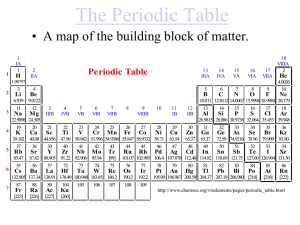
10C The Periodic Table
... 6. What does the atomic number tell you about an element? Symbol and atomic mass: For each of the following, write the element name that corresponds to the symbol. In addition, write the atomic mass for each element. 7. Fe ...
... 6. What does the atomic number tell you about an element? Symbol and atomic mass: For each of the following, write the element name that corresponds to the symbol. In addition, write the atomic mass for each element. 7. Fe ...
Uint one - pisscience
... -The number of elements until now is 118 elements .92 elements are natural and the rest are prepared artificially. -It consists of 7 horizontal periods and 18 groups. -The elements are classified into 4 blocks: * S-block elements are located on the left side and consists of two groups. *P-block elem ...
... -The number of elements until now is 118 elements .92 elements are natural and the rest are prepared artificially. -It consists of 7 horizontal periods and 18 groups. -The elements are classified into 4 blocks: * S-block elements are located on the left side and consists of two groups. *P-block elem ...
Wizard Test Maker
... 56. When heat energy is lost by a pure substance at its freezing point, its potential energy 1) decreases 3) remains the same 2) increases 57. At STP, which of the following gases will diffuse most rapidly? 1) hydrogen 3) fluorine 2) nitrogen 4) oxygen ...
... 56. When heat energy is lost by a pure substance at its freezing point, its potential energy 1) decreases 3) remains the same 2) increases 57. At STP, which of the following gases will diffuse most rapidly? 1) hydrogen 3) fluorine 2) nitrogen 4) oxygen ...
Periodic_Tendancies
... Down the Periodic Table •Family: Are arranged vertically down the periodic table (columns or group, 1- 18 or 1-8 A,B) •These elements have the same number electrons in the outer most shells, the valence shell. ...
... Down the Periodic Table •Family: Are arranged vertically down the periodic table (columns or group, 1- 18 or 1-8 A,B) •These elements have the same number electrons in the outer most shells, the valence shell. ...
STOICHIOMETRY:
... chemical reactions. Since we now know the mass of a mole of any compound, we can predict the correct quantities of reactants required to carry out a reaction. For example, 4.04 g (2 mol) of hydrogen will react completely with 32.00 g (1 mol) of oxygen gas to produce 36.02 g (2 mol) of water. ...
... chemical reactions. Since we now know the mass of a mole of any compound, we can predict the correct quantities of reactants required to carry out a reaction. For example, 4.04 g (2 mol) of hydrogen will react completely with 32.00 g (1 mol) of oxygen gas to produce 36.02 g (2 mol) of water. ...
03 Chapter 2 Atomic Structure Power point Periodic Table
... Group trend for Alkali metals – Increases as you move down group 1 in the periodic table – Since alkali metals are more likely to lose an electron, the ones with the lowest 1st ionization energy are the most reactive since they require the least amount of energy to lose a valence electron. ...
... Group trend for Alkali metals – Increases as you move down group 1 in the periodic table – Since alkali metals are more likely to lose an electron, the ones with the lowest 1st ionization energy are the most reactive since they require the least amount of energy to lose a valence electron. ...
Study Guide: Chemistry
... Characteristics of good fuel - Naturally occurs in large amount, non-toxic, easy to ignite, widely used, high heat output, does not produce too much waste when burnt Examples of Fossil Fuels - Oil, coal, natural gas ...
... Characteristics of good fuel - Naturally occurs in large amount, non-toxic, easy to ignite, widely used, high heat output, does not produce too much waste when burnt Examples of Fossil Fuels - Oil, coal, natural gas ...
summer fun - West Windsor-Plainsboro Regional School District
... The solubility of a solute is the amount that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at a given temperature. For example, the solubility of lead (II) nitrate is 56 g/100 mL at 20oC. The solubilities of ionic solids in water vary over a wide range of values. For convenience, we divide compou ...
... The solubility of a solute is the amount that can be dissolved in a given quantity of solvent at a given temperature. For example, the solubility of lead (II) nitrate is 56 g/100 mL at 20oC. The solubilities of ionic solids in water vary over a wide range of values. For convenience, we divide compou ...
