File
... They removed the pancreas of healthy dogs and found that they lost weight rapidly and became fatigued. Analysis of their urine showed that it contained glucose while the healthy dogs’ urine did not. This experiment was used later as proof that the pancreas contained a hormone responsible for glucose ...
... They removed the pancreas of healthy dogs and found that they lost weight rapidly and became fatigued. Analysis of their urine showed that it contained glucose while the healthy dogs’ urine did not. This experiment was used later as proof that the pancreas contained a hormone responsible for glucose ...
1e InteractiveHormonePPT(Student-made)
... Inhibitsinsipidus; diuresis Diabetes Inappropriate ADH under high blood Tubules of the dehydration from (urine production) Peptide Secretion” (SIADH), solute kidneys excessive urine common in CHS injury and increases concentrations, patientsintense trauma, thirst some output; blood pressure inhibite ...
... Inhibitsinsipidus; diuresis Diabetes Inappropriate ADH under high blood Tubules of the dehydration from (urine production) Peptide Secretion” (SIADH), solute kidneys excessive urine common in CHS injury and increases concentrations, patientsintense trauma, thirst some output; blood pressure inhibite ...
Homeostasis
... – If it was not removed it would affect the pH of the cells (make it more acidic). This would affect the working of the enzymes in cells. – Carbon dioxide moves out of cells into blood. – Blood carries it back to lungs. ...
... – If it was not removed it would affect the pH of the cells (make it more acidic). This would affect the working of the enzymes in cells. – Carbon dioxide moves out of cells into blood. – Blood carries it back to lungs. ...
DIAGNOSTIC TESTS of the Endocrine System (continued)
... identify, confirm, and monitor glucose levels in clients with diabetes mellitus. Those described are oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), fasting blood sugar (FBS), glycosylated hemoglobin (Hb A1C), and CT of the abdomen to identify pancreatic tumors or cysts. Regardless of the type of diagnostic tes ...
... identify, confirm, and monitor glucose levels in clients with diabetes mellitus. Those described are oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT), fasting blood sugar (FBS), glycosylated hemoglobin (Hb A1C), and CT of the abdomen to identify pancreatic tumors or cysts. Regardless of the type of diagnostic tes ...
How do diets that limit your carbohydrate consumption cause weight
... sugar as fuel. To turn sugars into fuel, your body uses the hormone insulin. Insulin enables our cells to turn carbohydrates into glucose by controlling the amount of sugar in our blood. The body secretes insulin to keep blood sugar from getting too high. Insulin is a storage hormone, meaning that i ...
... sugar as fuel. To turn sugars into fuel, your body uses the hormone insulin. Insulin enables our cells to turn carbohydrates into glucose by controlling the amount of sugar in our blood. The body secretes insulin to keep blood sugar from getting too high. Insulin is a storage hormone, meaning that i ...
Calcium Homeostasis(1)
... The symptoms are absent during rest but appears to emotional stress ,pregnancy &lactation. Manifest tetany: Plasma calcium level drop below 7mg%. ...
... The symptoms are absent during rest but appears to emotional stress ,pregnancy &lactation. Manifest tetany: Plasma calcium level drop below 7mg%. ...
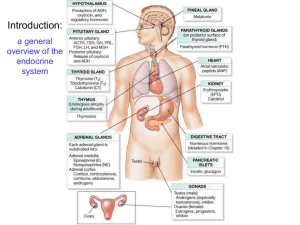
The Endocrine System
... The Insulin-glucagon Ratio Regulates Metabolism • Insulin and glucagon act in an antagonistic fashion to keep plasma glucose concentrations within an acceptable range (70-110 mg/dL). • Both are present in the blood most of the time. • The ratio of the two hormones determines which hormone dominates ...
... The Insulin-glucagon Ratio Regulates Metabolism • Insulin and glucagon act in an antagonistic fashion to keep plasma glucose concentrations within an acceptable range (70-110 mg/dL). • Both are present in the blood most of the time. • The ratio of the two hormones determines which hormone dominates ...
Regulation and Control Homeostasis
... Describe how the level of blood glucose in a human is maintained at a constant level by hormones with reference to the source of the hormones involved ...
... Describe how the level of blood glucose in a human is maintained at a constant level by hormones with reference to the source of the hormones involved ...
Growth Hormone Deficiency
... parents to track the growth of infants, children, and adolescents in the United States since 1977. The 1977 growth charts were developed by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) as a clinical tool for health professionals to determine if the growth of a child is adequate. The 1977 charts ...
