Endo_Emergencies
... Isoniazid MAO inhibitors Various drugs causing decreased liver metabolism of oral hypoglycemic agents ...
... Isoniazid MAO inhibitors Various drugs causing decreased liver metabolism of oral hypoglycemic agents ...
Table I. Insulin Therapy for CFRD (adapted from Moran et al
... injections or by insulin pump according to the following principles. They should be taught to adjust their insulin dose for special circumstances such as exercise, travel, and acute illness. Those already on insulin therapy usually require 2-4 times as much insulin during illness or steroid therapy. ...
... injections or by insulin pump according to the following principles. They should be taught to adjust their insulin dose for special circumstances such as exercise, travel, and acute illness. Those already on insulin therapy usually require 2-4 times as much insulin during illness or steroid therapy. ...
Alam na ng langgam, alam mo na ba?
... What Should I Eat? • It's not so much "what" you should eat but “how much” If overweight, lose weight. Eating more foods that are broiled and fewer foods that are fried. Cutting back on butter or oil in cooking. Eating fish and chicken more often and only lean cuts of beef and pork Eating ...
... What Should I Eat? • It's not so much "what" you should eat but “how much” If overweight, lose weight. Eating more foods that are broiled and fewer foods that are fried. Cutting back on butter or oil in cooking. Eating fish and chicken more often and only lean cuts of beef and pork Eating ...
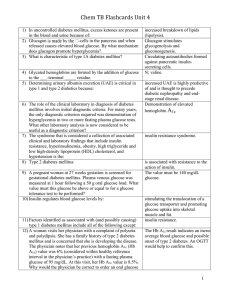
Chem TB Flashcards Unit 4
... important because: 23) The hyperglycemia observed in a diabetic causes many toxic effects such as retinopathy and nephropathy. Although it is unclear how these outcomes are caused by elevated blood sugar, it is thought that hyperglycemia: 24) What antibodies is found most commonly in over 90% of chi ...
... important because: 23) The hyperglycemia observed in a diabetic causes many toxic effects such as retinopathy and nephropathy. Although it is unclear how these outcomes are caused by elevated blood sugar, it is thought that hyperglycemia: 24) What antibodies is found most commonly in over 90% of chi ...
Case Studies Endocrine System KEY
... A 21-year-old noncompliant female with a history of type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus was found in a coma. Her blood glucose was high, as well as her urine glucose, urine ketones, and serum ketones. Her serum bicarbonate was < 12 mEq/L. Her respiration was exaggerated and his breath had a ...
... A 21-year-old noncompliant female with a history of type I (insulin-dependent) diabetes mellitus was found in a coma. Her blood glucose was high, as well as her urine glucose, urine ketones, and serum ketones. Her serum bicarbonate was < 12 mEq/L. Her respiration was exaggerated and his breath had a ...
DKA Precipitated by Iatrogenic Thyrotoxicosis
... several mechanisms. It decreases half-life of insulin, reduces the C-peptide/proinsulin ratio, and increases plasma concentration via intestinal absorption and hepatic gluconeogenesis. Prognosis is dependent on early diagnosis and appropriate timing of treatment and intervention. Auto-immune thyroid ...
... several mechanisms. It decreases half-life of insulin, reduces the C-peptide/proinsulin ratio, and increases plasma concentration via intestinal absorption and hepatic gluconeogenesis. Prognosis is dependent on early diagnosis and appropriate timing of treatment and intervention. Auto-immune thyroid ...
Diabetes Mellitus in Pregnancy Screening and Management
... capillary specimen. The following are criteria are based on the plasma reading from those meters Goals of management should be maintenance of 90% of glucose levels at a. fasting glucose < 95 mg/dL, or b. 1 hour post prandial glucose < 130-140 mg/dL or c. 2 hour post prandial glucose < 120 mg/dL. ...
... capillary specimen. The following are criteria are based on the plasma reading from those meters Goals of management should be maintenance of 90% of glucose levels at a. fasting glucose < 95 mg/dL, or b. 1 hour post prandial glucose < 130-140 mg/dL or c. 2 hour post prandial glucose < 120 mg/dL. ...
Abstract - Creighton University
... The aim of my project was to investigate the relationship between uncoupling protein expression and alterations in glucose metabolism in different pathological conditions. In the first part of these studies, the expression of uncoupling proteins in pancreatic cancer patients was determined. A signif ...
... The aim of my project was to investigate the relationship between uncoupling protein expression and alterations in glucose metabolism in different pathological conditions. In the first part of these studies, the expression of uncoupling proteins in pancreatic cancer patients was determined. A signif ...
Inpatient Glycemic Management - The Association of Physicians of
... Factors Influencing Glycemic Control In Hospitalized Patients The major factors that need to be overcome in order to achieve glycemic control in the hospitalized diabetic patient are discussed in Table I. Table I. Factors which Alter Glycemic Control In Hospital Increased counterregulatory hormon ...
