The Periodic Table - Science
... Atomic Symbol: The atomic symbol is one or two letters chosen to represent an element ("H" for "hydrogen," etc.). These symbols are used every where in the world Usually, a symbol is the abbreviation of the element or the abbreviated Latin name of the element. ...
... Atomic Symbol: The atomic symbol is one or two letters chosen to represent an element ("H" for "hydrogen," etc.). These symbols are used every where in the world Usually, a symbol is the abbreviation of the element or the abbreviated Latin name of the element. ...
Unit 4 Pack
... Why is Si bigger than S (explain why – do not just write because it is further left!) Why is Se bigger than S? (explain why) Why is Cu2+ smaller than Cu? Identify the two ions that are most important in the human body. Where are they found? What is their function? Given Al, I and F a. Place them in ...
... Why is Si bigger than S (explain why – do not just write because it is further left!) Why is Se bigger than S? (explain why) Why is Cu2+ smaller than Cu? Identify the two ions that are most important in the human body. Where are they found? What is their function? Given Al, I and F a. Place them in ...
Periodic Trends 2015 0
... 1. How are elements arranged on the periodic table? ___________________________________________ 2. How is the periodic table similar to a grocery store? ________________________________________ 3. What is the main form of order in which the periodic table is based on? _________________________ 4. Al ...
... 1. How are elements arranged on the periodic table? ___________________________________________ 2. How is the periodic table similar to a grocery store? ________________________________________ 3. What is the main form of order in which the periodic table is based on? _________________________ 4. Al ...
MENDELEEV`S PERIODIC TABLE
... By the middle of the 19th century, scientists had discovered 63 elements. There was no system to classify them, so they arranged them alphabetically. Grouping them alphabetically, however, resulted in awkward groups (aluminum, a metal, would be grouped with argon, a gas). Scientists needed a way of ...
... By the middle of the 19th century, scientists had discovered 63 elements. There was no system to classify them, so they arranged them alphabetically. Grouping them alphabetically, however, resulted in awkward groups (aluminum, a metal, would be grouped with argon, a gas). Scientists needed a way of ...
mendeleev*s periodic table
... By the middle of the 19th century, scientists had discovered 63 elements. There was no system to classify them, so they arranged them alphabetically. Grouping them alphabetically, however, resulted in awkward groups (aluminum, a metal, would be grouped with argon, a gas). Scientists needed a way of ...
... By the middle of the 19th century, scientists had discovered 63 elements. There was no system to classify them, so they arranged them alphabetically. Grouping them alphabetically, however, resulted in awkward groups (aluminum, a metal, would be grouped with argon, a gas). Scientists needed a way of ...
CHEMISTRY SEPTEMBER 11, 2014
... – First Ionization Energy decreases from top to bottom of a Group. • Reason: As the atomic number increases in a Group, the number of electron shells increases. As more energy level is added, the valence electrons are further away from the nucleus. Thus, the electrons are further from the nucleus an ...
... – First Ionization Energy decreases from top to bottom of a Group. • Reason: As the atomic number increases in a Group, the number of electron shells increases. As more energy level is added, the valence electrons are further away from the nucleus. Thus, the electrons are further from the nucleus an ...
Unit 3 Exam Level Questions
... 1. A catalyst is used in the Haber Process. N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) Which of the following best describes the action of the catalyst? A Increases the rate of the forward reaction only B Increases the rate of the reverse reaction only C Increases the rate of both the forward and reverse reactions D Ch ...
... 1. A catalyst is used in the Haber Process. N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) Which of the following best describes the action of the catalyst? A Increases the rate of the forward reaction only B Increases the rate of the reverse reaction only C Increases the rate of both the forward and reverse reactions D Ch ...
CIS Exam Questions
... 1. A catalyst is used in the Haber Process. N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) Which of the following best describes the action of the catalyst? A Increases the rate of the forward reaction only B Increases the rate of the reverse reaction only C Increases the rate of both the forward and reverse reactions D Ch ...
... 1. A catalyst is used in the Haber Process. N2(g) + 3H2(g) 2NH3(g) Which of the following best describes the action of the catalyst? A Increases the rate of the forward reaction only B Increases the rate of the reverse reaction only C Increases the rate of both the forward and reverse reactions D Ch ...
CHAPTER 21 NONMETALLIC ELEMENTS AND THEIR COMPOUNDS
... The density of a gas depends on temperature, pressure, and the molar mass of the substance. When two gases are at the same pressure and temperature, the ratio of their densities should be the same as the ratio of their molar masses. The molar mass of ammonium chloride is 53.5 g/mol, and the ratio of ...
