File - dr. stephen alfred
... Since “Groups” [columns] are similar because they have the same number of electrons in their outer energy level, the Periodic Table is also organized by degree of reactivity. ...
... Since “Groups” [columns] are similar because they have the same number of electrons in their outer energy level, the Periodic Table is also organized by degree of reactivity. ...
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
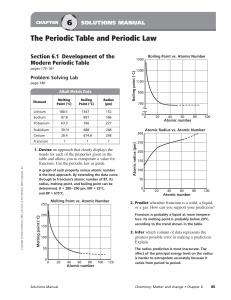
... groups and periods that the elements are in. Without this information, you cannot apply the periodic trends in atomic size to determine which element has the larger radius. ...
... groups and periods that the elements are in. Without this information, you cannot apply the periodic trends in atomic size to determine which element has the larger radius. ...
File
... • The following reaction shows table salt production. How many moles of sodium chloride are produced from 0.02 moles of chlorine? ...
... • The following reaction shows table salt production. How many moles of sodium chloride are produced from 0.02 moles of chlorine? ...
Experimental Study of Closed System in the Chlorine Dioxide
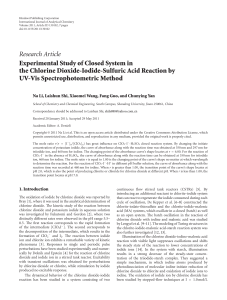
... the extension of reaction time at 350 nm and then does not change with the reaction time afterwards. Under the condition that r is greater than 1.00 (see curve 3 to curve 7), the absorbance increases along with the prolongation of reaction time, which indicates the increase of I3 − species concentra ...
... the extension of reaction time at 350 nm and then does not change with the reaction time afterwards. Under the condition that r is greater than 1.00 (see curve 3 to curve 7), the absorbance increases along with the prolongation of reaction time, which indicates the increase of I3 − species concentra ...
Periodic Classification of Elements
... C is in group 4. Therefore, the oxide will be CO2. Al is in group 3. Therefore, the oxide will be Al2O3. Si is in group 4. Therefore, the oxide will be SiO2. Ba is in group 2. Therefore, the oxide will be BaO. Question 5: Besides gallium, which other elements have since been discovered that were le ...
... C is in group 4. Therefore, the oxide will be CO2. Al is in group 3. Therefore, the oxide will be Al2O3. Si is in group 4. Therefore, the oxide will be SiO2. Ba is in group 2. Therefore, the oxide will be BaO. Question 5: Besides gallium, which other elements have since been discovered that were le ...
Unit 1 Safety and Science
... 1. it takes up space 2. it has mass (or weight) Any object you can think of is made of matter, from your pencil to a planet. What isn’t matter? Any form of Energy, such as heat, is not matter. This is a practical difference and serves as a starting point, however, Einstein showed us that energy and ...
... 1. it takes up space 2. it has mass (or weight) Any object you can think of is made of matter, from your pencil to a planet. What isn’t matter? Any form of Energy, such as heat, is not matter. This is a practical difference and serves as a starting point, however, Einstein showed us that energy and ...
Periodic Table Notes
... grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families in the periodic table. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, by their properties. Metals are found to the left of the zigzag line. Atoms of mo ...
... grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families in the periodic table. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, by their properties. Metals are found to the left of the zigzag line. Atoms of mo ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table of Elements: The Secret
... the top (30). It represents the number of protons, which equals the number of electrons, so the positive and negative charges cancel, and give the element’s atom an overall neutral charge. An abbreviated form of referring to the element is through its Atomic Symbol (Zn), though the actual name of th ...
... the top (30). It represents the number of protons, which equals the number of electrons, so the positive and negative charges cancel, and give the element’s atom an overall neutral charge. An abbreviated form of referring to the element is through its Atomic Symbol (Zn), though the actual name of th ...
The Periodic Table: Chapter Problems Periodic Table Class Work
... b. Nitrogen has a smaller atomic radius than phosphorous because it has a lower principal quantum number than phosphorus. Phosphorous has a higher principal quantum number than so the electrons in the outer energy level are farther away from the nucleus. c. Nitrogen is more electronegative than phos ...
