Silent but Deadly - Global Justice Now
... They include the direct (scope 1) emissions from things like the boilers and engines that burn fossil fuels on site. They also include the purchased (scope 2) emissions arising from the electricity consumed by the animal feed company. But they exclude the vast majority of indirect (scope 3) emission ...
... They include the direct (scope 1) emissions from things like the boilers and engines that burn fossil fuels on site. They also include the purchased (scope 2) emissions arising from the electricity consumed by the animal feed company. But they exclude the vast majority of indirect (scope 3) emission ...
Economic Growth and Climate Change: A Cross
... then remained stable between 1985 and 2005. Jorgenson and Clark also found that in less-developed countries the relationship between economic development and per capita emissions intensified over this period. Developed countries may have achieved their modest decoupling by transferring some carbon-i ...
... then remained stable between 1985 and 2005. Jorgenson and Clark also found that in less-developed countries the relationship between economic development and per capita emissions intensified over this period. Developed countries may have achieved their modest decoupling by transferring some carbon-i ...
CDM from LDC perspective by Pascale Junker, Lux Dev
... • General feeling that international Climate Change conferences aiming at universally binding reduction legislation is not the way forward (contrary to emerging economies’ take off). • Market based approaches are more accurate, if they guarantee real net reductions and environmental integrity • End ...
... • General feeling that international Climate Change conferences aiming at universally binding reduction legislation is not the way forward (contrary to emerging economies’ take off). • Market based approaches are more accurate, if they guarantee real net reductions and environmental integrity • End ...
Bunker Fuels and the Kyoto Protocol How ICAO and the IMO Failed
... Policy options identified to reduce emission further included more stringent engine regulations, the removal of subsidies and incentives that have negative environmental consequences, environmental levies (charges and taxes), emissions trading, and voluntary agreements. It was noted that ICAO had al ...
... Policy options identified to reduce emission further included more stringent engine regulations, the removal of subsidies and incentives that have negative environmental consequences, environmental levies (charges and taxes), emissions trading, and voluntary agreements. It was noted that ICAO had al ...
Calculating the Environmental Impact of Aviation
... own personal emissions - the money raised will fund energy efficiency or renewable energy projects which lead to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions equal to the amount offset. In order for offsetting to be credible, the greenhouse gas emissions to be offset have to be calculated accurately, and ...
... own personal emissions - the money raised will fund energy efficiency or renewable energy projects which lead to a reduction in greenhouse gas emissions equal to the amount offset. In order for offsetting to be credible, the greenhouse gas emissions to be offset have to be calculated accurately, and ...
vsi09 cc Grunewald 10154389 en
... sustainability or poverty reduction. Ellis (2007), Liu (2008) and Schubert et al. (2007) conclude that the decision for investing in a CDM project is rather driven by the amount of CERs gained, than by sustainability gains from the positive side effects of the projects in the implementing countries. ...
... sustainability or poverty reduction. Ellis (2007), Liu (2008) and Schubert et al. (2007) conclude that the decision for investing in a CDM project is rather driven by the amount of CERs gained, than by sustainability gains from the positive side effects of the projects in the implementing countries. ...
2012 co2 emissions overview - International Energy Agency
... Given the long lifetime of CO2 in the atmosphere, stabilising concentrations of greenhouse gases at any level would require large reductions of global CO2 emissions from current levels. The lower the chosen level for stabilisation, the sooner the decline in global CO2 emissions would need to begin, ...
... Given the long lifetime of CO2 in the atmosphere, stabilising concentrations of greenhouse gases at any level would require large reductions of global CO2 emissions from current levels. The lower the chosen level for stabilisation, the sooner the decline in global CO2 emissions would need to begin, ...
ISSUE BRIEF 14 mANDATORy REGUlATION OF NONTRADITIONAl GREENHOUSE GASES: POlICy OPTIONS FOR INDUSTRIAl
... gases more efficiently, or is less prone to leakage.15 Under a cap-and-trade system, allowance allocation could be used to ameliorate potential price shocks by awarding free allowances to the producers of fluorinated gases using an updating output-based approach, although this would tend to reduce o ...
... gases more efficiently, or is less prone to leakage.15 Under a cap-and-trade system, allowance allocation could be used to ameliorate potential price shocks by awarding free allowances to the producers of fluorinated gases using an updating output-based approach, although this would tend to reduce o ...