Periodic Table Study Guide
... 1) How did Mendeleev originally organize his periodic table? 2) What made Mendeleev’s periodic table better than prior attempts to organize the elements? 3) What is the main difference between the modern periodic table and the one Mendeleev came up with? 4) Why do we call it the “periodic” table? 5) ...
... 1) How did Mendeleev originally organize his periodic table? 2) What made Mendeleev’s periodic table better than prior attempts to organize the elements? 3) What is the main difference between the modern periodic table and the one Mendeleev came up with? 4) Why do we call it the “periodic” table? 5) ...
Introduction to the Periodic Table
... Group 1: ______________________________ Group 2: ______________________________ Group 3-12: ____________________________ Group 17: ______________________________ Group 18: ______________________________ ___________________________ on the bottom called Lanthanides and Actinides How else is it or ...
... Group 1: ______________________________ Group 2: ______________________________ Group 3-12: ____________________________ Group 17: ______________________________ Group 18: ______________________________ ___________________________ on the bottom called Lanthanides and Actinides How else is it or ...
Packet 4 - 16-17 Periodic Table
... Two or more forms of the same element that differ in their molecules. Allotropes have different properties. Oxygen has 2 allotropes: O2 is the oxygen we breathe, and O3 makes up the ozone layer. Carbon has many different allotropes which differ in arrangement of atoms • Diamond: every carbon bonded ...
... Two or more forms of the same element that differ in their molecules. Allotropes have different properties. Oxygen has 2 allotropes: O2 is the oxygen we breathe, and O3 makes up the ozone layer. Carbon has many different allotropes which differ in arrangement of atoms • Diamond: every carbon bonded ...
BOOKLETColoring-the-Periodic-Table-Families
... Arrangements of elements in order of increasing ...
... Arrangements of elements in order of increasing ...
Slide 1
... • Noble Gases = Inert gases = very little reactivity Even though it is not possible to consider any trends in chemical properties of the noble gases it is possible to study trends in their physical properties ...
... • Noble Gases = Inert gases = very little reactivity Even though it is not possible to consider any trends in chemical properties of the noble gases it is possible to study trends in their physical properties ...
Chemical Reactions and The Mole
... The Mole: By definition an AMU is 1/12th the mass of a C-12 atom. The unit of mass needs a reference point and a specific amount of matter to which all other matter can be referenced. This is a standard, as C-12 is very abundant, but this mass is very small, too small to work with. Generally, you w ...
... The Mole: By definition an AMU is 1/12th the mass of a C-12 atom. The unit of mass needs a reference point and a specific amount of matter to which all other matter can be referenced. This is a standard, as C-12 is very abundant, but this mass is very small, too small to work with. Generally, you w ...
The Mole - Humble ISD
... the moles of one chemical from the given amount of a different chemical Example: How many moles of chlorine are needed to react with 5 moles of sodium (without any sodium left over)? 2 Na + Cl2 2 NaCl 5 moles Na 1 mol Cl2 2 mol Na ...
... the moles of one chemical from the given amount of a different chemical Example: How many moles of chlorine are needed to react with 5 moles of sodium (without any sodium left over)? 2 Na + Cl2 2 NaCl 5 moles Na 1 mol Cl2 2 mol Na ...
Week 21 Lessons - Highline Public Schools
... - These observations, we can see that elements are different. - In the “Support claim with evidence” section, discuss the different physical and chemical properties. - In the “Possible Scientific Explanation”, talk about the different properties of atoms. - You may use other data for top marks. Skil ...
... - These observations, we can see that elements are different. - In the “Support claim with evidence” section, discuss the different physical and chemical properties. - In the “Possible Scientific Explanation”, talk about the different properties of atoms. - You may use other data for top marks. Skil ...
Periodic classificatiion of elements
... 26. What happens to valency electrons when we move from left to right in a period? A. Valence electrons increase by one unit as we move from left to right in a period. 27. Write the formula on which maximum number of electrons in a shell depends? A. 2n2 (where n is number of given shell from nucleu ...
... 26. What happens to valency electrons when we move from left to right in a period? A. Valence electrons increase by one unit as we move from left to right in a period. 27. Write the formula on which maximum number of electrons in a shell depends? A. 2n2 (where n is number of given shell from nucleu ...