... The density of a gas depends on temperature, pressure, and the molar mass of the substance. When two gases are at the same pressure and temperature, the ratio of their densities should be the same as the ratio of their molar masses. The molar mass of ammonium chloride is 53.5 g/mol, and the ratio of ...
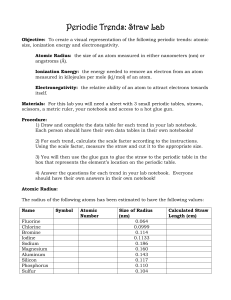
Periodic Trends: Straw Lab
... Objective: To create a visual representation of the following periodic trends: atomic size, ionization energy and electronegativity. Atomic Radius: the size of an atom measured in either nanometers (nm) or angstroms (Ǻ). Ionization Energy: the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom measure ...
... Objective: To create a visual representation of the following periodic trends: atomic size, ionization energy and electronegativity. Atomic Radius: the size of an atom measured in either nanometers (nm) or angstroms (Ǻ). Ionization Energy: the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom measure ...
FSN 1500 Week 7 - Oakland Community College
... Organic Compounds Organic compounds - carbon-containing compounds where carbon forms the structural framework of the molecule Remember: to our knowledge all life on Earth is organic compound based! Millions of organic compounds exist; organic compounds are over 10X more abundant than all inorga ...
... Organic Compounds Organic compounds - carbon-containing compounds where carbon forms the structural framework of the molecule Remember: to our knowledge all life on Earth is organic compound based! Millions of organic compounds exist; organic compounds are over 10X more abundant than all inorga ...
Module-2-s-and-d-elements - Львівський національний медичний
... physical and chemical properties occur at specific intervals. These groups of elements with similar physical and chemical properties are called families, examples of which are the alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, rare earth elements, halogens, and the noble gases. When two atoms have the same a ...
... physical and chemical properties occur at specific intervals. These groups of elements with similar physical and chemical properties are called families, examples of which are the alkali metals, alkaline earth metals, rare earth elements, halogens, and the noble gases. When two atoms have the same a ...
Theoretical problems - Scheikundeolympiade
... No intermolecular forces, ideal gas behaviour d) The compression ratio is pressure dependent. Consider the average separation between particles in a gas at different pressures (ranging from extremely low pressure to extremely high pressure), and the regions of the intermolecular potential that these ...
... No intermolecular forces, ideal gas behaviour d) The compression ratio is pressure dependent. Consider the average separation between particles in a gas at different pressures (ranging from extremely low pressure to extremely high pressure), and the regions of the intermolecular potential that these ...
Worksheet 1 - Oxidation/Reduction Reactions Oxidation number
... ___Br- + ___H+ + ___MnO4- ___Br2 + ___Mn2+ + ___H2O Which compound is the oxidizing agent? Which compound is the reducing agent? Notice that there are protons (H+) present in the reactants. This indicates that the reaction is carried out in an acidic solution. To carry this out in a basic solution ...
... ___Br- + ___H+ + ___MnO4- ___Br2 + ___Mn2+ + ___H2O Which compound is the oxidizing agent? Which compound is the reducing agent? Notice that there are protons (H+) present in the reactants. This indicates that the reaction is carried out in an acidic solution. To carry this out in a basic solution ...
Chapter 10 - Chemical Quantities
... molecular formulas of the compound, given the results of an analysis of a 310.8-g sample that reveals that the sample contains only boron (B) and iodine (I). The mass of the iodine in the sample is found to be 302.2 g. Ans: BI3 25. Calculate each of the following for the compound: ammonium sulfate, ...
... molecular formulas of the compound, given the results of an analysis of a 310.8-g sample that reveals that the sample contains only boron (B) and iodine (I). The mass of the iodine in the sample is found to be 302.2 g. Ans: BI3 25. Calculate each of the following for the compound: ammonium sulfate, ...
day4-periodictrends
... 3. Rank the following sets of elements in order of increasing electronegativity (small big). Set A: Bh, Mn, Re, Tc Set B: Sb, I, Ag, Ru Set C: Y, Ti, Sg, Ta 4. Rank the following sets of elements in order of decreasing electronegativity (big small). Set A: Cl, At, I, F, Br Set B: Te, Xe, Sn, In ...
