Biochemical and Molecular Characterization of the Chicken
... In addition to the LIM-homeodomain proteins, a number of small (10-30 kD) proteins that are comprised primarily of LIM domains have been identified. These include rhombotin (or Ttg-1) (McGuire et al., 1989; Boehm et al., 1990, 1991), the cysteine-rich intestinal protein (CRIP) t (Birkenmeier and Gor ...
... In addition to the LIM-homeodomain proteins, a number of small (10-30 kD) proteins that are comprised primarily of LIM domains have been identified. These include rhombotin (or Ttg-1) (McGuire et al., 1989; Boehm et al., 1990, 1991), the cysteine-rich intestinal protein (CRIP) t (Birkenmeier and Gor ...
6 Macromolecules
... A group of three bases - a codon - characterizes a particular amino acid, i.e. it gives the prescription to insert that amino acid into a protein chain being synthesized. For coding the 20 different amino acids from which natural proteins are made, there are thus 43 = 64 distinct codons, since 4 dif ...
... A group of three bases - a codon - characterizes a particular amino acid, i.e. it gives the prescription to insert that amino acid into a protein chain being synthesized. For coding the 20 different amino acids from which natural proteins are made, there are thus 43 = 64 distinct codons, since 4 dif ...
Positively selected sites on the surface glycoprotein (G) of infectious
... Fig. 1 were analysed separately by using MrBayes. The results obtained by using the sequences in clade A–B are shown in Table 2, Fig. 2(b) and Fig. 3(b). In this case, the amino acids with mean posterior probabilities of positive selection .95 % were 220, 256, 270, 272, 277 and 284. No other sequenc ...
... Fig. 1 were analysed separately by using MrBayes. The results obtained by using the sequences in clade A–B are shown in Table 2, Fig. 2(b) and Fig. 3(b). In this case, the amino acids with mean posterior probabilities of positive selection .95 % were 220, 256, 270, 272, 277 and 284. No other sequenc ...
Practical Proteins and Amino Acids` Identification
... Biuret’s test Principle: Biuret test is Specific for Proteins – To differentiate between Proteins (+ve) and Amino Acids (-ve). The biuret reagent (copper sulfate in a strong base) reacts with peptide bonds in proteins to form a violet complex known as the “Biuret complex”. Two peptide bonds are at ...
... Biuret’s test Principle: Biuret test is Specific for Proteins – To differentiate between Proteins (+ve) and Amino Acids (-ve). The biuret reagent (copper sulfate in a strong base) reacts with peptide bonds in proteins to form a violet complex known as the “Biuret complex”. Two peptide bonds are at ...
Poster
... Mentor: Madhusudan Dey, Ph.D., Department of Biological Sciences, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis and are major targets of antibiotics. While translation is a universally conserved cellular process, the ability of drugs to target prokaryotic ribosome ...
... Mentor: Madhusudan Dey, Ph.D., Department of Biological Sciences, University of Wisconsin-Milwaukee Ribosomes are responsible for protein synthesis and are major targets of antibiotics. While translation is a universally conserved cellular process, the ability of drugs to target prokaryotic ribosome ...
Amino Acids and Proteins - Gadarif University Repository
... The helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonding between the backbone carbonyl of one amino acid and the backbone NH of the amino acid four residues away. All main chain amino and carboxyl groups are hydrogen bonded, and the R groups stick out from the structure in a ...
... The helix is stabilized by hydrogen bonding between the backbone carbonyl of one amino acid and the backbone NH of the amino acid four residues away. All main chain amino and carboxyl groups are hydrogen bonded, and the R groups stick out from the structure in a ...
emboj200897-sup
... substrate (hence the autokinase activity is measured), it is important to control the initial phosphorylation level of the samples. Supplementary Figure 3 shows a similar starting phosphorylation level for all wild type Etk and mutant samples used in this study. The fully dephosphorylated protein sa ...
... substrate (hence the autokinase activity is measured), it is important to control the initial phosphorylation level of the samples. Supplementary Figure 3 shows a similar starting phosphorylation level for all wild type Etk and mutant samples used in this study. The fully dephosphorylated protein sa ...
biochem ch 45 [9-2
... o Factor XIII cross-links strands of of polymerized fibrin monomers to form secondary hemostatic plug o Ca2+ and γ-carboxyglutamate residues in proteins (formed by vitamin K-dependent process in liver) attach factor complexes to phospholipids exposed on platelet membranes, causing thrombus formation ...