... b. Nitrogen has a smaller atomic radius than phosphorous because it has a lower principal quantum number than phosphorus. Phosphorous has a higher principal quantum number than so the electrons in the outer energy level are farther away from the nucleus. c. Nitrogen is more electronegative than phos ...
Homework Answers - Chemistry from AZ
... • Organization of the Periodic Table (use your periodic table) horizontal rows called periods are numbered 1 to 7; elements in the same period have the same number of principle energy levels (PEL’s) or shells vertical columns called groups or families, are numbered 1 to 18; elements in the same grou ...
... • Organization of the Periodic Table (use your periodic table) horizontal rows called periods are numbered 1 to 7; elements in the same period have the same number of principle energy levels (PEL’s) or shells vertical columns called groups or families, are numbered 1 to 18; elements in the same grou ...
How can atomic theory explain patterns in the periodic table?
... properties of that element. For example, an atom of carbon is represented in Figure 2.15. Each atom has a tiny, dense nucleus containing neutrons and protons. (A hydrogen nucleus has a single proton only.) The nucleus is surrounded by electrons, which exist in specific electron energy shells. Most o ...
... properties of that element. For example, an atom of carbon is represented in Figure 2.15. Each atom has a tiny, dense nucleus containing neutrons and protons. (A hydrogen nucleus has a single proton only.) The nucleus is surrounded by electrons, which exist in specific electron energy shells. Most o ...
SOLUBILITY RULES FOR IONIC COMPOUNDS IN WATER
... (l) Solid barium metal is added to warm water. (m) A solution of bismuth (III) nitrate is added to a solution of potassium sulfide. (n) Solutions of ammonia and potassium bisulfate are mixed. (o) Ethane gas (C2H6) is burned in air. (p) Solutions of copper (II) sulfate and barium hydroxide are mixed. ...
... (l) Solid barium metal is added to warm water. (m) A solution of bismuth (III) nitrate is added to a solution of potassium sulfide. (n) Solutions of ammonia and potassium bisulfate are mixed. (o) Ethane gas (C2H6) is burned in air. (p) Solutions of copper (II) sulfate and barium hydroxide are mixed. ...
Coloring the Periodic Table - Families
... Elements in Group 16 only need two more electrons to fill their outer level. Elements in Group 17 only need one more electron to fill their outer level. ...
... Elements in Group 16 only need two more electrons to fill their outer level. Elements in Group 17 only need one more electron to fill their outer level. ...
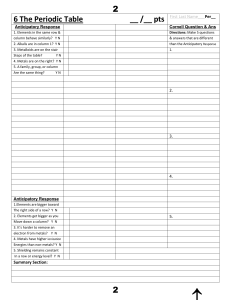
6 The Periodic Tableааааааааааааааааааааааааа__ /__ pts First
... 4. Name the element that matches the following description. a. one that has 5 electrons in the third energy level b. one with an electron configuration that ends in 4s24p5 c. the Group 6A element in period 4 5. Identify the elements that have electron configurations that end as follows. a. 2s22p4 b. ...
... 4. Name the element that matches the following description. a. one that has 5 electrons in the third energy level b. one with an electron configuration that ends in 4s24p5 c. the Group 6A element in period 4 5. Identify the elements that have electron configurations that end as follows. a. 2s22p4 b. ...
664
... silicon, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and iodine at ordinary temperatures. Nitryl fluoride can add a nitrate group to many organics forming their nitro derivatives: C6H6 + NO2F → C6H5NO2 + HF Analysis Nitryl fluoride may be identified from its physical and chemical properties. Its hydrolysis produ ...
... silicon, phosphorus, arsenic, antimony, and iodine at ordinary temperatures. Nitryl fluoride can add a nitrate group to many organics forming their nitro derivatives: C6H6 + NO2F → C6H5NO2 + HF Analysis Nitryl fluoride may be identified from its physical and chemical properties. Its hydrolysis produ ...
powerpoint
... A vertical column in periodic table of elements. The most important way of identifying the elements. In the group the elements in them share the same properties. • Groups that share the same properties happened to not have scientific names, for example: alkaline metals, alkaline earth metals, haloge ...
