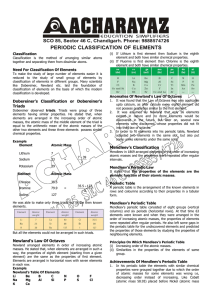
Periodic Properties of the Elements
... element’s physical properties. After selecting the element, you will analyze the patterns of these properties as they occur across a period as well as trends that exist down a group. You will identify several mystery elements by investigating and interpreting periodic trends. Remember that valence e ...
... element’s physical properties. After selecting the element, you will analyze the patterns of these properties as they occur across a period as well as trends that exist down a group. You will identify several mystery elements by investigating and interpreting periodic trends. Remember that valence e ...
Periodic Table Metals, Non
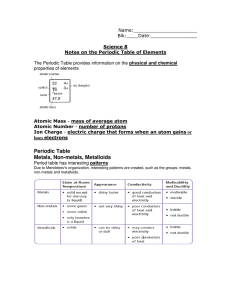
... The Periodic Table provides information on the physical and chemical properties of elements ...
... The Periodic Table provides information on the physical and chemical properties of elements ...
Unit 4 Pack
... Why is Si bigger than S (explain why – do not just write because it is further left!) Why is Se bigger than S? (explain why) Why is Cu2+ smaller than Cu? Identify the two ions that are most important in the human body. Where are they found? What is their function? Given Al, I and F a. Place them in ...
... Why is Si bigger than S (explain why – do not just write because it is further left!) Why is Se bigger than S? (explain why) Why is Cu2+ smaller than Cu? Identify the two ions that are most important in the human body. Where are they found? What is their function? Given Al, I and F a. Place them in ...
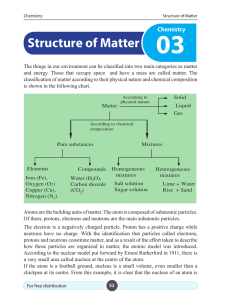
Structure of Matter - e
... - Only the first, second, third and fourth energy levels carry electrons Period 1 H ...
... - Only the first, second, third and fourth energy levels carry electrons Period 1 H ...
Scandium and Yttrium - Mercyhurst University
... The pure metal of both Sc and Y are silvery in color and are somewhat air stable, less so as the temperature increases and less so as the surface area of the metal increases.4 Yttrium forms a protective oxide, and thus must be heated even moreso than scandium (to about 1000 oC) to initiate reaction. ...
... The pure metal of both Sc and Y are silvery in color and are somewhat air stable, less so as the temperature increases and less so as the surface area of the metal increases.4 Yttrium forms a protective oxide, and thus must be heated even moreso than scandium (to about 1000 oC) to initiate reaction. ...
7.1 The Periodic Table
... • Characteristics that you can see through direct observation are called physical properties. • Physical properties include color, texture, density, brittleness, and state (solid, liquid, or gas). • Melting point, boiling point, and specific heat are also physical properties. ...
... • Characteristics that you can see through direct observation are called physical properties. • Physical properties include color, texture, density, brittleness, and state (solid, liquid, or gas). • Melting point, boiling point, and specific heat are also physical properties. ...
UNIT-3 Classification of elements and periodicity
... 7. What is more fundamental property for an atom of an element according to Moseley? 8. Which quantum number corresponds to the period number in the modern periodic table? 9. How many elements are there in the 4th period of long form of periodic table? 10. Write the atomic number of the element unni ...
... 7. What is more fundamental property for an atom of an element according to Moseley? 8. Which quantum number corresponds to the period number in the modern periodic table? 9. How many elements are there in the 4th period of long form of periodic table? 10. Write the atomic number of the element unni ...
6 The Periodic Tableааааааааааааааааааааааааа__ /__ pts First
... Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 10. In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of atomic number. ________ 11. There are six periods in a periodic table. ________ 12. Most of the elements in the periodic table ...
... Classify each of these statements as always true, AT; sometimes true, ST; or never true, NT. ________ 10. In his periodic table, Mendeleev arranged the elements in order of atomic number. ________ 11. There are six periods in a periodic table. ________ 12. Most of the elements in the periodic table ...
Chapter 3 Physical Science - St. Pius X Classical Academy
... in an unstable nucleus during each form of radioactive decay? ...
... in an unstable nucleus during each form of radioactive decay? ...
Families on the Periodic Table
... 9. r would correspond to our alkali metals and is in the 4th energy level. 10. The ! family is made up of the elements !, =, s and p in order of increasing atomic radii. 11. j is the most dense of all Martian atoms and is radioactive and its electron configuration would end with 5p 3.. ...
... 9. r would correspond to our alkali metals and is in the 4th energy level. 10. The ! family is made up of the elements !, =, s and p in order of increasing atomic radii. 11. j is the most dense of all Martian atoms and is radioactive and its electron configuration would end with 5p 3.. ...