... o Factor XIII cross-links strands of of polymerized fibrin monomers to form secondary hemostatic plug o Ca2+ and γ-carboxyglutamate residues in proteins (formed by vitamin K-dependent process in liver) attach factor complexes to phospholipids exposed on platelet membranes, causing thrombus formation ...
spin-system assignments
... assignments, followed by sequence-specific assignment using unique fragments of sequence, is known as sequential assignment (Wuthrich) • there are alternatives to this protocol: one is known as main-chain directed assignment (Englander). This technique does not focus on assigning all the spin system ...
... assignments, followed by sequence-specific assignment using unique fragments of sequence, is known as sequential assignment (Wuthrich) • there are alternatives to this protocol: one is known as main-chain directed assignment (Englander). This technique does not focus on assigning all the spin system ...
CH_16_4_Levels_Protein_Structure
... nonpolar R groups move away from the aqueous environment to form a hydrophobic center at the interior of the protein molecule. 2. Hydrophilic interactions are attractions between the external aqueous environment and the R groups of polar amino acids moving the polar amino acids toward the outer surf ...
... nonpolar R groups move away from the aqueous environment to form a hydrophobic center at the interior of the protein molecule. 2. Hydrophilic interactions are attractions between the external aqueous environment and the R groups of polar amino acids moving the polar amino acids toward the outer surf ...
Fast and simple purification of GST fusion proteins using prepacked
... Fig 3. SDS-PAGE analysis of a GST fusion protein purified with GSTrap affinity columns. A cytoplasmic extract from an E. coli culture expressing a GST fusion protein was loaded onto GSTrap 1 ml and GSTrap 5 ml columns (8 ml and 40 ml of lysate, respectively). Fusion protein was eluted using 10 mM re ...
... Fig 3. SDS-PAGE analysis of a GST fusion protein purified with GSTrap affinity columns. A cytoplasmic extract from an E. coli culture expressing a GST fusion protein was loaded onto GSTrap 1 ml and GSTrap 5 ml columns (8 ml and 40 ml of lysate, respectively). Fusion protein was eluted using 10 mM re ...
NIH Public Access
... hydrophobic motif (HM; T389) peptide regions of its catalytic kinase domain (residues 1-398). In addition to its kinase domain, S6K1 contains a C-terminal autoinhibitory domain (AID; residues 399-502), which prevents T-loop and HM phosphorylation; and autoinhibition is relieved on multisite Ser-Thr ...
... hydrophobic motif (HM; T389) peptide regions of its catalytic kinase domain (residues 1-398). In addition to its kinase domain, S6K1 contains a C-terminal autoinhibitory domain (AID; residues 399-502), which prevents T-loop and HM phosphorylation; and autoinhibition is relieved on multisite Ser-Thr ...
Encontro de Jovens Investigadores de Biologia Computacional
... of three drug-binding sites within P-gp\'s internal drug-binding pocket (DBP), a series of molecular dynamics studies were performed using a refined P-gp structure to further clarify how drug efflux occurs and how drug adsorption to either the protein or the membrane affects P-gp activity. It was hy ...
... of three drug-binding sites within P-gp\'s internal drug-binding pocket (DBP), a series of molecular dynamics studies were performed using a refined P-gp structure to further clarify how drug efflux occurs and how drug adsorption to either the protein or the membrane affects P-gp activity. It was hy ...
34750 - Radboud Repository
... groups [1], steroids [2], amino acids, and iron-sulphur (Fe-S) clusters [3]. Phylogenetic analyses of mitochondrial genes indicate that all mitochondria derive from a single alphaproteobacterial ancestor, the so-called proto-mitochondrion [4]. During the transformation of proto-mitochondrion to orga ...
... groups [1], steroids [2], amino acids, and iron-sulphur (Fe-S) clusters [3]. Phylogenetic analyses of mitochondrial genes indicate that all mitochondria derive from a single alphaproteobacterial ancestor, the so-called proto-mitochondrion [4]. During the transformation of proto-mitochondrion to orga ...
WordPerfect Office Document
... compartments and are involved in stress adaptation and acclimation. While production mechanisms for ROS are relatively well understood, the perception of ROS signals has remained unresolved. We have identified proteins that might serve as ROS sensors. Members of a family of receptor-like kinases (RL ...
... compartments and are involved in stress adaptation and acclimation. While production mechanisms for ROS are relatively well understood, the perception of ROS signals has remained unresolved. We have identified proteins that might serve as ROS sensors. Members of a family of receptor-like kinases (RL ...
Delivery of a Secreted Soluble Protein to the Vacuole via a
... not to have plant vacuolar targeting information. When yeast invertase is equipped with a plant signal peptide, catalytically active protein is secreted in the apoplast (von Schaewen et al., 1990; Dickinson et al., 1991). We chose the transmembrane domain of yeast calnexin because we assumed that th ...
