Chapter 6
... Group VIIIA: noble gases Transition Metals: Group B elements (in middle of the Periodic Table) The behavior and properties of transition metals is not very predictable. Inner Transition Elements (beneath the main body of Periodic Table) Lanthanide series: Ce-Lu, also called rare earth metals Actinid ...
... Group VIIIA: noble gases Transition Metals: Group B elements (in middle of the Periodic Table) The behavior and properties of transition metals is not very predictable. Inner Transition Elements (beneath the main body of Periodic Table) Lanthanide series: Ce-Lu, also called rare earth metals Actinid ...
d. Group 1
... a. They have no valence electrons b. They have full electron orbitals c. They have the most protons d. They have low ionization energy ...
... a. They have no valence electrons b. They have full electron orbitals c. They have the most protons d. They have low ionization energy ...
Periodic Table of Elements
... _______________ metals are never found as free elements in nature. Elements that are ________________ bond easily with other elements to make ____________. All atoms, except hydrogen, want to have _______ electrons in their outermost energy level. This is called the rule of ...
... _______________ metals are never found as free elements in nature. Elements that are ________________ bond easily with other elements to make ____________. All atoms, except hydrogen, want to have _______ electrons in their outermost energy level. This is called the rule of ...
Chemistry Chapter 5 The Periodic Law
... and their meaning. Know the definitions of ionization energy, electronegativity, and atomic radius and their trends both across a period and down a group. Know the definition of valence electrons & how to find their number in s & p groups. ...
... and their meaning. Know the definitions of ionization energy, electronegativity, and atomic radius and their trends both across a period and down a group. Know the definition of valence electrons & how to find their number in s & p groups. ...
periodictrendsss - rlsciencecurriculum
... READ THE FOLLOWING BEFORE MOVING ON TO PART IV: When elements are listed in order by their atomic numbers and grouped according to similar properties, they form seven horizontal rows called periods. Each vertical column in the table contains elements with similar properties. These are called groups ...
... READ THE FOLLOWING BEFORE MOVING ON TO PART IV: When elements are listed in order by their atomic numbers and grouped according to similar properties, they form seven horizontal rows called periods. Each vertical column in the table contains elements with similar properties. These are called groups ...
vocab - SALAZAR!!
... Sentence: The Lanthanide series is the second row from the bottom. 6. Actinide series- The actinide series is much different. They are all radioactive and some are not found in nature. Sentence: The Actinide series is very reactive. 7. Noble Gas- The noble gases make a group of chemical elements wit ...
... Sentence: The Lanthanide series is the second row from the bottom. 6. Actinide series- The actinide series is much different. They are all radioactive and some are not found in nature. Sentence: The Actinide series is very reactive. 7. Noble Gas- The noble gases make a group of chemical elements wit ...
The Periodic Table
... used atomic number instead of mass. Periodic law: properties of elements are periodic functions of atomic numbers. ...
... used atomic number instead of mass. Periodic law: properties of elements are periodic functions of atomic numbers. ...
Periodic Table HW Unit
... Elements can be differentiated by chemical properties. Chemical properties describe how an element behaves during a chemical reaction. Some elements exist in two or more forms in the same phase. These ...
... Elements can be differentiated by chemical properties. Chemical properties describe how an element behaves during a chemical reaction. Some elements exist in two or more forms in the same phase. These ...
PROFESSIONAL LEARNING COMMUNITY MODEL FOR ENTRY
... Prominent groups include alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, and noble gases. Regions of the periodic table are also broken up into two different regions: main group (or representative) elements and transition elements. An 'unknown' element's properties can be identified by examining the ...
... Prominent groups include alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, and noble gases. Regions of the periodic table are also broken up into two different regions: main group (or representative) elements and transition elements. An 'unknown' element's properties can be identified by examining the ...
hc1(5)notes
... • Atoms tend to be smaller the farther to the right they are found across a period. • The trend to smaller atoms across a period is caused by the (increasing / decreasing) positive charge of the nucleus, which attracts electrons toward the nucleus. • Atoms tend to be larger the farther down in a gro ...
... • Atoms tend to be smaller the farther to the right they are found across a period. • The trend to smaller atoms across a period is caused by the (increasing / decreasing) positive charge of the nucleus, which attracts electrons toward the nucleus. • Atoms tend to be larger the farther down in a gro ...
The Periodic Law
... Hydrogen and Helium • Hydrogen’s properties are not similar to any of the other groups. • Can be placed in group one because it has one valance electron ...
... Hydrogen and Helium • Hydrogen’s properties are not similar to any of the other groups. • Can be placed in group one because it has one valance electron ...
Students should be able to describe
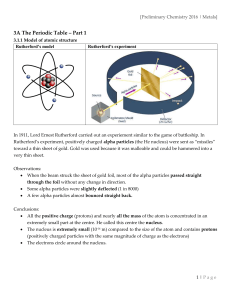
... Part 1) A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes 1) Atoms, elements and compounds All substances are made of atoms. An atom is the smallest part of an element that can exist. Atoms of each element are represented by a chemical symbol, e.g. O represent ...