... Factors Influencing Glycemic Control In Hospitalized Patients The major factors that need to be overcome in order to achieve glycemic control in the hospitalized diabetic patient are discussed in Table I. Table I. Factors which Alter Glycemic Control In Hospital Increased counterregulatory hormon ...
Thyroid replacement hormone (levothyroxine sodium)
... 2. Too much exercise 3. Anorexia Signs: Weakness, incoordination, seizures, coma ...
... 2. Too much exercise 3. Anorexia Signs: Weakness, incoordination, seizures, coma ...
Endocrine Disorders in the Neonatal Period
... with gender assignment.5 DISORDERS OF GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS Hypoglycemia of the newborn is a common problem, and its symptoms in neonates range from irritability to hypothermia to seizures. One of the clinical challenges is determining the circumstances under which a neonate may be hypoglycemic, when ...
... with gender assignment.5 DISORDERS OF GLUCOSE HOMEOSTASIS Hypoglycemia of the newborn is a common problem, and its symptoms in neonates range from irritability to hypothermia to seizures. One of the clinical challenges is determining the circumstances under which a neonate may be hypoglycemic, when ...
A Microsoft Word printable version of these cases is here.
... 3. Is Oscar anemic? Which of the test results answers this question? 4. Does Oscar have an infection? Which of the test results answers this question? 5. Which hormone is most likely associated with the symptoms of weaknesss, fatigue, weight loss and decreased cold tolerance? 6a. What endocrine orga ...
... 3. Is Oscar anemic? Which of the test results answers this question? 4. Does Oscar have an infection? Which of the test results answers this question? 5. Which hormone is most likely associated with the symptoms of weaknesss, fatigue, weight loss and decreased cold tolerance? 6a. What endocrine orga ...
printable version of the five cases here
... 3. Is Oscar anemic? Which of the test results answers this question? 4. Does Oscar have an infection? Which of the test results answers this question? 5. Which hormone is most likely associated with the symptoms of weaknesss, fatigue, weight loss and decreased cold tolerance? ...
... 3. Is Oscar anemic? Which of the test results answers this question? 4. Does Oscar have an infection? Which of the test results answers this question? 5. Which hormone is most likely associated with the symptoms of weaknesss, fatigue, weight loss and decreased cold tolerance? ...
Hormones - Remède Physique
... So the liver gets two diametrically opposed signals simultaneously, one to store sugar and one to make sugar available. This puts a great deal of strain on the liver, contributing to liver congestion and dysfunction, which in turn contribute to hormonal imbalances. Additionally, as we know from stud ...
... So the liver gets two diametrically opposed signals simultaneously, one to store sugar and one to make sugar available. This puts a great deal of strain on the liver, contributing to liver congestion and dysfunction, which in turn contribute to hormonal imbalances. Additionally, as we know from stud ...
Endocrine System Wrap-up
... Type II – insulin is not the problem Need drugs to increase sensitivity of cells to insulin ...
... Type II – insulin is not the problem Need drugs to increase sensitivity of cells to insulin ...
Hormonal Regulation of Growth, Development, and Metabolism
... • hypothalamus sends thyroid releasing hormone (TRH) to the anterior pituitary • Anterior pituitary releases thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) • TSH acts on thyroid to stimulate release of thyroxine. • thyroxine raises metabolism by increasing sugar usage by body tissues • thyroxine levels feedback ...
... • hypothalamus sends thyroid releasing hormone (TRH) to the anterior pituitary • Anterior pituitary releases thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) • TSH acts on thyroid to stimulate release of thyroxine. • thyroxine raises metabolism by increasing sugar usage by body tissues • thyroxine levels feedback ...
Diabetes in Pregnancy
... 1. Castorino K, Jovanovic L. Clin Chem. 2011;57(2):221-30. 2. Kitzmiller JL, et al. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(5):1060-79. 3. Jovanovic L, et al. Mt Sinai J Med. 2009;76(3):269-80. 4. ADA. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(suppl 1):S88-90. 5. National Academy of Sciences, Institute of Medicine, Food and Nutrition ...
... 1. Castorino K, Jovanovic L. Clin Chem. 2011;57(2):221-30. 2. Kitzmiller JL, et al. Diabetes Care. 2008;31(5):1060-79. 3. Jovanovic L, et al. Mt Sinai J Med. 2009;76(3):269-80. 4. ADA. Diabetes Care. 2004;27(suppl 1):S88-90. 5. National Academy of Sciences, Institute of Medicine, Food and Nutrition ...
PITUITARY FUNCTION TESTS: An Overview
... achieved during the test; In apparently healthy individuals, Hypoglycemia causes: • Increase in Plasma [HGH] to more than 20m U/L; • Plasma [Cortisol] increases to maximum (about 425nmol/L) in 60 to 90 minutes; In patient with Partial Pituitary Failure, Hypoglycemia causes: • Limited increases in ...