Unit 3 - The Periodic Table
... Found in the ___________ of the periodic table (the D block) Form ___________________ in solution (ex: Cu is bright blue when dissolved in water) This concept is ALWAYS on the REGENTS EXAM!!! Tend to be _____________________ will lose electrons or gain them depending on what other ________ ...
... Found in the ___________ of the periodic table (the D block) Form ___________________ in solution (ex: Cu is bright blue when dissolved in water) This concept is ALWAYS on the REGENTS EXAM!!! Tend to be _____________________ will lose electrons or gain them depending on what other ________ ...
Chem Periodicity, Reactivity, Redox 2009 Yingxin
... makes it harder for the halogen to gain electrons as the forces of attraction between the nucleus and the electrons are not very high. Displacement reaction: More reactive halogen will displace less reactive one from an aqueous solution of its ions @ Eg Cl2 + 2KBr 2KCl + Br2 @ Solution will turn t ...
... makes it harder for the halogen to gain electrons as the forces of attraction between the nucleus and the electrons are not very high. Displacement reaction: More reactive halogen will displace less reactive one from an aqueous solution of its ions @ Eg Cl2 + 2KBr 2KCl + Br2 @ Solution will turn t ...
Electrons/Periodic Table Review Packet Name______________________________ Period_________
... 15. Which group tends to form +2 ions? ________________________________________________ 16. Which group tends to form -1 ions? _________________________________________________ 17. Which group tends not to form ions or react? _________________________________________ 18. Based on the concept of peri ...
... 15. Which group tends to form +2 ions? ________________________________________________ 16. Which group tends to form -1 ions? _________________________________________________ 17. Which group tends not to form ions or react? _________________________________________ 18. Based on the concept of peri ...
Describe the Periodic Table
... Atomic Symbol: 0The atomic symbol is one or two letters chosen to represent an element ("H" for "hydrogen," etc.). 0 These symbols are used every where in the world 0 Usually, a symbol is the abbreviation of the element or the abbreviated Latin name of the element. ...
... Atomic Symbol: 0The atomic symbol is one or two letters chosen to represent an element ("H" for "hydrogen," etc.). 0 These symbols are used every where in the world 0 Usually, a symbol is the abbreviation of the element or the abbreviated Latin name of the element. ...
Problem 5. The Second Law of thermodynamics
... point corresponding to the final state on the diagram will thus be approximately 0.1 + 3.4 = 3.5 kJ·mol–1. The ordinate is log p = 1.2. The ratio of the lengths of the line segments from this point to the borders of the phase coexistence curve (blue and red line segments in the figure below) is equa ...
... point corresponding to the final state on the diagram will thus be approximately 0.1 + 3.4 = 3.5 kJ·mol–1. The ordinate is log p = 1.2. The ratio of the lengths of the line segments from this point to the borders of the phase coexistence curve (blue and red line segments in the figure below) is equa ...
Ch. 4.3 – Distinguishing Among Atoms
... element, multiply the mass of each isotope by its percent relative abundance, expressed as a decimal, and then add the products. ...
... element, multiply the mass of each isotope by its percent relative abundance, expressed as a decimal, and then add the products. ...
Solutions (DOC format, upgraded July 20)
... point corresponding to the final state on the diagram will thus be approximately 0.1 + 3.4 = 3.5 kJ·mol–1. The ordinate is log p = 1.2. The ratio of the lengths of the line segments from this point to the borders of the phase coexistence curve (blue and red line segments in the figure below) is equa ...
... point corresponding to the final state on the diagram will thus be approximately 0.1 + 3.4 = 3.5 kJ·mol–1. The ordinate is log p = 1.2. The ratio of the lengths of the line segments from this point to the borders of the phase coexistence curve (blue and red line segments in the figure below) is equa ...
Problem 5. The Second Law of thermodynamics
... point corresponding to the final state on the diagram will thus be approximately 0.1 + 3.4 = 3.5 kJ·mol–1. The ordinate is log p = 1.2. The ratio of the lengths of the line segments from this point to the borders of the phase coexistence curve (blue and red line segments in the figure below) is equa ...
... point corresponding to the final state on the diagram will thus be approximately 0.1 + 3.4 = 3.5 kJ·mol–1. The ordinate is log p = 1.2. The ratio of the lengths of the line segments from this point to the borders of the phase coexistence curve (blue and red line segments in the figure below) is equa ...