... 3. Rank the following sets of elements in order of increasing electronegativity (small big). Set A: Bh, Mn, Re, Tc Set B: Sb, I, Ag, Ru Set C: Y, Ti, Sg, Ta 4. Rank the following sets of elements in order of decreasing electronegativity (big small). Set A: Cl, At, I, F, Br Set B: Te, Xe, Sn, In ...
How is the Periodic Table organized?
... • With the elements arranged by atomic number, their chemical and physical properties are found to show a repeating, or periodic, pattern. • Elements within a family have similar properties. ...
... • With the elements arranged by atomic number, their chemical and physical properties are found to show a repeating, or periodic, pattern. • Elements within a family have similar properties. ...
Chemistry - Sanskriti School
... Activities: i) Experiments will be performed to show that matter has particulate nature. ii) Experiments to show diffusion. 2. States of matter. Activities: i) To show that ink diffuses in water much faster than honey. ii) To show that gases are more compressible than liquids. 3. Inter conversion of ...
... Activities: i) Experiments will be performed to show that matter has particulate nature. ii) Experiments to show diffusion. 2. States of matter. Activities: i) To show that ink diffuses in water much faster than honey. ii) To show that gases are more compressible than liquids. 3. Inter conversion of ...
02_Atoms_AP015update
... The Charge cloud model: Nucleus containing Protons and neutrons Electrons circling rapidly around outside nucleus would appear as a cloud Protons Note: AMU = atomic mass unit Mass = 1.67262 x 10-24 g atoms so tiny, the gram is not a very convenient unit to ...
... The Charge cloud model: Nucleus containing Protons and neutrons Electrons circling rapidly around outside nucleus would appear as a cloud Protons Note: AMU = atomic mass unit Mass = 1.67262 x 10-24 g atoms so tiny, the gram is not a very convenient unit to ...
PREPARATION, STRUCTURAL STUDIES AND CHEMICAL
... 1. The first reported preparation of a hypervalent iodine (III) compound…………..……1 2. Structural types of hypervalent iodine compounds…………………………………….2 3. Common classes of hypervalent iodine(III) and (V) compounds…………………….. 4 4. Known classes of heterocyclic hypervalent iodine compounds………………..………5 5 ...
... 1. The first reported preparation of a hypervalent iodine (III) compound…………..……1 2. Structural types of hypervalent iodine compounds…………………………………….2 3. Common classes of hypervalent iodine(III) and (V) compounds…………………….. 4 4. Known classes of heterocyclic hypervalent iodine compounds………………..………5 5 ...
Redox - SAVE MY EXAMS!
... What happens when zinc foil is placed in an aqueous solution of copper(II) sulfate? ...
... What happens when zinc foil is placed in an aqueous solution of copper(II) sulfate? ...
Experimental skills and abilities
... 1 Some dyes have a greater solubility than others in the different solvents. The dyes which have moved the greatest distance have the greatest solubility in the solvents. Their Rf values are also greater. 2 The dye which was least soluble is the one which does not travel as far up the chromatogram ...
... 1 Some dyes have a greater solubility than others in the different solvents. The dyes which have moved the greatest distance have the greatest solubility in the solvents. Their Rf values are also greater. 2 The dye which was least soluble is the one which does not travel as far up the chromatogram ...
Question (1): Explain `Dobereiner`s Triads and its drawback. Answer
... shell and posses low ionisation energies. This makes them lose their electrons and become highly metallic. They are called alkalis because their hydroxides are strong alkalis. Examples: Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs and Fr are alkali metals. ...
... shell and posses low ionisation energies. This makes them lose their electrons and become highly metallic. They are called alkalis because their hydroxides are strong alkalis. Examples: Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs and Fr are alkali metals. ...
Periodic Table - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • Valence = outermost energy level in which contains electrons (in unexcited state). • Valence electrons are the electrons on the outermost energy level of the element. • The number of valence electrons determines the type of chemical reactions available to the element! ...
... • Valence = outermost energy level in which contains electrons (in unexcited state). • Valence electrons are the electrons on the outermost energy level of the element. • The number of valence electrons determines the type of chemical reactions available to the element! ...
Periodic Table - Doral Academy Preparatory
... • Valence = outermost energy level in which contains electrons (in unexcited state). • Valence electrons are the electrons on the outermost energy level of the element. • The number of valence electrons determines the type of chemical reactions available to the element! ...
... • Valence = outermost energy level in which contains electrons (in unexcited state). • Valence electrons are the electrons on the outermost energy level of the element. • The number of valence electrons determines the type of chemical reactions available to the element! ...