day4-periodictrends
... 1. Which family is least reactive? 2. Which family is most metallic? 3. Where are the nonmetals on the periodic table? ...
... 1. Which family is least reactive? 2. Which family is most metallic? 3. Where are the nonmetals on the periodic table? ...
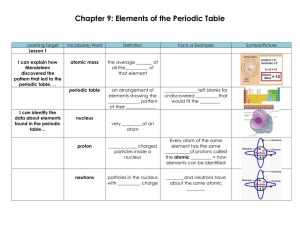
Chapter 9: Elements of the Periodic Table
... __________reactive top _______of elements placed _____________ the periodic table used to make _________ light ______________ row of elements placed below periodic table ...
... __________reactive top _______of elements placed _____________ the periodic table used to make _________ light ______________ row of elements placed below periodic table ...
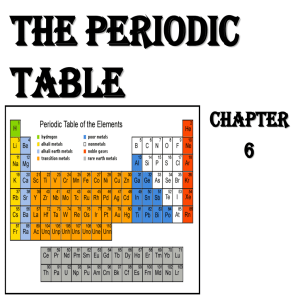
The Periodic Table
... Trends in Atomic Size Atomic size is an atom’s atomic radius, or one-half the distance between two like atoms when they are joined together. Atomic size generally increases from top to bottom within a group because the number of energy levels increases. Atomic size decreases from left to right acros ...
... Trends in Atomic Size Atomic size is an atom’s atomic radius, or one-half the distance between two like atoms when they are joined together. Atomic size generally increases from top to bottom within a group because the number of energy levels increases. Atomic size decreases from left to right acros ...
Describe the Periodic Table
... Atomic Symbol: 0The atomic symbol is one or two letters chosen to represent an element ("H" for "hydrogen," etc.). 0 These symbols are used every where in the world 0 Usually, a symbol is the abbreviation of the element or the abbreviated Latin name of the element. ...
... Atomic Symbol: 0The atomic symbol is one or two letters chosen to represent an element ("H" for "hydrogen," etc.). 0 These symbols are used every where in the world 0 Usually, a symbol is the abbreviation of the element or the abbreviated Latin name of the element. ...
CP-Chem Ch 5 PowerPoint(The Periodic Table)
... • The extremely low reactivity of noble gases leads to some special uses. ...
... • The extremely low reactivity of noble gases leads to some special uses. ...
File
... 1. The atomic number of element X is 6 less than the atomic number of element W. Element W is one of the elements that make up water. What are elements X and W? ___________________________________________ 2. To find element Z, start at the beginning of Period 2 on the periodic table. Move to the rig ...
... 1. The atomic number of element X is 6 less than the atomic number of element W. Element W is one of the elements that make up water. What are elements X and W? ___________________________________________ 2. To find element Z, start at the beginning of Period 2 on the periodic table. Move to the rig ...
Chapter 5: Electrons
... Section Review – page 139 Questions 1, 2, 4 and 5 End of chapter problems – page 156-157 Questions 27, 28 and 29 ...
... Section Review – page 139 Questions 1, 2, 4 and 5 End of chapter problems – page 156-157 Questions 27, 28 and 29 ...
The Periodic Table - Duplin County Schools
... Atomic Symbol: The atomic symbol is one or two letters chosen to represent an element ("H" for "hydrogen," etc.). These symbols are used every where in the world Usually, a symbol is the abbreviation of the element or the abbreviated Latin name of the element. ...
... Atomic Symbol: The atomic symbol is one or two letters chosen to represent an element ("H" for "hydrogen," etc.). These symbols are used every where in the world Usually, a symbol is the abbreviation of the element or the abbreviated Latin name of the element. ...
Groups in a Periodic Table
... • Some periodic tables provide more information such as physical state, electron configuration, and classification of each element. ...
... • Some periodic tables provide more information such as physical state, electron configuration, and classification of each element. ...
Mendeleef`s Periodic Table
... According to this theory, hydrogen atom was considered as the fundamental unit from which all other atoms were made. It is also known as unitary theory. Dobereiner’s Triads (1829) Dobereiner classified the elements into groups of three elements with similar properties in such a manner so that the at ...
