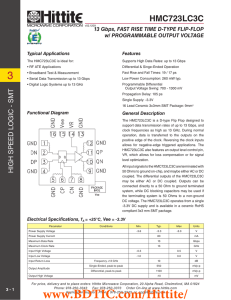
HMC723LC3C 数据资料DataSheet下载
... operation, data is transferred to the outputs on the positive edge of the clock. Reversing the clock inputs allows for negative-edge triggered applications. The HMC723LC3C also features an output level control pin, VR, which allows for loss compensation or for signal level optimization. All input si ...
... operation, data is transferred to the outputs on the positive edge of the clock. Reversing the clock inputs allows for negative-edge triggered applications. The HMC723LC3C also features an output level control pin, VR, which allows for loss compensation or for signal level optimization. All input si ...
LT5519 - 0.7GHz to 1.4GHz High Linearity Upconverting Mixer.
... The LT®5519 mixer is designed to meet the high linearity requirements of wireless and cable infrastructure transmission systems. A high speed, internally 50Ω matched, LO amplifier drives a double-balanced mixer core, allowing the use of a low power, single-ended LO source. An RF output transformer i ...
... The LT®5519 mixer is designed to meet the high linearity requirements of wireless and cable infrastructure transmission systems. A high speed, internally 50Ω matched, LO amplifier drives a double-balanced mixer core, allowing the use of a low power, single-ended LO source. An RF output transformer i ...
LN2541
... controllers. The IC uses very few external components and enables both Linear and PWM dimming of the LED current. A capacitor connected to the Toff pin programs the off-time. The oscillator produces pulses at regular intervals. These pulses set the SR flip-flop in the LN2543 which causes the GATE dr ...
... controllers. The IC uses very few external components and enables both Linear and PWM dimming of the LED current. A capacitor connected to the Toff pin programs the off-time. The oscillator produces pulses at regular intervals. These pulses set the SR flip-flop in the LN2543 which causes the GATE dr ...
Using Digital Verification Techniques on Mixed-Signal
... With this architecture, it is possible to decide when to start injecting analog traffic, when to stop, and when to sample the output results. For example, consider a typical scenario to initialize and configure the subsystem registers, wait for the clock generation to stabilize, start injecting anal ...
... With this architecture, it is possible to decide when to start injecting analog traffic, when to stop, and when to sample the output results. For example, consider a typical scenario to initialize and configure the subsystem registers, wait for the clock generation to stabilize, start injecting anal ...
MAX16963 Dual 2.2MHz, Low-Voltage Step-Down DC-DC Converter General Description
... The MAX16963 is a high-efficiency, dual synchronous step-down converter that operates with a 2.7V to 5.5V input voltage range and provides a 0.8V to 3.6V output voltage range. The MAX16963 delivers up to 1.5A of load current per output and achieves Q3% output error over load, line, and temperature r ...
... The MAX16963 is a high-efficiency, dual synchronous step-down converter that operates with a 2.7V to 5.5V input voltage range and provides a 0.8V to 3.6V output voltage range. The MAX16963 delivers up to 1.5A of load current per output and achieves Q3% output error over load, line, and temperature r ...
Microphones - Music Technology 2
... S Output level in volts, given specific standardized input S Equivalent Noise Rating S Device’s electrical self-noise S Overload Characteristics S Distortion capabilities (eg. Dynamic range of dynamic mic = ...
... S Output level in volts, given specific standardized input S Equivalent Noise Rating S Device’s electrical self-noise S Overload Characteristics S Distortion capabilities (eg. Dynamic range of dynamic mic = ...
AN-6961 Critical Conduction Mode PFC Controller Description
... around 35μs is added to prevent false triggering. If the voltage VINV is below 0.45V due to short-circuit conditions, PWM output is turned off. Figure 13. ...
... around 35μs is added to prevent false triggering. If the voltage VINV is below 0.45V due to short-circuit conditions, PWM output is turned off. Figure 13. ...
Analog-to-digital converter

An analog-to-digital converter (ADC, A/D, or A to D) is a device that converts a continuous physical quantity (usually voltage) to a digital number that represents the quantity's amplitude.The conversion involves quantization of the input, so it necessarily introduces a small amount of error. Furthermore, instead of continuously performing the conversion, an ADC does the conversion periodically, sampling the input. The result is a sequence of digital values that have been converted from a continuous-time and continuous-amplitude analog signal to a discrete-time and discrete-amplitude digital signal.An ADC is defined by its bandwidth (the range of frequencies it can measure) and its signal to noise ratio (how accurately it can measure a signal relative to the noise it introduces). The actual bandwidth of an ADC is characterized primarily by its sampling rate, and to a lesser extent by how it handles errors such as aliasing. The dynamic range of an ADC is influenced by many factors, including the resolution (the number of output levels it can quantize a signal to), linearity and accuracy (how well the quantization levels match the true analog signal) and jitter (small timing errors that introduce additional noise). The dynamic range of an ADC is often summarized in terms of its effective number of bits (ENOB), the number of bits of each measure it returns that are on average not noise. An ideal ADC has an ENOB equal to its resolution. ADCs are chosen to match the bandwidth and required signal to noise ratio of the signal to be quantized. If an ADC operates at a sampling rate greater than twice the bandwidth of the signal, then perfect reconstruction is possible given an ideal ADC and neglecting quantization error. The presence of quantization error limits the dynamic range of even an ideal ADC, however, if the dynamic range of the ADC exceeds that of the input signal, its effects may be neglected resulting in an essentially perfect digital representation of the input signal.An ADC may also provide an isolated measurement such as an electronic device that converts an input analog voltage or current to a digital number proportional to the magnitude of the voltage or current. However, some non-electronic or only partially electronic devices, such as rotary encoders, can also be considered ADCs. The digital output may use different coding schemes. Typically the digital output will be a two's complement binary number that is proportional to the input, but there are other possibilities. An encoder, for example, might output a Gray code.The inverse operation is performed by a digital-to-analog converter (DAC).