11-chemistry-exemplar-chapter-3
... same principal quantum level, the shielding effect of inner core of electrons does not increase very much to compensate for the increased attraction of the electron to the nucleus. ...
... same principal quantum level, the shielding effect of inner core of electrons does not increase very much to compensate for the increased attraction of the electron to the nucleus. ...
Chapter 6 the Periodic Table
... solids, lower boiling and melting points than metals (except carbon), usually have lower densities than metals. • Metaloids have properties between metals and non metals. ...
... solids, lower boiling and melting points than metals (except carbon), usually have lower densities than metals. • Metaloids have properties between metals and non metals. ...
Name:
... elements. Scientists during Dmitri’s time were trying to figure out an easy way in which they could organize the elements of matter so that it would be easy for them to communicate about their properties (i.e. scientists, even back then, were lazy and they didn’t want to have to memorize all the ele ...
... elements. Scientists during Dmitri’s time were trying to figure out an easy way in which they could organize the elements of matter so that it would be easy for them to communicate about their properties (i.e. scientists, even back then, were lazy and they didn’t want to have to memorize all the ele ...
Periodic Table Student Outline
... silicon + silicon ad infinitum links up into crystalline lattices, used to make semiconductors for computers. 16 Carbon atoms—also Group 4—bond in long chains and sugars. The chemical flexibility of carbon is what makes it the key molecule of life. 17 Mendeleyev wrongly assumed that all elements are ...
... silicon + silicon ad infinitum links up into crystalline lattices, used to make semiconductors for computers. 16 Carbon atoms—also Group 4—bond in long chains and sugars. The chemical flexibility of carbon is what makes it the key molecule of life. 17 Mendeleyev wrongly assumed that all elements are ...
TOPIC 12. THE ELEMENTS
... is used and lost - filling party balloons! An object made from some metals retains a memory of its initial shape and if distorted, it will return to the original shape when heated. Origin of the elements. As discussed in Topic 1, there are 90 naturally occurring elements. In addition, there are abou ...
... is used and lost - filling party balloons! An object made from some metals retains a memory of its initial shape and if distorted, it will return to the original shape when heated. Origin of the elements. As discussed in Topic 1, there are 90 naturally occurring elements. In addition, there are abou ...
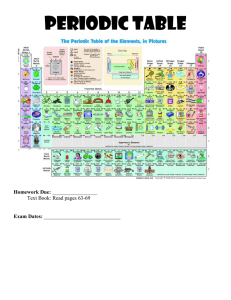
Homework Packet - Chemistry from AZ
... horizontal rows called periods are numbered 1 to 7; elements in the same period have the same number of principle energy levels (PEL’s) or shells vertical columns called groups or families, are numbered 1 to 18; elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons and therefore have ...
... horizontal rows called periods are numbered 1 to 7; elements in the same period have the same number of principle energy levels (PEL’s) or shells vertical columns called groups or families, are numbered 1 to 18; elements in the same group have the same number of valence electrons and therefore have ...
Element Project - Dover Bay
... group 1, period 1, which is just down the street. Hydrogen has two siblings isotopes, deuterium and tritium, who has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. He also has a neighbor, the Alkali Metals who lives in the same street. Their names are Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidi ...
... group 1, period 1, which is just down the street. Hydrogen has two siblings isotopes, deuterium and tritium, who has the same number of protons but different number of neutrons. He also has a neighbor, the Alkali Metals who lives in the same street. Their names are Lithium, Sodium, Potassium, Rubidi ...
History of Periodic Table
... Broke the trend of arranging elements solely by their atomic mass Wanted to keep elements with similar properties in the same columns Left gaps in his early tables; predicted elements that had not been discovered would fill in those gaps ...
... Broke the trend of arranging elements solely by their atomic mass Wanted to keep elements with similar properties in the same columns Left gaps in his early tables; predicted elements that had not been discovered would fill in those gaps ...
Period
... Finding Your Way Around the Periodic Table Worksheet 1. What is the atomic number of cobalt? __________ 2. What is the atomic number of osmium? __________ 3. What is the atomic mass of germanium? __________ 4. What element is in group 1 and period 2? __________ 5. What element is in group 6 and per ...
... Finding Your Way Around the Periodic Table Worksheet 1. What is the atomic number of cobalt? __________ 2. What is the atomic number of osmium? __________ 3. What is the atomic mass of germanium? __________ 4. What element is in group 1 and period 2? __________ 5. What element is in group 6 and per ...
The Periodic Table of Elements
... •Noble gases have 8 valence electrons • (except helium, which has only 2) •This makes them extremely stable and unreactive because they have filled valence shells. They don’t bond/react with other elements because they don’t need to gain or lose e-) • Noble gases are ONLY found alone in • nature – m ...
... •Noble gases have 8 valence electrons • (except helium, which has only 2) •This makes them extremely stable and unreactive because they have filled valence shells. They don’t bond/react with other elements because they don’t need to gain or lose e-) • Noble gases are ONLY found alone in • nature – m ...
