Study Guide for Electrons Mini-Test - seys
... burning and rusting are two familiar types of reactions involving oxygen) - carbon - compounds containing carbon = essential to living things - two forms of the elements = graphite (soft, slippery black material) and diamond (hard crystal) - sulfur = a bright yellow powder that can be mined from dep ...
... burning and rusting are two familiar types of reactions involving oxygen) - carbon - compounds containing carbon = essential to living things - two forms of the elements = graphite (soft, slippery black material) and diamond (hard crystal) - sulfur = a bright yellow powder that can be mined from dep ...
Chemistry - Higher tier - Paper 4 - Sample assessment material
... The Group 7 elements are known as the halogens. The halogens have similar chemical properties. Their physical properties vary with increasing atomic number. (a) ...
... The Group 7 elements are known as the halogens. The halogens have similar chemical properties. Their physical properties vary with increasing atomic number. (a) ...
Periodic Table Properties Notes s1
... – arranged known chemical elements in order of atomic mass – placed elements with similar properties in the same group He predicted the existence of unknown elements, and left spaces open in his periodic table for them. ...
... – arranged known chemical elements in order of atomic mass – placed elements with similar properties in the same group He predicted the existence of unknown elements, and left spaces open in his periodic table for them. ...
Unit 3 Homework Booklet
... Two chemicals A and B react in solution to form C. The reaction has an activation energy of 150 kJ mol-1. If hydrogen ions are used as a catalyst the activation energy is 50 kJ mol-1. The enthalpy change for the reaction is -125 kJ mol-1. Present this information as a potential energy diagram using ...
... Two chemicals A and B react in solution to form C. The reaction has an activation energy of 150 kJ mol-1. If hydrogen ions are used as a catalyst the activation energy is 50 kJ mol-1. The enthalpy change for the reaction is -125 kJ mol-1. Present this information as a potential energy diagram using ...
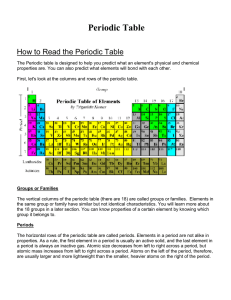
How to Read the Periodic Table
... Since metals tend to lose electrons and nonmetals tend to gain electrons, metals and nonmetals like to form compounds with each other. These compounds are called ionic compounds. When two or more nonmetals bond with each other, they form a covalent compound. Metalloids Elements on both sides of the ...
... Since metals tend to lose electrons and nonmetals tend to gain electrons, metals and nonmetals like to form compounds with each other. These compounds are called ionic compounds. When two or more nonmetals bond with each other, they form a covalent compound. Metalloids Elements on both sides of the ...
Work Booklet - Brooks Composite High School
... substances into it. 10. Clean up any spilled substances immediately as instructed by your teacher. 11. Never look into test tubes or containers from the top. Always look through the sides. 12. Never use cracked or broken glassware. Make sure you follow your teacher’s instructions when getting rid of ...
... substances into it. 10. Clean up any spilled substances immediately as instructed by your teacher. 11. Never look into test tubes or containers from the top. Always look through the sides. 12. Never use cracked or broken glassware. Make sure you follow your teacher’s instructions when getting rid of ...
Periodic Table 2015
... Group trend for Alkali metals – Increases as you move down group 1 in the periodic table – Since alkali metals are more likely to lose an electron, the ones with the lowest 1st ionization energy are the most reactive since they require the least amount of energy to lose a valence electron. ...
... Group trend for Alkali metals – Increases as you move down group 1 in the periodic table – Since alkali metals are more likely to lose an electron, the ones with the lowest 1st ionization energy are the most reactive since they require the least amount of energy to lose a valence electron. ...
PERIODIC TABLE
... The elements between atomic #s: 90 and 103 Many are synthetic and they do not follow the properties of the metals around them in the periodic table ...
