Elements and Atoms: The Building Blocks of Matter
... atoms in a way that results in the addition of two electrons to oxygen's valence shell, bringing the number to eight. When two hydrogen atoms each share their single electron with oxygen, covalent bonds are formed, resulting in a molecule of water, H2 O. In nature, atoms of one element tend to join ...
... atoms in a way that results in the addition of two electrons to oxygen's valence shell, bringing the number to eight. When two hydrogen atoms each share their single electron with oxygen, covalent bonds are formed, resulting in a molecule of water, H2 O. In nature, atoms of one element tend to join ...
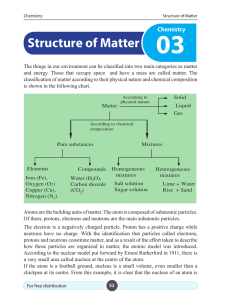
Structure of Matter - e
... The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom of the element. Atomic number of the element = number of protons in an atom of the element For example, there are 11 protons in the nucleus of a sodium atom. Thus, the atomic number of sodium is 11.The number of protons in every atom of the same ...
... The atomic number is the number of protons in an atom of the element. Atomic number of the element = number of protons in an atom of the element For example, there are 11 protons in the nucleus of a sodium atom. Thus, the atomic number of sodium is 11.The number of protons in every atom of the same ...
Homework
... Directions: Fill in the blank with the correct word from the list at the bottom of the page. Not all words from the list will be used. 1. Atomic ________________________ refers to the arrangement and number of smaller particles in an atom. 2. The ________________________ is the center or core of an ...
... Directions: Fill in the blank with the correct word from the list at the bottom of the page. Not all words from the list will be used. 1. Atomic ________________________ refers to the arrangement and number of smaller particles in an atom. 2. The ________________________ is the center or core of an ...
w_4-3 Chemistry of Nitrogen Compounds
... plot is much less pronounced and is more like a plateau, i.e., it occurs at a higher combined residual chlorine level. Thus, the combined chlorine beyond breakpoint is due to NCl3 and slower reacting organic chloramines, e.g., chlorinated derivatives of amino acids, creatinine, and other organic nit ...
... plot is much less pronounced and is more like a plateau, i.e., it occurs at a higher combined residual chlorine level. Thus, the combined chlorine beyond breakpoint is due to NCl3 and slower reacting organic chloramines, e.g., chlorinated derivatives of amino acids, creatinine, and other organic nit ...
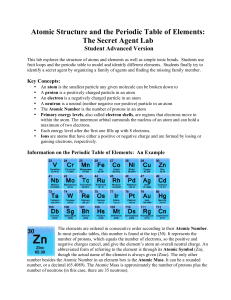
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table of Elements: The Secret
... 4. Once you have several distinct piles focusing on one or two shared characteristics, now try looking at the big picture and combine the agents into one large family portrait. 5. If you have compiled the Secret Agents into the correct arrangement, there will be one empty spot in the family portrait ...
... 4. Once you have several distinct piles focusing on one or two shared characteristics, now try looking at the big picture and combine the agents into one large family portrait. 5. If you have compiled the Secret Agents into the correct arrangement, there will be one empty spot in the family portrait ...
biogenic s, p, d-block elements, biological role, application in medicine
... Chemical properties of s-elements of IA and IIA-groups are similar. sBlock elements easily give their valences-electrons, which means that they are strong reducers. Stable ions with an external electronic shell of the previous inert gas are formed by losing their s-electrons. Radiuses of the ions in ...
... Chemical properties of s-elements of IA and IIA-groups are similar. sBlock elements easily give their valences-electrons, which means that they are strong reducers. Stable ions with an external electronic shell of the previous inert gas are formed by losing their s-electrons. Radiuses of the ions in ...
chemistry intermediate may 2010 marking scheme
... mechanism showing propagation and termination steps is not required. (2) (3 marks) 13. Give the name and structural formula of the main organic product obtained when but-1-ene reacts with hydrogen iodide. 2-iodobutane (1); assign 2 marks for correct structural formula (3 marks) 14. Explain why a sol ...
... mechanism showing propagation and termination steps is not required. (2) (3 marks) 13. Give the name and structural formula of the main organic product obtained when but-1-ene reacts with hydrogen iodide. 2-iodobutane (1); assign 2 marks for correct structural formula (3 marks) 14. Explain why a sol ...