... Part 1) A simple model of the atom, symbols, relative atomic mass, electronic charge and isotopes 1) Atoms, elements and compounds All substances are made of atoms. An atom is the smallest part of an element that can exist. Atoms of each element are represented by a chemical symbol, e.g. O represent ...
Biology - Mr. Julien`s Homepage
... 2. Biological, chemical, and physical properties of matter result from the ability of atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. As a basis for understanding this concept: g.*Students know how electronegativity and ionization energy r ...
... 2. Biological, chemical, and physical properties of matter result from the ability of atoms to form bonds from electrostatic forces between electrons and protons and between atoms and molecules. As a basis for understanding this concept: g.*Students know how electronegativity and ionization energy r ...
Periodic Table Virtual Activity http://my.uzinggo.com/cplogin/ The
... checkmark. This is a 5 question quiz. Do the quiz. Place your answers and your score here: ___________________________________________________ Part 4: General structure of the periodic table 1. Where are metals and nonmetals located on the periodic table? 2. Why are the elements on the far side (las ...
... checkmark. This is a 5 question quiz. Do the quiz. Place your answers and your score here: ___________________________________________________ Part 4: General structure of the periodic table 1. Where are metals and nonmetals located on the periodic table? 2. Why are the elements on the far side (las ...
Name
... (1) They are determined by the number of neutrons. (2) They are determined by the number of electrons in the first principal energy level. (3) They change in a generally systematic manner. (4) They change in a random, unpredictable manner. ___6. Which statement describes the elements in Period 3? (1 ...
... (1) They are determined by the number of neutrons. (2) They are determined by the number of electrons in the first principal energy level. (3) They change in a generally systematic manner. (4) They change in a random, unpredictable manner. ___6. Which statement describes the elements in Period 3? (1 ...
The Periodic Table
... 5. The nobel gases are found in group 18. Their outer energy level is filled, and they are very nonreactive, colorless gases. Shade the nobel gases red. 6. Halogens have seven electrons in the outer shell. They are located in group 17 on the periodic table. Halogens react with metals to form salts. ...
... 5. The nobel gases are found in group 18. Their outer energy level is filled, and they are very nonreactive, colorless gases. Shade the nobel gases red. 6. Halogens have seven electrons in the outer shell. They are located in group 17 on the periodic table. Halogens react with metals to form salts. ...
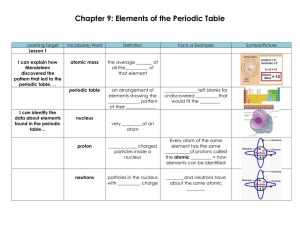
Chapter 9: Elements of the Periodic Table
... The properties of an element can be ________________ from its ________________ on the periodic table. ...
... The properties of an element can be ________________ from its ________________ on the periodic table. ...
Periodic Table
... electron shells , and so have a tendency to form a singlycharged negative ion. This negative ion is referred to as a halide ion; salts For other meanings of the word salt see salt (disambiguation In chemistry, a salt is a composed of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, so that ...
... electron shells , and so have a tendency to form a singlycharged negative ion. This negative ion is referred to as a halide ion; salts For other meanings of the word salt see salt (disambiguation In chemistry, a salt is a composed of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, so that ...
Topic 5: The periodic Table
... • The nucleus contains the neutrons and protons of the atom • The surrounding electron “cloud” consists of energy levels (a.k.a. orbitals or shells). Electrons are spread out across the energy levels • The outer energy level of the atom is called the valence shell. The electrons that live in the val ...
... • The nucleus contains the neutrons and protons of the atom • The surrounding electron “cloud” consists of energy levels (a.k.a. orbitals or shells). Electrons are spread out across the energy levels • The outer energy level of the atom is called the valence shell. The electrons that live in the val ...
PreAP Chemistry
... _______________ are elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. _______________ _______________ are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. _______________ _______________ metals are in g ...
... _______________ are elements that are generally shiny when smooth and clean, solid at room temperature, and good conductors of heat and electricity. _______________ _______________ are all the elements in group 1 except hydrogen, and are very reactive. _______________ _______________ metals are in g ...
chemistry chapter 11 & 12
... – React readily with halogens to form common salts • Example: NaCl (table salt) – React readily with water to form basic solutions (alkali), hydrogen and Energy. ...
... – React readily with halogens to form common salts • Example: NaCl (table salt) – React readily with water to form basic solutions (alkali), hydrogen and Energy. ...
CH 6: The Periodic Table
... • Chemists had been looking for a method to classify the elements. • In 1829, the German chemist J.W. Döbereiner observed that several elements could be classified into groups of three, or triads. • All three elements in a triad showed very similar chemical properties and an orderly trend in physica ...
... • Chemists had been looking for a method to classify the elements. • In 1829, the German chemist J.W. Döbereiner observed that several elements could be classified into groups of three, or triads. • All three elements in a triad showed very similar chemical properties and an orderly trend in physica ...