... achieved during the test; In apparently healthy individuals, Hypoglycemia causes: • Increase in Plasma [HGH] to more than 20m U/L; • Plasma [Cortisol] increases to maximum (about 425nmol/L) in 60 to 90 minutes; In patient with Partial Pituitary Failure, Hypoglycemia causes: • Limited increases in ...
Pituitary Agents. Thyroid and Antithyroid Agents. Antidiabe
... • Leads to excessive blood glucose levels • Normal: 100 mg/dL ...
... • Leads to excessive blood glucose levels • Normal: 100 mg/dL ...
Fact Sheet Series - Job Accommodation Network
... needed for the glucose to be used by the body. Diabetes occurs when the body cannot make use of the glucose in the blood for energy because either the pancreas is not able to make enough insulin or the insulin that is available is not effective. Diabetes can affect a person in many different ways. A ...
... needed for the glucose to be used by the body. Diabetes occurs when the body cannot make use of the glucose in the blood for energy because either the pancreas is not able to make enough insulin or the insulin that is available is not effective. Diabetes can affect a person in many different ways. A ...
Metabolic effects of insulin & glucagon
... Fuels are biomolecules (as carbohydrates, lipids & proteins) that can yield energy in the form of ATP on (catabolism or degradation). This energy (ATP) that can be used for all biological processes of the cells. Fuels can be also stored in certain sites of the body in the form of larger molecules (a ...
... Fuels are biomolecules (as carbohydrates, lipids & proteins) that can yield energy in the form of ATP on (catabolism or degradation). This energy (ATP) that can be used for all biological processes of the cells. Fuels can be also stored in certain sites of the body in the form of larger molecules (a ...
ROSE CRYSTA-70(Rose Petal Extract)
... vegetables are necessary. ROSE POLYPHENOL relieves that exertion. ROSE POLYPHENOL can control blood glucose level, and it keeps blood glucose level low after eating. It also derives to keep insulin level low, to suppress producing fats from sugars. It is reported that ROSE POLYPHENOL inhibits lipase ...
... vegetables are necessary. ROSE POLYPHENOL relieves that exertion. ROSE POLYPHENOL can control blood glucose level, and it keeps blood glucose level low after eating. It also derives to keep insulin level low, to suppress producing fats from sugars. It is reported that ROSE POLYPHENOL inhibits lipase ...
1. Role of Blood Glucose Level
... Ketosis and Acidosis. In the absence of insulin but in the presence of excess fatty acids in the liver cells, the carnitine transport mechanism for transporting fatty acids into the mitochondria becomes increasingly activated. In the mitochondria, beta oxidation of the fatty acids then proceeds very ...
... Ketosis and Acidosis. In the absence of insulin but in the presence of excess fatty acids in the liver cells, the carnitine transport mechanism for transporting fatty acids into the mitochondria becomes increasingly activated. In the mitochondria, beta oxidation of the fatty acids then proceeds very ...
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also known as low blood sugar or low blood glucose, is when blood sugar decreases to below normal. This may result in a variety of symptoms including clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, loss of consciousness and seizures, or in death. A feeling of hunger, sweating, shakiness, and weakness may also be present. Symptoms typically come on quickly.The most common cause of hypoglycemia is medications used to treat diabetes mellitus such as insulin, sulfonylureas, and biguanides. Risk is greater in diabetics who have eaten less than usual, exercised more than usual, or drunk alcohol. Other causes of hypoglycemia include kidney failure, certain tumors, liver disease, hypothyroidism, starvation, inborn error of metabolism, severe infections, reactive hypoglycemia, and a number of drugs including alcohol. Low blood sugar may occur in babies who are otherwise healthy who have not eaten for a few hours.The glucose level that defines hypoglycemia is variable. In people with diabetes levels below 3.9 mmol/L (70 mg/dL) is diagnostic. In adults without diabetes, symptoms related to low blood sugar, low blood sugar at the time of symptoms, and improvement when blood sugar is restored to normal confirm the diagnosis. Otherwise a level below 2.8 mmol/L (50 mg/dL) after not eating or following exercise may be used. In newborns a level below 2.2 mmol/L (40 mg/dL) or less than 3.3 mmol/L (60 mg/dL) if symptoms are present indicates hypoglycemia. Other tests that may be useful in determining the cause include insulin and C peptide levels in the blood. Hyperglycemia, a high blood sugar, is the opposite condition.Among people with diabetes, prevention is by matching the foods eaten, with the amount of exercise, and the medications used. When people feel their blood sugar is low testing with a glucose monitor is recommended. Some people have few initial symptoms of low blood sugar and frequent routine testing in this group is recommended. Treatment of hypoglycemia is by eating foods high in simple sugars or taking dextrose. If a person is not able to take food by mouth, an injection of glucagon may help. The treatment of hypoglycemia unrelated to diabetes include treating the underlying problem as well and a healthy diet. The term ""hypoglycemia"" is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to idiopathic postprandial syndrome, a controversial condition with similar symptoms that occur following eating but with normal blood sugar levels.