Homeostasis and Negative Feedback
... glucose levels are around 4-7millimoles per litre (mmol/L). Glucose not required for immediate use is converted into glycogen for storage in the liver and muscles. When blood glucose and glycogen levels are within normal limits, any left over glucose is converted into fat and stored under the sk ...
... glucose levels are around 4-7millimoles per litre (mmol/L). Glucose not required for immediate use is converted into glycogen for storage in the liver and muscles. When blood glucose and glycogen levels are within normal limits, any left over glucose is converted into fat and stored under the sk ...
Type 2 Diabetes at a Glance
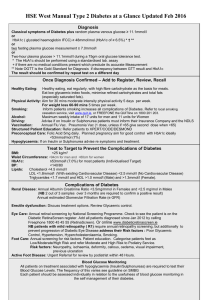
... HSE West Manual Type 2 Diabetes at a Glance Updated Feb 2016 Diagnosis Classical symptoms of Diabetes plus random plasma venous glucose ≥ 11.1mmol/l or HbA1c ( glycated haemoglobin IFCC) ≥ 48mmol/mol (HbA1c of ≥ 6.5%) * † ** or two fasting plasma glucose measurement ≥ 7.0mmol/l or Two-hour plasma gl ...
... HSE West Manual Type 2 Diabetes at a Glance Updated Feb 2016 Diagnosis Classical symptoms of Diabetes plus random plasma venous glucose ≥ 11.1mmol/l or HbA1c ( glycated haemoglobin IFCC) ≥ 48mmol/mol (HbA1c of ≥ 6.5%) * † ** or two fasting plasma glucose measurement ≥ 7.0mmol/l or Two-hour plasma gl ...
Lecture 28
... • What are the major second messenger systems used by the hormones that regulate blood glucose? What is the end result of activation of these second messenger systems? ...
... • What are the major second messenger systems used by the hormones that regulate blood glucose? What is the end result of activation of these second messenger systems? ...
i. justification for intensive diabetes control
... 3. INITIAL T(x) for acute : RAISE GLUCOSE LEVELS One cannot determine whether a patient is hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic during an acute attack unless blood tests are performed. Therefore, the initial treatment for an unknown acute attack is to raise glucose levels. Raising glucose levels in a hyper ...
... 3. INITIAL T(x) for acute : RAISE GLUCOSE LEVELS One cannot determine whether a patient is hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic during an acute attack unless blood tests are performed. Therefore, the initial treatment for an unknown acute attack is to raise glucose levels. Raising glucose levels in a hyper ...
outline3985
... 3. INITIAL T(x) for acute : RAISE GLUCOSE LEVELS One cannot determine whether a patient is hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic during an acute attack unless blood tests are performed. Therefore, the initial treatment for an unknown acute attack is to raise glucose levels. Raising glucose levels in a hyper ...
... 3. INITIAL T(x) for acute : RAISE GLUCOSE LEVELS One cannot determine whether a patient is hypoglycemic or hyperglycemic during an acute attack unless blood tests are performed. Therefore, the initial treatment for an unknown acute attack is to raise glucose levels. Raising glucose levels in a hyper ...
12 Endocrine Disorders - Crestwood Local Schools
... • Diabetes Mellitus – results from an insulin deficiency, blood sugar rises (hypoglycemia) and excess is excreted in the urine. ...
... • Diabetes Mellitus – results from an insulin deficiency, blood sugar rises (hypoglycemia) and excess is excreted in the urine. ...
Let`s Talk Running…
... thirst, lethargy, blurred vision, confusion, flushed face, nausea, “fruity” breath, and deep sighing (Kussmaul) breathing. In severe cases, diabetic coma is a medical concern. Symptoms of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar/excessive insulin present) are typically sudden in onset and include, but not limi ...
... thirst, lethargy, blurred vision, confusion, flushed face, nausea, “fruity” breath, and deep sighing (Kussmaul) breathing. In severe cases, diabetic coma is a medical concern. Symptoms of hypoglycemia (low blood sugar/excessive insulin present) are typically sudden in onset and include, but not limi ...
Body Systems - Bishop Ireton High School
... Example- when blood glucose levels are high, insulin is produced to remove glucose from blood. Glucose is stored in the cells. When blood glucose levels are low, glucagon is produced to cause cells to release stored glucose into the blood. When desired level is reached, hormone production is turne ...
... Example- when blood glucose levels are high, insulin is produced to remove glucose from blood. Glucose is stored in the cells. When blood glucose levels are low, glucagon is produced to cause cells to release stored glucose into the blood. When desired level is reached, hormone production is turne ...
Insulin
... Negative feedback Reduce stimuli Glucose levels are regulated Shut off original stimuli ...
... Negative feedback Reduce stimuli Glucose levels are regulated Shut off original stimuli ...
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also known as low blood sugar or low blood glucose, is when blood sugar decreases to below normal. This may result in a variety of symptoms including clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, loss of consciousness and seizures, or in death. A feeling of hunger, sweating, shakiness, and weakness may also be present. Symptoms typically come on quickly.The most common cause of hypoglycemia is medications used to treat diabetes mellitus such as insulin, sulfonylureas, and biguanides. Risk is greater in diabetics who have eaten less than usual, exercised more than usual, or drunk alcohol. Other causes of hypoglycemia include kidney failure, certain tumors, liver disease, hypothyroidism, starvation, inborn error of metabolism, severe infections, reactive hypoglycemia, and a number of drugs including alcohol. Low blood sugar may occur in babies who are otherwise healthy who have not eaten for a few hours.The glucose level that defines hypoglycemia is variable. In people with diabetes levels below 3.9 mmol/L (70 mg/dL) is diagnostic. In adults without diabetes, symptoms related to low blood sugar, low blood sugar at the time of symptoms, and improvement when blood sugar is restored to normal confirm the diagnosis. Otherwise a level below 2.8 mmol/L (50 mg/dL) after not eating or following exercise may be used. In newborns a level below 2.2 mmol/L (40 mg/dL) or less than 3.3 mmol/L (60 mg/dL) if symptoms are present indicates hypoglycemia. Other tests that may be useful in determining the cause include insulin and C peptide levels in the blood. Hyperglycemia, a high blood sugar, is the opposite condition.Among people with diabetes, prevention is by matching the foods eaten, with the amount of exercise, and the medications used. When people feel their blood sugar is low testing with a glucose monitor is recommended. Some people have few initial symptoms of low blood sugar and frequent routine testing in this group is recommended. Treatment of hypoglycemia is by eating foods high in simple sugars or taking dextrose. If a person is not able to take food by mouth, an injection of glucagon may help. The treatment of hypoglycemia unrelated to diabetes include treating the underlying problem as well and a healthy diet. The term ""hypoglycemia"" is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to idiopathic postprandial syndrome, a controversial condition with similar symptoms that occur following eating but with normal blood sugar levels.