Document
... • The Periodic Table is broken up in which 3 groups? (two answers) • Elements in a group have what kind of chemical properties? • Mendeleev arranged the Periodic Table by? • Today’s Periodic Table is arranged by? • Know how to read the Periodic Table. • Be able to give the atomic mass, atomic number ...
... • The Periodic Table is broken up in which 3 groups? (two answers) • Elements in a group have what kind of chemical properties? • Mendeleev arranged the Periodic Table by? • Today’s Periodic Table is arranged by? • Know how to read the Periodic Table. • Be able to give the atomic mass, atomic number ...
Review Topic 3: Elements, Radioactivity, and the Periodic Table
... C 4. How does the radioactive isotope C14 differ from its stable counterpart C12? a. It has a different number of protons and two less neutrons than C12. b. It has the same number of protons and two more electrons than C12. c. It has the same number of protons but two more neutrons than C1 ...
... C 4. How does the radioactive isotope C14 differ from its stable counterpart C12? a. It has a different number of protons and two less neutrons than C12. b. It has the same number of protons and two more electrons than C12. c. It has the same number of protons but two more neutrons than C1 ...
File
... solids and liquids, g/L for gases. b. Dashed lines for a property indicate that data is available. Some elements, for example, may not form a compound with hydrogen. 3. Working together, discuss the possibilities for arrangement of the element cards with all members of the group, and look for a logi ...
... solids and liquids, g/L for gases. b. Dashed lines for a property indicate that data is available. Some elements, for example, may not form a compound with hydrogen. 3. Working together, discuss the possibilities for arrangement of the element cards with all members of the group, and look for a logi ...
Instructional-Objectives
... 3. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table 3.1 Internal Structure of an Atom Summarize the experimental basis for the discovery of charged particles and the nucleus. Describe the subatomic particles and how they arranged in the internal structure of the atom. Describe the basic properties of p ...
... 3. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table 3.1 Internal Structure of an Atom Summarize the experimental basis for the discovery of charged particles and the nucleus. Describe the subatomic particles and how they arranged in the internal structure of the atom. Describe the basic properties of p ...
Instructional Objectives 3. Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... • Summarize the experimental basis for the discovery of charged particles and the nucleus. • Describe the subatomic particles and how they arranged in the internal structure of the atom. • Describe the basic properties of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 3.2 Atomic Number and Mass Number 3.2 Desc ...
... • Summarize the experimental basis for the discovery of charged particles and the nucleus. • Describe the subatomic particles and how they arranged in the internal structure of the atom. • Describe the basic properties of protons, neutrons, and electrons. 3.2 Atomic Number and Mass Number 3.2 Desc ...
module-21 (worksheet-1)
... 6) Which of the following statements is not a correct statement about the trends when going from left to right across the periods of Periodic Table. (a) The elements become less metallic in nature. (b) The number of valence electrons increases. (c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily. (d) The ...
... 6) Which of the following statements is not a correct statement about the trends when going from left to right across the periods of Periodic Table. (a) The elements become less metallic in nature. (b) The number of valence electrons increases. (c) The atoms lose their electrons more easily. (d) The ...
Unit Expectations – Periodic Table
... SWBAT - Identify the number of valence electrons, whether the elements would gain or lose electrons and give the oxidation number / charge. Students will also be able to differentiate between oxidation number and charge in words and through symbols using elements.; C4.9x Electron Energy Levels The r ...
... SWBAT - Identify the number of valence electrons, whether the elements would gain or lose electrons and give the oxidation number / charge. Students will also be able to differentiate between oxidation number and charge in words and through symbols using elements.; C4.9x Electron Energy Levels The r ...
Ch 6 - Midway ISD
... according to atomic number • Periodic Law – the periodic repetition of chemical and physical properties of elements when they are arranged by increasing atomic number ...
... according to atomic number • Periodic Law – the periodic repetition of chemical and physical properties of elements when they are arranged by increasing atomic number ...
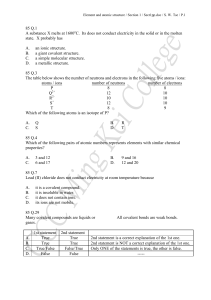
85 Q.1 A substance X melts at 1600oC. Its does
... (3) it is non-conductor of electricity in the solid state. A. (1) only B. (3) only C. (1) and (2) only D. (2) and (3) only 86 Q.48 Astatine (At) is a halogen at the bottom of group VII in the Periodic Table. From knowledge of trends in periodicity, which of the following predictions is UNLIKELY? A. ...
... (3) it is non-conductor of electricity in the solid state. A. (1) only B. (3) only C. (1) and (2) only D. (2) and (3) only 86 Q.48 Astatine (At) is a halogen at the bottom of group VII in the Periodic Table. From knowledge of trends in periodicity, which of the following predictions is UNLIKELY? A. ...
Unit 1 Module 3 The Periodic Table
... • End-of-module practice examination questions have been selected to show you the types of question that may appear in your examination. ...
... • End-of-module practice examination questions have been selected to show you the types of question that may appear in your examination. ...
THE MINISTRY OF HIGHER AND SECONDARY SPECIAL
... 2. They both constructed their tables … a similar manner. 3. Modern tables have progressively longer periods further … the table. 4. The first was … leave gaps in the table. 5. The second decision was … occasionally ignore the order suggested … the atomic weights and switch adjacent elements. ...
... 2. They both constructed their tables … a similar manner. 3. Modern tables have progressively longer periods further … the table. 4. The first was … leave gaps in the table. 5. The second decision was … occasionally ignore the order suggested … the atomic weights and switch adjacent elements. ...