... The elements between atomic #s: 90 and 103 Many are synthetic and they do not follow the properties of the metals around them in the periodic table ...
Stoichiometry – Chapter 9
... carbon dioxide during the reaction between sodium bicarbonate and citric acid. 3NaHCO3 + H 3C6 H 5O7 → 3CO 2 + 3H 2O + Na 3C6 H 5O7 Suppose 2.0 grams of sodium bicarbonate and 0.50 g of citric acid are present, which is the limiting reactant and what volume of carbon dioxide will be produced (assume ...
... carbon dioxide during the reaction between sodium bicarbonate and citric acid. 3NaHCO3 + H 3C6 H 5O7 → 3CO 2 + 3H 2O + Na 3C6 H 5O7 Suppose 2.0 grams of sodium bicarbonate and 0.50 g of citric acid are present, which is the limiting reactant and what volume of carbon dioxide will be produced (assume ...
1.02 x 10 = 3 mol lit 3.4 x 10
... Pale yellow Greenish yellow Reddish brown Violet The colour of halogens is due to the fact that their molecules absorb radiations from visible light and the outer electrons are easily excited to higher energy levels. The amount of energy required for excitation depends upon the size of the atom. Flu ...
... Pale yellow Greenish yellow Reddish brown Violet The colour of halogens is due to the fact that their molecules absorb radiations from visible light and the outer electrons are easily excited to higher energy levels. The amount of energy required for excitation depends upon the size of the atom. Flu ...
2014_S4_CHM_NORMAL (ALL)
... 53. Element X (atomic number 11) reacts with element Y (atomic number 16) to form an ionic compound. Each atom of X loses one electron and each atom of Y accepts two electrons to form a compound with formula X2Y. 54. Consider the following information: ...
... 53. Element X (atomic number 11) reacts with element Y (atomic number 16) to form an ionic compound. Each atom of X loses one electron and each atom of Y accepts two electrons to form a compound with formula X2Y. 54. Consider the following information: ...
STOICHIOMETRY REVIEW WORKSHEET
... (d) How much oxygen was used up in moles? (e) How much oxygen was used up in grams? 2) Using the following equation: NaOH + ...
... (d) How much oxygen was used up in moles? (e) How much oxygen was used up in grams? 2) Using the following equation: NaOH + ...
Basic Organic Chemistry Laboratory Course
... the chloroform solution gives a hint on the identity of the halogen present. Brown means that there is bromine, a violet colour points at iodine while chlorine is present if the colour of the solution does not change at all. If the iodine or the bromine test is positive, chlorine can be detected a ...
... the chloroform solution gives a hint on the identity of the halogen present. Brown means that there is bromine, a violet colour points at iodine while chlorine is present if the colour of the solution does not change at all. If the iodine or the bromine test is positive, chlorine can be detected a ...
1 Mole
... Standard 3a: describing chemical reactions An equation describes a chemical reaction or ...
... Standard 3a: describing chemical reactions An equation describes a chemical reaction or ...
Chemistry Test Ch 11 Stoichiometry
... 6. Use the following equation to answer these questions: 2 Na (s) + 2 H20 (l) ---> 2 NaOH (aq) + H2 (g) A. How many liters of water is needed to produce 87.69 L H2? B. If 90.0 grams of sodium is dropped into 80.0 g of water, how many liters of hydrogen would be produced? (hint this is a limiting rea ...
... 6. Use the following equation to answer these questions: 2 Na (s) + 2 H20 (l) ---> 2 NaOH (aq) + H2 (g) A. How many liters of water is needed to produce 87.69 L H2? B. If 90.0 grams of sodium is dropped into 80.0 g of water, how many liters of hydrogen would be produced? (hint this is a limiting rea ...
Trends in the Periodic Table
... Polar Molecules and Hydrogen Bonds The electronegativity of the elements in a compound can be used to predict the polarity of the bonds that form. Electrons will accumulate towards the atom with the higher electronegativity. This gives them a slightly negative charge. If both atoms have similar elec ...