3. d-Block elements. Biological role, application in medicine.
... Chemical properties of s-elements of IA and IIA-groups are similar. sBlock elements easily give their valences-electrons, which means that they are strong reducers. Stable ions with an external electronic shell of the previous inert gas are formed by losing their s-electrons. Radiuses of the ions in ...
... Chemical properties of s-elements of IA and IIA-groups are similar. sBlock elements easily give their valences-electrons, which means that they are strong reducers. Stable ions with an external electronic shell of the previous inert gas are formed by losing their s-electrons. Radiuses of the ions in ...
Medical Chemistry Lecture By : Asst. LectTariq Al Mgheer of
... left. Near this line are the metalloids. These elements such as silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge), have some properties that are similar to those of nonmetals and some that are similar to those of metals. Only 90 of the 106 elements are found in nature. The others are prepared in the laboratory by ins ...
... left. Near this line are the metalloids. These elements such as silicon (Si) and germanium (Ge), have some properties that are similar to those of nonmetals and some that are similar to those of metals. Only 90 of the 106 elements are found in nature. The others are prepared in the laboratory by ins ...
2010 Exam
... Use Lewis dot diagrams to show the formation of the ionic compound barium nitride from atoms of barium and nitrogen. ...
... Use Lewis dot diagrams to show the formation of the ionic compound barium nitride from atoms of barium and nitrogen. ...
Periodic Trends: Straw Lab
... Objective: To create a visual representation of the following periodic trends: atomic size, ionization energy and electronegativity. Atomic Radius: the size of an atom measured in either nanometers (nm) or angstroms (Ǻ). Ionization Energy: the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom measure ...
... Objective: To create a visual representation of the following periodic trends: atomic size, ionization energy and electronegativity. Atomic Radius: the size of an atom measured in either nanometers (nm) or angstroms (Ǻ). Ionization Energy: the energy needed to remove an electron from an atom measure ...
Mole Concept and Stoichiometry
... molecular masses. The concept of mole did not even exist in Avogadro’s time. Much of Avogadro’s work was based on that of Gay-Lussac ( 1778 – 1850 ) . Gay – Lussac developed the law of combining volumes which states that ‘ In any chemical reaction involving gaseous substance, the volumes of various ...
... molecular masses. The concept of mole did not even exist in Avogadro’s time. Much of Avogadro’s work was based on that of Gay-Lussac ( 1778 – 1850 ) . Gay – Lussac developed the law of combining volumes which states that ‘ In any chemical reaction involving gaseous substance, the volumes of various ...
National 5 - Deans Community High School
... was chlorine. We had to keep clear of the chlorine he said. When the copper went in the gas, it shrivelled up. Then it went on fire. When it stopped there was yellow stuff in the jar This is a CHEMICAL REACTION. ...
... was chlorine. We had to keep clear of the chlorine he said. When the copper went in the gas, it shrivelled up. Then it went on fire. When it stopped there was yellow stuff in the jar This is a CHEMICAL REACTION. ...
Chapter 5 Reading Guide Please answer the following questions in
... At quick glance of the Mendeleev’s periodic table (bottom of page 127), what are some differences you spot from the modern periodic table (like the one on the wall or in your ...
... At quick glance of the Mendeleev’s periodic table (bottom of page 127), what are some differences you spot from the modern periodic table (like the one on the wall or in your ...
Document
... 1. Volcanoes produce a variety of molten substances including sulphur and silicon dioxide. (a) Complete the table to show the strongest type of attraction that is broken when each substance melts. ...
... 1. Volcanoes produce a variety of molten substances including sulphur and silicon dioxide. (a) Complete the table to show the strongest type of attraction that is broken when each substance melts. ...
Chemistry Spell check on
... 1. Volcanoes produce a variety of molten substances including sulphur and silicon dioxide. (a) Complete the table to show the strongest type of attraction that is broken when each substance melts. ...
... 1. Volcanoes produce a variety of molten substances including sulphur and silicon dioxide. (a) Complete the table to show the strongest type of attraction that is broken when each substance melts. ...