Chemistry Chapter 5 The Periodic Law
... what groups of elements have been added to it. Know the groups and names and unique properties of the alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. Know the definition of the periodic law, periods, groups. Identify the period & grou ...
... what groups of elements have been added to it. Know the groups and names and unique properties of the alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, halogens, noble gases, transition metals, lanthanides, and actinides. Know the definition of the periodic law, periods, groups. Identify the period & grou ...
Physical Science Comprehensive Fall 2010 SAMPLE QUESTIONS
... 1. Most of the elements in the periodic table can be described as: A. metals. B. nonmetals. C. metalloids. D. halogens. 2. The vertical columns of the periodic table are called: A. periods. B. groups. C. halogens. D. isotopes. 3. Horizontal rows on the periodic table are called: A. periods. B. group ...
... 1. Most of the elements in the periodic table can be described as: A. metals. B. nonmetals. C. metalloids. D. halogens. 2. The vertical columns of the periodic table are called: A. periods. B. groups. C. halogens. D. isotopes. 3. Horizontal rows on the periodic table are called: A. periods. B. group ...
Inorganic Chemistry ELEMENTS AND
... Chemical Bond : Chemical bond may be defined as the attractive force that binds together the constituent atoms in a molecule. Following are some different types of chemical bonds which usually occur in various molecules. (i) Electrovalent bond (Ionic bond) : This type of bond is formed by transfer o ...
... Chemical Bond : Chemical bond may be defined as the attractive force that binds together the constituent atoms in a molecule. Following are some different types of chemical bonds which usually occur in various molecules. (i) Electrovalent bond (Ionic bond) : This type of bond is formed by transfer o ...
Powerpoint for Periodicity and Density
... determined the actual nuclear charge (atomic number) of the elements*. He rearranged the elements in order of increasing atomic number. ...
... determined the actual nuclear charge (atomic number) of the elements*. He rearranged the elements in order of increasing atomic number. ...
Periodicity PPt
... determined the actual nuclear charge (atomic number) of the elements*. He rearranged the elements in order of increasing atomic number. ...
... determined the actual nuclear charge (atomic number) of the elements*. He rearranged the elements in order of increasing atomic number. ...
SrF 2(s)
... Lesson #R7: Review of Chemical Reactions A. For each of the following reactions, identify the reaction type and balance the reaction. ________________1. _____Al(s) + _____O2(g) ...
... Lesson #R7: Review of Chemical Reactions A. For each of the following reactions, identify the reaction type and balance the reaction. ________________1. _____Al(s) + _____O2(g) ...
Lab 6
... In case of the liquid state, the constancy of the liquid material should be observed (mobile, oily or viscous). Also, determine if the unknown is true liquid or solution by adding anhydrous copper sulphate placed in a watch glass. The color will not be changed with true liquids while with solutions ...
... In case of the liquid state, the constancy of the liquid material should be observed (mobile, oily or viscous). Also, determine if the unknown is true liquid or solution by adding anhydrous copper sulphate placed in a watch glass. The color will not be changed with true liquids while with solutions ...
Standards Practice
... 6. In the periodic table, metals are best described as located A. on the left side. B. on the right side. D. in the first two rows. C. in the last two columns. 7. In the periodic table, which column (group) contains the most nonmetals? ...
... 6. In the periodic table, metals are best described as located A. on the left side. B. on the right side. D. in the first two rows. C. in the last two columns. 7. In the periodic table, which column (group) contains the most nonmetals? ...
TIPS for NET-IONIC EQUATIONS A.P. Chemistry (long form)
... 4. manganese(II) nitrate solution is mixed with sodium hydroxide solution 5. solutions of zinc sulfate and sodium phosphate are mixed 6. solutions of silver nitrate and sodium chromate are mixed 7. dilute solutions of lithium hydroxide and hydrobromic acid are mixed 8. a solution of ammonia is added ...
... 4. manganese(II) nitrate solution is mixed with sodium hydroxide solution 5. solutions of zinc sulfate and sodium phosphate are mixed 6. solutions of silver nitrate and sodium chromate are mixed 7. dilute solutions of lithium hydroxide and hydrobromic acid are mixed 8. a solution of ammonia is added ...
Ordinary Level - State Examination Commission
... Figure 14 shows the arrangement of the outer electrons in a molecule of ammonia. How many (i) bond pairs, (ii) lone pairs, of electrons are there in the outer shell of the nitrogen atom in an ammonia molecule? The number of bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons in the outer shell of the central ato ...
... Figure 14 shows the arrangement of the outer electrons in a molecule of ammonia. How many (i) bond pairs, (ii) lone pairs, of electrons are there in the outer shell of the nitrogen atom in an ammonia molecule? The number of bond pairs and lone pairs of electrons in the outer shell of the central ato ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... • Atoms tend to be smaller the farther to the right they are found across a period. • The trend to smaller atoms across a period is caused by the increasing positive charge of the nucleus, which attracts electrons toward the nucleus. • Atoms tend to be larger the farther down in a group they are fou ...
... • Atoms tend to be smaller the farther to the right they are found across a period. • The trend to smaller atoms across a period is caused by the increasing positive charge of the nucleus, which attracts electrons toward the nucleus. • Atoms tend to be larger the farther down in a group they are fou ...
Chemistry 4.2
... conductors of heat and electric current. • Most nonmetals are gases at room temperature. • A few nonmetals are solids, such as sulfur and phosphorus. • One nonmetal, bromine, is a dark-red liquid. ...
... conductors of heat and electric current. • Most nonmetals are gases at room temperature. • A few nonmetals are solids, such as sulfur and phosphorus. • One nonmetal, bromine, is a dark-red liquid. ...