Unit 4 Periodic Table Packet 2016-2017
... 9. r would correspond to our alkali metals and is in the 4th energy level. 10. The ! family is made up of the elements !, =, s and p in order of increasing atomic radii. 11. j is the most dense of all Martian atoms and is radioactive and its electron configuration would end with 5p 3.. ...
... 9. r would correspond to our alkali metals and is in the 4th energy level. 10. The ! family is made up of the elements !, =, s and p in order of increasing atomic radii. 11. j is the most dense of all Martian atoms and is radioactive and its electron configuration would end with 5p 3.. ...
Inorganic Chemistry ELEMENTS AND
... substances by usual chemical methods of applying heat, light or electric energy. It is made up of atoms. Eg. Gold, Silver, Iron, Copper, Sodium, Hydrogen, Helium etc. Elements have been divided into metals and non-metals. Metals are usully solids with the exception of mercury which is liquid. Hydrog ...
... substances by usual chemical methods of applying heat, light or electric energy. It is made up of atoms. Eg. Gold, Silver, Iron, Copper, Sodium, Hydrogen, Helium etc. Elements have been divided into metals and non-metals. Metals are usully solids with the exception of mercury which is liquid. Hydrog ...
CHAPTER 5
... Formation of Ions Most metals tend to lose electrons, taking on a positive charge. The positively charged ions are called cations. Written Na+ or Mg2+ For metallic elements, the cation name is the same as the name of the ...
... Formation of Ions Most metals tend to lose electrons, taking on a positive charge. The positively charged ions are called cations. Written Na+ or Mg2+ For metallic elements, the cation name is the same as the name of the ...
periodic classification of elements
... (ii) It is easier to remember the properties of an element if it’s position in the periodic table is known. (iii) The type of compounds formed by an element can be easily predicted by knowing its position in the periodic table. (iv) Many elements have been discovered with the help of periodic table. ...
... (ii) It is easier to remember the properties of an element if it’s position in the periodic table is known. (iii) The type of compounds formed by an element can be easily predicted by knowing its position in the periodic table. (iv) Many elements have been discovered with the help of periodic table. ...
The Periodic Table - Anderson High School
... number of valence electrons. • They will form the same kinds of ions. ...
... number of valence electrons. • They will form the same kinds of ions. ...
Topic 5 - Holy Cross Collegiate
... table in Part 1 and the diagram above to answer the following questions. Record the symbols of the elements in Period 2 so they are stretched out horizontally across a page. Place the symbols of the elements in Period 3 directly beneath them, as they appear in the table. Most of the elements are sol ...
... table in Part 1 and the diagram above to answer the following questions. Record the symbols of the elements in Period 2 so they are stretched out horizontally across a page. Place the symbols of the elements in Period 3 directly beneath them, as they appear in the table. Most of the elements are sol ...
File
... table in Part 1 and the diagram above to answer the following questions. Record the symbols of the elements in Period 2 so they are stretched out horizontally across a page. Place the symbols of the elements in Period 3 directly beneath them, as they appear in the table. Most of the elements are sol ...
... table in Part 1 and the diagram above to answer the following questions. Record the symbols of the elements in Period 2 so they are stretched out horizontally across a page. Place the symbols of the elements in Period 3 directly beneath them, as they appear in the table. Most of the elements are sol ...
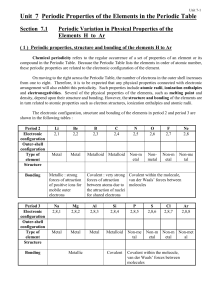
Unit 7 Periodic Properties of the Elements in the Periodic Table
... In each period, the oxides of metals and metalloids have giant structures, whereas the oxides of non-metals are composed of simple molecules. Notice the gradations in structure and bond type across each period from ionic oxides to simple molecular oxides. The graduation can be correlated with change ...
... In each period, the oxides of metals and metalloids have giant structures, whereas the oxides of non-metals are composed of simple molecules. Notice the gradations in structure and bond type across each period from ionic oxides to simple molecular oxides. The graduation can be correlated with change ...
Periodic Properties of the Elements
... 3. Record the element’s properties from the list provided in part 1 of Table 1. 4. Note that you can select various periodic trends for the element and period. These trends appear as graphs on the right side of the screen. 5. Observe the graph for atomic radius (pm). Describe the relationship betwee ...
... 3. Record the element’s properties from the list provided in part 1 of Table 1. 4. Note that you can select various periodic trends for the element and period. These trends appear as graphs on the right side of the screen. 5. Observe the graph for atomic radius (pm). Describe the relationship betwee ...
Chapter 5.1 History of PT - Effingham County Schools
... The energy required to remove one electron from a neutral atom of an element ...
... The energy required to remove one electron from a neutral atom of an element ...
alkali metal
... Which of the sets of elements have similar physical and chemical properties? a. b. c. ...
... Which of the sets of elements have similar physical and chemical properties? a. b. c. ...
(Periodic Trends) - stroh
... Discovered by boiling urine There are 2 forms: white and red The white forms combusts in air ...
... Discovered by boiling urine There are 2 forms: white and red The white forms combusts in air ...