... parents to track the growth of infants, children, and adolescents in the United States since 1977. The 1977 growth charts were developed by the National Center for Health Statistics (NCHS) as a clinical tool for health professionals to determine if the growth of a child is adequate. The 1977 charts ...
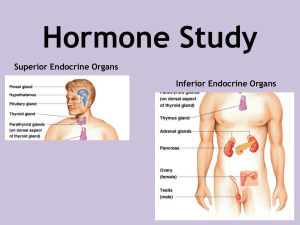
endocrine2organs2013 30KB
... Iodine when its levels are low. At “best”, iodine deficiency causes cretinism (retardation)— mechanism of recruitment (channel) is a symporter that exchanges Na+ for I-...solution to this problem is simply the iodization of salt. general reference, aud 656…more thyroid function/mech: Iodine recruitm ...
... Iodine when its levels are low. At “best”, iodine deficiency causes cretinism (retardation)— mechanism of recruitment (channel) is a symporter that exchanges Na+ for I-...solution to this problem is simply the iodization of salt. general reference, aud 656…more thyroid function/mech: Iodine recruitm ...
Ch 45 Endocrine System
... Hormones and other chemical signals bind to target cell receptors, initiating pathways that culminate in specific cell responses Hormones convey information via the ...
... Hormones and other chemical signals bind to target cell receptors, initiating pathways that culminate in specific cell responses Hormones convey information via the ...
Diabetes Mellitus
... Abdominal ultrasound is a non-invasive test that uses sound waves to create images of internal organs and structures Blood pressure can be elevated in patients with DM What treatment options are available for DM? DM is a treatable condition and both dogs and cats can do very well with appropriat ...
... Abdominal ultrasound is a non-invasive test that uses sound waves to create images of internal organs and structures Blood pressure can be elevated in patients with DM What treatment options are available for DM? DM is a treatable condition and both dogs and cats can do very well with appropriat ...
How do our organ systems maintain homeostasis?
... Bone is the major storage site for calcium in the body, and movement of calcium into and out of bone helps to determine blood calcium levels. Calcium moves into bone as osteoblasts build new bone and out of bone as osteoclasts break down bone. Hormones help regulate blood calcium levels. For inst ...
... Bone is the major storage site for calcium in the body, and movement of calcium into and out of bone helps to determine blood calcium levels. Calcium moves into bone as osteoblasts build new bone and out of bone as osteoclasts break down bone. Hormones help regulate blood calcium levels. For inst ...
Lect22
... Fat Tissue • Insulin initiates transfer of glucose transporters to cell membrane • blood glucose • production of glycogen ...
... Fat Tissue • Insulin initiates transfer of glucose transporters to cell membrane • blood glucose • production of glycogen ...
Study Guide for Chapter 19 Fox
... What are the “preferred energy sources” for different organs? ...
... What are the “preferred energy sources” for different organs? ...
Endocrine System Tortora, Chapter 18, 13th ed.
... 2- Lipolysis: the breakdown of triglycerides to release fatty acids. 3- Glucose formation from certain amino acids or lactic acid by liver (gluconeogenesis) 4- Resistance to stress: by glucose supply and ATP to combat stress and by sensitizing blood vessels to vasoconstrictive hormones. ...
... 2- Lipolysis: the breakdown of triglycerides to release fatty acids. 3- Glucose formation from certain amino acids or lactic acid by liver (gluconeogenesis) 4- Resistance to stress: by glucose supply and ATP to combat stress and by sensitizing blood vessels to vasoconstrictive hormones. ...
Hypothalamus and Homeostasis
... Proteins-->Amino acids Fats-->Fatty acids These are stored in the body: Fat cells (long-term) 80-90% of total Muscle and liver glycogen (starch) Blood glucose, fatty acids and amino acids. (short-term) • Ketones used if blood glucose low. ...
... Proteins-->Amino acids Fats-->Fatty acids These are stored in the body: Fat cells (long-term) 80-90% of total Muscle and liver glycogen (starch) Blood glucose, fatty acids and amino acids. (short-term) • Ketones used if blood glucose low. ...
Diabetes Packet - Vernon Township School District
... A fast-acting carbohydrate such as _________________________________________________________ should be available at the site of exercise or sports. Restrictions on physical activity: ___________________________________________________________ Students should not exercise if blood glucose level is be ...