... not to have plant vacuolar targeting information. When yeast invertase is equipped with a plant signal peptide, catalytically active protein is secreted in the apoplast (von Schaewen et al., 1990; Dickinson et al., 1991). We chose the transmembrane domain of yeast calnexin because we assumed that th ...
Amino Acid Sequence Homology of Coat Proteins as a Basis for
... fraction of the total genomic information. However, as has been pointed out by Van Regenmortel (1986), successful classifications based on very few parameters have been developed, such as the reconstruction of phylogenetic trees of higher organisms on the basis of the degree of sequence homology fou ...
... fraction of the total genomic information. However, as has been pointed out by Van Regenmortel (1986), successful classifications based on very few parameters have been developed, such as the reconstruction of phylogenetic trees of higher organisms on the basis of the degree of sequence homology fou ...
Antibody Humanization Workflow And Price List
... and chimeric antibody control at 5mg/sample) need to be paid to Ab Studio. Protein production will complete in 6 weeks. After that, Ab Studio will start the secondary round screen service after receiving $20,000 service fee from clients. The secondary round screen service includes Biacore for affini ...
... and chimeric antibody control at 5mg/sample) need to be paid to Ab Studio. Protein production will complete in 6 weeks. After that, Ab Studio will start the secondary round screen service after receiving $20,000 service fee from clients. The secondary round screen service includes Biacore for affini ...
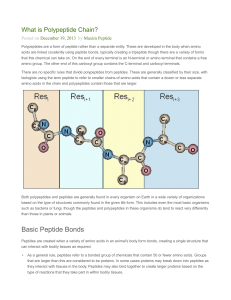
Basic Peptide Bonds
... Peptides are also being researched for their inhibitory properties which may have potential in restricting the growth of cancers and similar diseases. In animal test subjects peptides have shown promise in detecting and targeting items such as LHRH and regulating the receptors. This process could be ...
... Peptides are also being researched for their inhibitory properties which may have potential in restricting the growth of cancers and similar diseases. In animal test subjects peptides have shown promise in detecting and targeting items such as LHRH and regulating the receptors. This process could be ...
Identification of the nuclear localization signals within the Epstein
... was determined by DNA sequencing and immunoblotting. To ensure easy visualization of both the nucleus and cytoplasm the constructs were transfected into HeLa cells. All of the constructs were transiently expressed in HeLa cells and the cellular location of the fusion proteins was determined by confo ...
... was determined by DNA sequencing and immunoblotting. To ensure easy visualization of both the nucleus and cytoplasm the constructs were transfected into HeLa cells. All of the constructs were transiently expressed in HeLa cells and the cellular location of the fusion proteins was determined by confo ...
Fractionation of rice glutelin polypeptides using gel filtration
... samplesof dissociatedglutelin polypeptides suitable for further characterization and study. Urea was the preferred extractant, becauseit would be less likely to interfere with further attempts at characterization and, if required, could be readily removed. In addition, a highly enriched fraction of ...
... samplesof dissociatedglutelin polypeptides suitable for further characterization and study. Urea was the preferred extractant, becauseit would be less likely to interfere with further attempts at characterization and, if required, could be readily removed. In addition, a highly enriched fraction of ...
Infectious Salmon Anaemia Virus (ISAV) RNA Binding Protein
... protein (M2) from collinear and spliced mRNA, respectively. No homologue to the influenza virus ion channel protein has been identified in ISAV. Infection with ISAV leads to activation and production of type I interferon (IFN) in Atlantic salmon and in cell lines derived from Atlantic salmon [7–9]. ...
... protein (M2) from collinear and spliced mRNA, respectively. No homologue to the influenza virus ion channel protein has been identified in ISAV. Infection with ISAV leads to activation and production of type I interferon (IFN) in Atlantic salmon and in cell lines derived from Atlantic salmon [7–9]. ...
Protein–protein interaction

Protein–protein interactions (PPIs) refer to physical contacts established between two or more proteins as a result of biochemical events and/or electrostatic forces.In fact, proteins are vital macromolecules, at both cellular and systemic levels, but they rarely act alone. Diverse essential molecular processes within a cell are carried out by molecular machines that are built from a large number of protein components organized by their PPIs. Indeed, these interactions are at the core of the entire interactomics system of any living cell and so, unsurprisingly, aberrant PPIs are on the basis of multiple diseases, such as Creutzfeld-Jacob, Alzheimer's disease, and cancer.PPIs have been studied from different perspectives: biochemistry, quantum chemistry, molecular dynamics, signal transduction, among others. All this information enables the creation of large protein interaction networks – similar to metabolic or genetic/epigenetic networks – that empower the current knowledge on biochemical cascades and disease pathogenesis, as well as provide putative new therapeutic targets.