An Economic Analysis of the Kyoto Protocol
... thereby combating global climate change. Unfortuglobal warming represents a formidable threat to hunately, this treaty fails to present a valid solution to man welfare and merits global action. global warming. The Kyoto Protocol neglects ecoAs a result of this growing, widespread connomic as well as ...
... thereby combating global climate change. Unfortuglobal warming represents a formidable threat to hunately, this treaty fails to present a valid solution to man welfare and merits global action. global warming. The Kyoto Protocol neglects ecoAs a result of this growing, widespread connomic as well as ...
All developing countries where there is any ability to measure
... businesspeople on the other. But both sides might come to realize that this commitment is far more important than it sounds: it precludes the carbon leakage which absent such an agreement will undermine the environmental goal and it precludes the competitiveness losses which absent such an agreement ...
... businesspeople on the other. But both sides might come to realize that this commitment is far more important than it sounds: it precludes the carbon leakage which absent such an agreement will undermine the environmental goal and it precludes the competitiveness losses which absent such an agreement ...
PDF
... of halving global carbon emissions from 1990 levels by up to 50% in 2030 and by up to 40% in 2050. Finally, Dixon et al. (2008) using a numerical multi-country, two-sector partial equilibrium model of the global carbon market concluded that international permit price would be reduced by 45% when, in ...
... of halving global carbon emissions from 1990 levels by up to 50% in 2030 and by up to 40% in 2050. Finally, Dixon et al. (2008) using a numerical multi-country, two-sector partial equilibrium model of the global carbon market concluded that international permit price would be reduced by 45% when, in ...
Ireland`s Response to the EU`s 2030 Energy and Climate Change
... compared to 1990. The Emissions Trading System (ETS) sector will contribute 43% of this target and the non-ETS sectors 30%. The European Council has also agreed an EU target of at least 27% for the share of renewable energy consumed in the EU by 2030 and a similar indicative percentage for energy ef ...
... compared to 1990. The Emissions Trading System (ETS) sector will contribute 43% of this target and the non-ETS sectors 30%. The European Council has also agreed an EU target of at least 27% for the share of renewable energy consumed in the EU by 2030 and a similar indicative percentage for energy ef ...
english - Sustainable Development of Tourism
... addition to the direct economic impact on air transport, this may lead to discrimination 6 . Also, in the absence of a global solution, traffic flow may be diverted to or via less costly carbon-levied points - such “carbon leakage” distortions are environmentally unhelpful. Concerns regarding fragme ...
... addition to the direct economic impact on air transport, this may lead to discrimination 6 . Also, in the absence of a global solution, traffic flow may be diverted to or via less costly carbon-levied points - such “carbon leakage” distortions are environmentally unhelpful. Concerns regarding fragme ...
Bilateral Cooperation between China and the United States
... Assembly Bill 32 (AB 32) constitute significant sub-national climate change initiatives in the United States. RGGI is a CO2 cap-and-trade system for the power sector in nine northeastern states. Nearly all allowances are auctioned, with revenues used by the respective states largely for clean-energy ...
... Assembly Bill 32 (AB 32) constitute significant sub-national climate change initiatives in the United States. RGGI is a CO2 cap-and-trade system for the power sector in nine northeastern states. Nearly all allowances are auctioned, with revenues used by the respective states largely for clean-energy ...
progress toward a consensus on carbon emissions from tropical
... This net flux takes into account the fact that the fallow phases of shifting cultivation and post-harvest regrowth of forests can sequester substantial amounts of carbon, partly or wholly offsetting the previous emissions (Figure 1). Gross emissions from all forest land use and land-use change repor ...
... This net flux takes into account the fact that the fallow phases of shifting cultivation and post-harvest regrowth of forests can sequester substantial amounts of carbon, partly or wholly offsetting the previous emissions (Figure 1). Gross emissions from all forest land use and land-use change repor ...
All developing countries where there is any ability to measure
... businesspeople on the other. But both sides might come to realize that this commitment is far more important than it sounds: it precludes the carbon leakage which absent such an agreement will undermine the environmental goal and it precludes the competitiveness losses which absent such an agreement ...
... businesspeople on the other. But both sides might come to realize that this commitment is far more important than it sounds: it precludes the carbon leakage which absent such an agreement will undermine the environmental goal and it precludes the competitiveness losses which absent such an agreement ...
The study - WWF
... According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fifth Assessment Report, the global average air temperature has increased by approximately 0.85C since 1890.i By the end of this century, the IPCC projects that warming is likely to exceed 1.5C, with the possibility of the global av ...