... A fast-acting carbohydrate such as _________________________________________________________ should be available at the site of exercise or sports. Restrictions on physical activity: ___________________________________________________________ Students should not exercise if blood glucose level is be ...
Glucose - Harvard Pilgrim Health Care
... What does your blood glucose (sugar) number mean? The blood glucose number tells you what your blood sugar is right now. Normal blood sugar is between 70 and 125 mg/dL. What does it mean if my blood sugar is high? Blood sugar levels that remain high can damage your eyes, kidneys, nerves and blood ve ...
... What does your blood glucose (sugar) number mean? The blood glucose number tells you what your blood sugar is right now. Normal blood sugar is between 70 and 125 mg/dL. What does it mean if my blood sugar is high? Blood sugar levels that remain high can damage your eyes, kidneys, nerves and blood ve ...
Endocrine system Review What governs magnitude of hormone
... pancreas (autoimmune disease) –No insulin - must take insulin ...
... pancreas (autoimmune disease) –No insulin - must take insulin ...
Drugs affecting the ENDOCRINE system
... Drugs used in disorders of the PANCREAS • When the pancreas no longer secrete sufficient effective insulin the glucose cannot enter the cells. • NIDDM, IDDM, Glucogon. • Glucagon acts on the liver to increase blood glucose levels by stimulating the breakdown of glycogen into glucose, and amino acid ...
... Drugs used in disorders of the PANCREAS • When the pancreas no longer secrete sufficient effective insulin the glucose cannot enter the cells. • NIDDM, IDDM, Glucogon. • Glucagon acts on the liver to increase blood glucose levels by stimulating the breakdown of glycogen into glucose, and amino acid ...
Endocrine System - ABC-MissAngelochsBiologyClass
... amount of hormones in the blood) Works like a thermostat in your home. The room is maintained at a certain temp. When the temp. drops the heat kicks in. When it starts to get hot it slows production. *** This helps to maintain homeostasis ...
... amount of hormones in the blood) Works like a thermostat in your home. The room is maintained at a certain temp. When the temp. drops the heat kicks in. When it starts to get hot it slows production. *** This helps to maintain homeostasis ...
Hypoglycemia
Hypoglycemia, also known as low blood sugar or low blood glucose, is when blood sugar decreases to below normal. This may result in a variety of symptoms including clumsiness, trouble talking, confusion, loss of consciousness and seizures, or in death. A feeling of hunger, sweating, shakiness, and weakness may also be present. Symptoms typically come on quickly.The most common cause of hypoglycemia is medications used to treat diabetes mellitus such as insulin, sulfonylureas, and biguanides. Risk is greater in diabetics who have eaten less than usual, exercised more than usual, or drunk alcohol. Other causes of hypoglycemia include kidney failure, certain tumors, liver disease, hypothyroidism, starvation, inborn error of metabolism, severe infections, reactive hypoglycemia, and a number of drugs including alcohol. Low blood sugar may occur in babies who are otherwise healthy who have not eaten for a few hours.The glucose level that defines hypoglycemia is variable. In people with diabetes levels below 3.9 mmol/L (70 mg/dL) is diagnostic. In adults without diabetes, symptoms related to low blood sugar, low blood sugar at the time of symptoms, and improvement when blood sugar is restored to normal confirm the diagnosis. Otherwise a level below 2.8 mmol/L (50 mg/dL) after not eating or following exercise may be used. In newborns a level below 2.2 mmol/L (40 mg/dL) or less than 3.3 mmol/L (60 mg/dL) if symptoms are present indicates hypoglycemia. Other tests that may be useful in determining the cause include insulin and C peptide levels in the blood. Hyperglycemia, a high blood sugar, is the opposite condition.Among people with diabetes, prevention is by matching the foods eaten, with the amount of exercise, and the medications used. When people feel their blood sugar is low testing with a glucose monitor is recommended. Some people have few initial symptoms of low blood sugar and frequent routine testing in this group is recommended. Treatment of hypoglycemia is by eating foods high in simple sugars or taking dextrose. If a person is not able to take food by mouth, an injection of glucagon may help. The treatment of hypoglycemia unrelated to diabetes include treating the underlying problem as well and a healthy diet. The term ""hypoglycemia"" is sometimes incorrectly used to refer to idiopathic postprandial syndrome, a controversial condition with similar symptoms that occur following eating but with normal blood sugar levels.