... A vertical column in periodic table of elements. The most important way of identifying the elements. In the group the elements in them share the same properties. • Groups that share the same properties happened to not have scientific names, for example: alkaline metals, alkaline earth metals, haloge ...
Chemistry IGCSE
... Often it does not matter if a substance is not pure. We wash in tap water; without thinking too much about what is in it, but sometimes purity is very important. If you are making a new medical drug, or a flavouring for food, you must make sure it contains nothing that could harm people. An unwanted ...
... Often it does not matter if a substance is not pure. We wash in tap water; without thinking too much about what is in it, but sometimes purity is very important. If you are making a new medical drug, or a flavouring for food, you must make sure it contains nothing that could harm people. An unwanted ...
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table
... Groups and Periods • Elements in a vertical column show similarities in their chemical and physical properties – Known as a group – Labeled by a number at the top of the column – Sometimes a group is called a family of elements because they seem to be related – Ex: Group 17 – “Halogen” group • Tend ...
... Groups and Periods • Elements in a vertical column show similarities in their chemical and physical properties – Known as a group – Labeled by a number at the top of the column – Sometimes a group is called a family of elements because they seem to be related – Ex: Group 17 – “Halogen” group • Tend ...
Gas Stoichiometry
... Example of a Gas Stoichiometry Problem Airbags in automobiles contain sodium azide (NaN3), potassium nitrate, and silicon dioxide. (All are solids.) 1. Upon impact, the bag is inflated by the thermal decomposition of sodium azide (NaN3) to sodium metal and nitrogen gas. 2. Because sodium is toxic a ...
... Example of a Gas Stoichiometry Problem Airbags in automobiles contain sodium azide (NaN3), potassium nitrate, and silicon dioxide. (All are solids.) 1. Upon impact, the bag is inflated by the thermal decomposition of sodium azide (NaN3) to sodium metal and nitrogen gas. 2. Because sodium is toxic a ...
Placing Elements on the Periodic Table
... grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families in the periodic table. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, by their properties. Metals are found to the left of the zigzag line. Atoms of mo ...
... grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families in the periodic table. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, by their properties. Metals are found to the left of the zigzag line. Atoms of mo ...
The Periodic Table
... at regular intervals —like the appearance of Haley’s comet every 76 years ...
... at regular intervals —like the appearance of Haley’s comet every 76 years ...
N5 Chemistry 2014
... Potassium - The Super Element Potassium is an essential element for almost all living things. The human body requires a regular intake of potassium because humans have no mechanism for storing it. Foods rich in potassium include raisins and almonds. Raisins contain 0·86 g of potassium in every 100 g ...
... Potassium - The Super Element Potassium is an essential element for almost all living things. The human body requires a regular intake of potassium because humans have no mechanism for storing it. Foods rich in potassium include raisins and almonds. Raisins contain 0·86 g of potassium in every 100 g ...
The Periodic Table
... are very reactive and have a low melting point. Shade the alkali metals blue. 5. The nobel gases are found in group 18. Their outer energy level is filled, and they are very nonreactive, colorless gases. Shade the nobel gases red. 6. Halogens have seven electrons in the outer shell. They are located ...
... are very reactive and have a low melting point. Shade the alkali metals blue. 5. The nobel gases are found in group 18. Their outer energy level is filled, and they are very nonreactive, colorless gases. Shade the nobel gases red. 6. Halogens have seven electrons in the outer shell. They are located ...
Ex. 41 Answer
... Thus, compared with O, the effective nuclear charge felt by the outermost shell electrons of F is greater. The electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus. So, the atomic radius of F is smaller than that of O. O and S belong to the same group. An atom of S has 1 more occupied electron shell than an a ...
... Thus, compared with O, the effective nuclear charge felt by the outermost shell electrons of F is greater. The electrons are pulled closer to the nucleus. So, the atomic radius of F is smaller than that of O. O and S belong to the same group. An atom of S has 1 more occupied electron shell than an a ...