... Polar Molecules and Hydrogen Bonds The electronegativity of the elements in a compound can be used to predict the polarity of the bonds that form. Electrons will accumulate towards the atom with the higher electronegativity. This gives them a slightly negative charge. If both atoms have similar elec ...
File
... ii. It contained only 56 elements. Further, it was assumed by Newlands that only 56 elements existed in nature and no more elements would be discovered in the future. iii. To fit elements into the table, Newlands adjusted two elements in the same slot and also put some unlike elements under the same ...
... ii. It contained only 56 elements. Further, it was assumed by Newlands that only 56 elements existed in nature and no more elements would be discovered in the future. iii. To fit elements into the table, Newlands adjusted two elements in the same slot and also put some unlike elements under the same ...
CFE Higher Chemistry in Society Homework EB
... starch and potassium iodide solution. The paper changes colour when ozone is present. Ozone reacts with potassium iodide and water to form iodine, oxygen and potassium hydroxide. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction. ...
... starch and potassium iodide solution. The paper changes colour when ozone is present. Ozone reacts with potassium iodide and water to form iodine, oxygen and potassium hydroxide. Write the balanced chemical equation for this reaction. ...
Chapter Twelve: Atoms and the Periodic Table
... • Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same column. • Mendeleev used the properties of existing elements to predict properties of undiscovered elements. • The close match between Mendeleev’s predictions and the actual prope ...
... • Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of increasing mass so that elements with similar properties were in the same column. • Mendeleev used the properties of existing elements to predict properties of undiscovered elements. • The close match between Mendeleev’s predictions and the actual prope ...
Stoichiometry Notes
... V. Calculating Empirical Formulas from Chemical (Combustion) Analysis When a compound containing C and H is subject to combustion with oxygen in a special combustion apparatus all the C is converted to CO2 and the H is converted to H2O. The amount of C produced can be determined by measuring the am ...
... V. Calculating Empirical Formulas from Chemical (Combustion) Analysis When a compound containing C and H is subject to combustion with oxygen in a special combustion apparatus all the C is converted to CO2 and the H is converted to H2O. The amount of C produced can be determined by measuring the am ...
What Are Compounds?
... Oxidation Numbers • The charges on the ions in an ionic compound reflect the electron distribution of the compound. • In order to indicate the general distribution of electrons among the bonded atoms in a molecular compound or a polyatomic ion, oxidation numbers are assigned to the atoms composing ...
... Oxidation Numbers • The charges on the ions in an ionic compound reflect the electron distribution of the compound. • In order to indicate the general distribution of electrons among the bonded atoms in a molecular compound or a polyatomic ion, oxidation numbers are assigned to the atoms composing ...
VIBRATIONS AND WAVES
... The first periodic table is mostly credited to (5) ___________________. In his table, the elements were arranged according to increasing (6) ___________________. One important result of this table was that the existence and properties of undiscovered (7) _________________ could be predicted. The ele ...
... The first periodic table is mostly credited to (5) ___________________. In his table, the elements were arranged according to increasing (6) ___________________. One important result of this table was that the existence and properties of undiscovered (7) _________________ could be predicted. The ele ...
Unit C3 - Chemistry In Action
... 4) How much volume would 80g of argon occupy? 5) A balloon contains 12dm3 of carbon dioxide. What is the mass of this much CO2? ...
... 4) How much volume would 80g of argon occupy? 5) A balloon contains 12dm3 of carbon dioxide. What is the mass of this much CO2? ...
Unit C3 - Chemistry in Action
... 4) How much volume would 80g of argon occupy? 5) A balloon contains 12dm3 of carbon dioxide. What is the mass of this much CO2? ...
... 4) How much volume would 80g of argon occupy? 5) A balloon contains 12dm3 of carbon dioxide. What is the mass of this much CO2? ...