HONORS CHEMISTRY
... A gaseous mixture containing 7.50 mol H2(g) and 9.0 mol Cl2(g) reacts to form hydrogen chloride gas. a. W rite a balanced equation for the reaction. b. W hich reactant is limiting? c. If all the limiting reactant are consumed, how many moles of hydrogen chloride are formed? d. How many moles of exce ...
... A gaseous mixture containing 7.50 mol H2(g) and 9.0 mol Cl2(g) reacts to form hydrogen chloride gas. a. W rite a balanced equation for the reaction. b. W hich reactant is limiting? c. If all the limiting reactant are consumed, how many moles of hydrogen chloride are formed? d. How many moles of exce ...
Summer Study Assignment – Honors Chem 2/AP Chemistry
... 31. Write the electron configuration using the Noble Gas core method for californium. 32. Write a balanced equation for the following double replacement reactions: a. Calcium hydroxide (aq) + nitric acid (aq) b. Chromium (III) sulfite (aq) + sulfuric acid (aq) c. Zinc chloride (aq) + ammonium su ...
... 31. Write the electron configuration using the Noble Gas core method for californium. 32. Write a balanced equation for the following double replacement reactions: a. Calcium hydroxide (aq) + nitric acid (aq) b. Chromium (III) sulfite (aq) + sulfuric acid (aq) c. Zinc chloride (aq) + ammonium su ...
Chapter 1 - Study Guide Solutions
... Group 1 - ALKALI METALS (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr) Soft, low melting, shiny metals: conduct heat and electricity. They are stored in oil due to their high reactivity (also named oily metals). ...
... Group 1 - ALKALI METALS (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr) Soft, low melting, shiny metals: conduct heat and electricity. They are stored in oil due to their high reactivity (also named oily metals). ...
Chemical Periodicity
... a) How does the size of the atom vary as you move left to right across the periodic table? Why? The atomic radius of atoms typically decreases from left to right across a period. This is because the force of attraction between nuclei and electrons lessens as you move down the table due to the electr ...
... a) How does the size of the atom vary as you move left to right across the periodic table? Why? The atomic radius of atoms typically decreases from left to right across a period. This is because the force of attraction between nuclei and electrons lessens as you move down the table due to the electr ...
word - My eCoach
... ____ 27. In which of the following is the name and formula given correctly? a. sodium oxide, NaO c. copper(II) chloride, CuCl2 b. barium nitride, Ba(NO3)2 d. iron(II) oxide, Fe2O3 ____ 28. An element with an electronegativity of 0.9 bonds with an element with an electronegativity of 3.1. Which of th ...
... ____ 27. In which of the following is the name and formula given correctly? a. sodium oxide, NaO c. copper(II) chloride, CuCl2 b. barium nitride, Ba(NO3)2 d. iron(II) oxide, Fe2O3 ____ 28. An element with an electronegativity of 0.9 bonds with an element with an electronegativity of 3.1. Which of th ...
1 CHAPTER 5 – THE PERIODIC LAW What types of useful
... -- all react strongly with water and air, so they are stored under kerosene. -- all can be cut with a knife Hydrogen – makes up 76% of universe. Placed above Group 1 (not init, even though it has 1 outer e-) because a. It is not a metal b. It is chemically unlike the Group 1 elements Group 2: “the a ...
... -- all react strongly with water and air, so they are stored under kerosene. -- all can be cut with a knife Hydrogen – makes up 76% of universe. Placed above Group 1 (not init, even though it has 1 outer e-) because a. It is not a metal b. It is chemically unlike the Group 1 elements Group 2: “the a ...
1 CHAPTER 5 – THE PERIODIC LAW What types of useful
... -- all react strongly with water and air, so they are stored under kerosene. -- all can be cut with a knife Hydrogen – makes up 76% of universe. Placed above Group 1 (not init, even though it has 1 outer e-) because a. It is not a metal b. It is chemically unlike the Group 1 elements Group 2: “the a ...
... -- all react strongly with water and air, so they are stored under kerosene. -- all can be cut with a knife Hydrogen – makes up 76% of universe. Placed above Group 1 (not init, even though it has 1 outer e-) because a. It is not a metal b. It is chemically unlike the Group 1 elements Group 2: “the a ...