7-1 Notes: Arranging the Elements
... arranged by atomic ___________. In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged _______________ in order of increasing atomic number. Elements that have similar chemical properties are grouped in ___________ columns. Elements are classified according to their ____________ as metals, nonmetals, a ...
... arranged by atomic ___________. In the modern periodic table, elements are arranged _______________ in order of increasing atomic number. Elements that have similar chemical properties are grouped in ___________ columns. Elements are classified according to their ____________ as metals, nonmetals, a ...
Chapter #5 Notes
... • Group 17- Halogens the most reactive nonmetals they form “salts” • Group 18- Noble Gases- Least reactive family. WHY???? ...
... • Group 17- Halogens the most reactive nonmetals they form “salts” • Group 18- Noble Gases- Least reactive family. WHY???? ...
Increasing Radii
... poor conductors of heat and electricity brittle-break into pieces when hit or are gases dull looking solids if not a gas Non-metals are on the right side of the periodic table. Metalloids: elements that have properties of both metals and non-metals (these are also called semiconductors) B, Si, Ge, A ...
... poor conductors of heat and electricity brittle-break into pieces when hit or are gases dull looking solids if not a gas Non-metals are on the right side of the periodic table. Metalloids: elements that have properties of both metals and non-metals (these are also called semiconductors) B, Si, Ge, A ...
Are there atoms in the air? Why or why not?
... Elements, Compounds and Mixtures! Let’s Review: Element: pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substance by physical or chemical means. An atom is the smallest part of an element. Atoms are made of protons, neutrons, and electrons. All things on Earth, except energy, are made of atom ...
... Elements, Compounds and Mixtures! Let’s Review: Element: pure substance that cannot be separated into simpler substance by physical or chemical means. An atom is the smallest part of an element. Atoms are made of protons, neutrons, and electrons. All things on Earth, except energy, are made of atom ...
Unit Six: Atomic structure
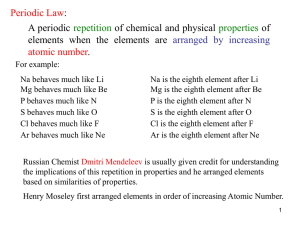
... 1. Dimitri Mendeleev , a Russian scientist, is credits for creating the first periodic table in 1869. At that time, there were only 60 known element and Mendeleev organized them according to their atomic mass. Mendeleev was able to predict the properties of missing elements which were later discover ...
... 1. Dimitri Mendeleev , a Russian scientist, is credits for creating the first periodic table in 1869. At that time, there were only 60 known element and Mendeleev organized them according to their atomic mass. Mendeleev was able to predict the properties of missing elements which were later discover ...
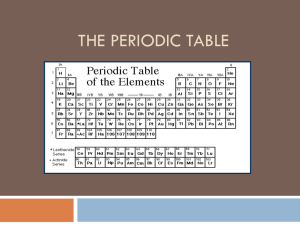
Periodic Table Properties Notes s1
... • The vertical columns of the periodic table are called groups or families. • Each group contains elements with similar chemical properties. • Every element within a group has the same number of valence electrons. • The number of valence electrons determines an element’s chemical characteristics ...
... • The vertical columns of the periodic table are called groups or families. • Each group contains elements with similar chemical properties. • Every element within a group has the same number of valence electrons. • The number of valence electrons determines an element’s chemical characteristics ...
Periodicity - ilc.edu.hk
... Refer to notes on ‘Electronic structure of atoms and the periodic table’, pp.25-27 ...
... Refer to notes on ‘Electronic structure of atoms and the periodic table’, pp.25-27 ...
Periodic Table
... you look at the modern periodic table, you will see several examples, such as cobalt and nickel, where the mass decreases from left to right. ...
... you look at the modern periodic table, you will see several examples, such as cobalt and nickel, where the mass decreases from left to right. ...
Periodic Table of Elements
... atomic radius, ionization energy, and electron affinity. Atomic radius usually decreases from left to right across a period. This occurs because each successive element has an added proton and electron, which causes the electron to be drawn closer to the nucleus, decreasing the radius. ...
... atomic radius, ionization energy, and electron affinity. Atomic radius usually decreases from left to right across a period. This occurs because each successive element has an added proton and electron, which causes the electron to be drawn closer to the nucleus, decreasing the radius. ...
The Periodic Table
... A few years passed and sure enough they came, Gallium, scandium, germanium were their names. Chemists everywhere were impressed with what they saw. There really must be something to this periodic law. ...
... A few years passed and sure enough they came, Gallium, scandium, germanium were their names. Chemists everywhere were impressed with what they saw. There really must be something to this periodic law. ...
File - eScience@Kings
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
11. Patterns in the Periodic Table
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
11. Patterns in the Periodic Table
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...
... Electron trends in the periodic table Trends down a group: the number of outer shell electrons is the same; the number of complete electron shells increases by one. The number of a group is the same as the number of electrons in the outer shell of elements in that group, ...