C Carbon Cu Copper
... Atoms bond until this level is complete. Atoms with few valence electrons lose them during bonding. Atoms with 6, 7, or 8 valence electrons gain electrons during bonding. ...
... Atoms bond until this level is complete. Atoms with few valence electrons lose them during bonding. Atoms with 6, 7, or 8 valence electrons gain electrons during bonding. ...
File - McArthur Media
... most familiar: copper, tin, zinc, iron, nickel, gold, and silver. • They are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
... most familiar: copper, tin, zinc, iron, nickel, gold, and silver. • They are good conductors of heat and electricity. ...
Notes - RCSD
... Group 18 is called the Noble Gases. These gases are completely unreactive (they do not make compounds with any other elements). The large block of elements in the middle of the Periodic Table is called the Transition Metals. These metals are very good conductors and are not very reactive, which ...
... Group 18 is called the Noble Gases. These gases are completely unreactive (they do not make compounds with any other elements). The large block of elements in the middle of the Periodic Table is called the Transition Metals. These metals are very good conductors and are not very reactive, which ...
Ch. 14 notes (teacher)3
... tend to __________ e-’s anyway, and this makes them highly ________________ attracted to e-’s when forming a chemical bond. ...
... tend to __________ e-’s anyway, and this makes them highly ________________ attracted to e-’s when forming a chemical bond. ...
Elements of Chemistry The Periodic Table ES14 - rdt-maps-lab
... rules, but their electrons are configured differently. All of the elements in this block have the same number of valence electrons because electrons are added to interior shells instead of the valence shell. 8. Identify the following families on the periodic table, and assign one to each classroom g ...
... rules, but their electrons are configured differently. All of the elements in this block have the same number of valence electrons because electrons are added to interior shells instead of the valence shell. 8. Identify the following families on the periodic table, and assign one to each classroom g ...
Atoms in the Periodic Table
... They are never found uncombined in nature. They have two valence electrons. Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
... They are never found uncombined in nature. They have two valence electrons. Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
Chapter 6 Review
... ________ 10. In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of atomic number. ________ 11. There are six periods in a periodic table. ________ 12. Most of the elements in the periodic table are metals. ________ 13. The elements within a period have similar properties. ...
... ________ 10. In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of atomic number. ________ 11. There are six periods in a periodic table. ________ 12. Most of the elements in the periodic table are metals. ________ 13. The elements within a period have similar properties. ...
Section 15.1
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
Section 12.3
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
The History of the Modern Periodic Table
... Metals • hard, shiny (lustrous), good conductor, loses e- to form compounds, usually 2 or less ein the outer energy level • malleable – hammered into sheets • ductile – drawn into wires ...
... Metals • hard, shiny (lustrous), good conductor, loses e- to form compounds, usually 2 or less ein the outer energy level • malleable – hammered into sheets • ductile – drawn into wires ...
Writing and Naming Chemical Formulas
... Metals lose electrons, so they form cations Non-metals gain electrons, so they form anions Can be determined by looking at the Periodic Table Since ions are formed by losing or gaining valence electrons, the group number also represents the charge the elements in that group like to form! ...
... Metals lose electrons, so they form cations Non-metals gain electrons, so they form anions Can be determined by looking at the Periodic Table Since ions are formed by losing or gaining valence electrons, the group number also represents the charge the elements in that group like to form! ...
Groups and Families
... Shellat (Valence Electrons): 1 or 2 bottom of periodic Actinides: radioactive table Less to keep table (unstable) Elements after Reactivity: reactive than from being toooccur wide. plutonium do not in alkaline-earth nature in similar a lab) Each(created row has metals properties Other Shared Propert ...
... Shellat (Valence Electrons): 1 or 2 bottom of periodic Actinides: radioactive table Less to keep table (unstable) Elements after Reactivity: reactive than from being toooccur wide. plutonium do not in alkaline-earth nature in similar a lab) Each(created row has metals properties Other Shared Propert ...