... According to the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC) Fifth Assessment Report, the global average air temperature has increased by approximately 0.85C since 1890.i By the end of this century, the IPCC projects that warming is likely to exceed 1.5C, with the possibility of the global av ...
air traffic controls: the hidden costs of a new london runway
... to route flown”.10 This change, which greatly reduces the level of emissions reductions that would be needed, has not been widely scrutinised. For example, it is not clear whether the DfT now agrees that its 2013 forecast was incorrect and has been significantly improved by Commission’s model. Indee ...
... to route flown”.10 This change, which greatly reduces the level of emissions reductions that would be needed, has not been widely scrutinised. For example, it is not clear whether the DfT now agrees that its 2013 forecast was incorrect and has been significantly improved by Commission’s model. Indee ...
Addressing Climate Change Challenges in Ireland (07-CCRP-3.1) CCRP Report
... suggests that a shift in investment patterns towards low or zero carbon technologies and infrastructure in areas such as power generation is required by 2015 to avoid the higher costs associated with locked-in technologies and infrastructure. The current carbon price is insufficient to promote such ...
... suggests that a shift in investment patterns towards low or zero carbon technologies and infrastructure in areas such as power generation is required by 2015 to avoid the higher costs associated with locked-in technologies and infrastructure. The current carbon price is insufficient to promote such ...
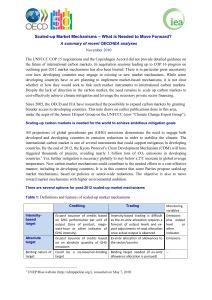
Scaled-up Market Mechanisms – What is Needed to
... countries. By the end of 2012, the Kyoto Protocol’s Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) will have triggered thousands of projects, avoiding nearly 1 billion tons of CO2 emissions in developing countries.1 Yet, further mitigation is necessary globally to stay below a 2oC increase in global average temp ...
... countries. By the end of 2012, the Kyoto Protocol’s Clean Development Mechanism (CDM) will have triggered thousands of projects, avoiding nearly 1 billion tons of CO2 emissions in developing countries.1 Yet, further mitigation is necessary globally to stay below a 2oC increase in global average temp ...
Regulation on Carbon Emission Trading Pricing-to-Market: Based on
... organs to invest carbon markets, America’s government encourage the entity to transact in the on-site exchange by means of signing voluntary contracts. In view of social responsibilities and cultural brand, enterprises are bind to legal reduction of carbon emissions by concluding contracts with Amer ...
... organs to invest carbon markets, America’s government encourage the entity to transact in the on-site exchange by means of signing voluntary contracts. In view of social responsibilities and cultural brand, enterprises are bind to legal reduction of carbon emissions by concluding contracts with Amer ...
Climate Treaties and Enforcement - Yale Center for the Study of
... These problems with Kyoto are more easily understood by contrasting this agreement with one that works well. In 2002, the United States imposed tariffs on steel imports. The European Union, supported by other countries, complained to the World Trade Organization (WTO) that the US tariffs were in non ...
... These problems with Kyoto are more easily understood by contrasting this agreement with one that works well. In 2002, the United States imposed tariffs on steel imports. The European Union, supported by other countries, complained to the World Trade Organization (WTO) that the US tariffs were in non ...
A Credible Foundation for Long Term International
... large financial stake in seeing the policy continue, and all future users of fossil fuels would be motivated to lobby against it. Apart from satisfying the terms of an international agreement, the only incentive a government would have to keep the tax in place is the revenue it generates. However, ...
... large financial stake in seeing the policy continue, and all future users of fossil fuels would be motivated to lobby against it. Apart from satisfying the terms of an international agreement, the only incentive a government would have to keep the tax in place is the revenue it generates. However, ...
Greenhouse gas emissions and the role of the Kyoto Protocol
... the United Nation Environment Programme (UNEP) and the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) established the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The United Nation Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) was adopted by the congress in 1992. The Kyoto Protocol was established a ...
... the United Nation Environment Programme (UNEP) and the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) established the Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change (IPCC). The United Nation Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) was adopted by the congress in 1992. The Kyoto Protocol was established a ...
Tokyo - IETA
... Excess credits: 22 When a covered facility reduces emissions by more than its compliance obligation, it can apply for credit issuance within a given period after the emissions are determined. In this instance, the facility can sell its excess credits amounting up to one-half of its base year emissio ...
... Excess credits: 22 When a covered facility reduces emissions by more than its compliance obligation, it can apply for credit issuance within a given period after the emissions are determined. In this instance, the facility can sell its excess credits amounting up to one-half of its base year emissio ...