Chapter 5 Notes
... will readily react with metals to form salts. Group 18 contain the NOBLE GASES. Noble gases are unreactive because electrons from the gases fill the p orbitals. The s-block and p-block elements make up the MAIN GROUP elements. D-block The metals in groups 3-12 make up the d-block. These metals are c ...
... will readily react with metals to form salts. Group 18 contain the NOBLE GASES. Noble gases are unreactive because electrons from the gases fill the p orbitals. The s-block and p-block elements make up the MAIN GROUP elements. D-block The metals in groups 3-12 make up the d-block. These metals are c ...
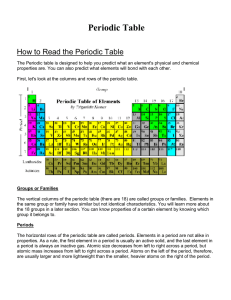
How to Read the Periodic Table
... like to form compounds with each other. These compounds are called ionic compounds. When two or more nonmetals bond with each other, they form a covalent compound. Metalloids Elements on both sides of the zigzag line have properties of both metals and nonmetals. These elements are called metalloids. ...
... like to form compounds with each other. These compounds are called ionic compounds. When two or more nonmetals bond with each other, they form a covalent compound. Metalloids Elements on both sides of the zigzag line have properties of both metals and nonmetals. These elements are called metalloids. ...
Document
... consider wave mechanics. The 4s orbital is lower in energy than the 3d before Sc because the electrons in a 4s orbital can be closer to the nucleus. Remember that S orbitals look like a series of rings. There is a ring relatively close to the nucleus where an electron might be found. We say that the ...
... consider wave mechanics. The 4s orbital is lower in energy than the 3d before Sc because the electrons in a 4s orbital can be closer to the nucleus. Remember that S orbitals look like a series of rings. There is a ring relatively close to the nucleus where an electron might be found. We say that the ...
Atomic Number - Mrs. McGee`s Class
... • They are never found uncombined in nature. • They have two valence electrons. • Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
... • They are never found uncombined in nature. • They have two valence electrons. • Alkaline earth metals include magnesium and calcium, among others. ...
Parts of the Periodic Table
... • Alkaline Earth Metals are harder, denser, and stronger than alkali metals. They also have higher melting points. (Remember: Melting Point is an intensive property. It stays the same, no matter how much of a substance you have.) • Although less reactive than alkali metals, they are still too react ...
... • Alkaline Earth Metals are harder, denser, and stronger than alkali metals. They also have higher melting points. (Remember: Melting Point is an intensive property. It stays the same, no matter how much of a substance you have.) • Although less reactive than alkali metals, they are still too react ...
Full Chapter - CPO Science
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
Periodic Table - Marian High School
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
... Remember, the atomic number is the number of protons all atoms of that element have in their nuclei. If the atom is neutral, it will have the same number of electrons as protons. ...
Click Here
... The size of an anion will be larger than that of the parent atom because the addition of one or more electrons would result in increased repulsion among the electrons and a decrease in effective nuclear charge When we find some atoms and ions which contain the same number of electrons, we call them ...
... The size of an anion will be larger than that of the parent atom because the addition of one or more electrons would result in increased repulsion among the electrons and a decrease in effective nuclear charge When we find some atoms and ions which contain the same number of electrons, we call them ...
orbital form the s block (groups 1 and 2). Elements in
... electrons in a chemical bond, depends on the dimension of a given atom, on the number of valence electrons and on the nuclear charge. More electronegative elements attract electrons more strongly than the less electronegative ones. Electronegativity increases from left to right across a period and d ...
... electrons in a chemical bond, depends on the dimension of a given atom, on the number of valence electrons and on the nuclear charge. More electronegative elements attract electrons more strongly than the less electronegative ones. Electronegativity increases from left to right across a period and d ...
Ch 5 Notes
... (shiny), conductive (heat and electricity), malleable (bendable), ductile (stretchable), high density, high melting point • Chemical Properties: Most will react with oxygen ...
... (shiny), conductive (heat and electricity), malleable (bendable), ductile (stretchable), high density, high melting point • Chemical Properties: Most will react with oxygen ...