... According to this theory, hydrogen atom was considered as the fundamental unit from which all other atoms were made. It is also known as unitary theory. Dobereiner’s Triads (1829) Dobereiner classified the elements into groups of three elements with similar properties in such a manner so that the at ...
Oct 17-Oct 21
... I can use the periodic table to identify the characteristics and properties of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids ...
... I can use the periodic table to identify the characteristics and properties of metals, nonmetals, and metalloids ...
Chapter 5
... 14. Elements with atomic number 57 to 71 are called lanthanide series and elements with atomic number 89 to 103 are called actinide. 15. Elements having 1 valence electron are placed in group one. Elements having 2 valence electrons are placed in group 2. 16. Elements having 3 valence electrons are ...
... 14. Elements with atomic number 57 to 71 are called lanthanide series and elements with atomic number 89 to 103 are called actinide. 15. Elements having 1 valence electron are placed in group one. Elements having 2 valence electrons are placed in group 2. 16. Elements having 3 valence electrons are ...
Ch. 4.3 – Distinguishing Among Atoms
... A periodic table is an arrangement of elements in which the elements are separated into groups based on a set of repeating properties. A periodic table allows you to easily compare the properties of one element (or a group of elements) to another element (or group of elements). ...
... A periodic table is an arrangement of elements in which the elements are separated into groups based on a set of repeating properties. A periodic table allows you to easily compare the properties of one element (or a group of elements) to another element (or group of elements). ...
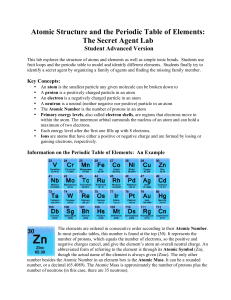
Atomic Structure and the Periodic Table of Elements: The Secret
... common trends or patterns found within the Periodic Table of Elements. The elements found within the Periodic Table are arranged in a very particular pattern, based on several common similarities or characteristics. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev produced a table of elements based on their atomic weights ...
... common trends or patterns found within the Periodic Table of Elements. The elements found within the Periodic Table are arranged in a very particular pattern, based on several common similarities or characteristics. In 1869, Dmitri Mendeleev produced a table of elements based on their atomic weights ...
The Periodic Table
... reacting vigorously with metals to form salts •Most halogens exist in nature as diatomic molecules (i.e. F2, Cl2, Br2 and I2.) ...
... reacting vigorously with metals to form salts •Most halogens exist in nature as diatomic molecules (i.e. F2, Cl2, Br2 and I2.) ...
The Periodic Table
... Describe the Periodic Table • The different rows of elements are called periods. – Tell you the number of energy levels (ex: Period 3 has 3 energy levels) • The different columns of elements are called groups or families – Elements in the same family have similar properties and the same number of e ...
... Describe the Periodic Table • The different rows of elements are called periods. – Tell you the number of energy levels (ex: Period 3 has 3 energy levels) • The different columns of elements are called groups or families – Elements in the same family have similar properties and the same number of e ...
Novel Class of Heterometallic Cubane and Boride Clusters
... ABSTRACT: Thermolysis of an in situ generated intermediate, produced from the reaction of [Cp*MoCl4] (Cp* = η5C5Me5) and [LiBH4.THF], with excess Te powder yielded isomeric [(Cp*Mo)2B4TeH5Cl] (2 and 3), [(Cp*Mo)2B4(μ3OEt)TeH3Cl] (4), and [(Cp*Mo)4B4H4(μ4-BH)3] (5). Cluster 4 is a notable example of ...
... ABSTRACT: Thermolysis of an in situ generated intermediate, produced from the reaction of [Cp*MoCl4] (Cp* = η5C5Me5) and [LiBH4.THF], with excess Te powder yielded isomeric [(Cp*Mo)2B4TeH5Cl] (2 and 3), [(Cp*Mo)2B4(μ3OEt)TeH3Cl] (4), and [(Cp*Mo)4B4H4(μ4-BH)3] (5). Cluster 4 is a notable example of ...
vocab - SALAZAR!!
... Sentence: The Lanthanide series is the second row from the bottom. 6. Actinide series- The actinide series is much different. They are all radioactive and some are not found in nature. Sentence: The Actinide series is very reactive. 7. Noble Gas- The noble gases make a group of chemical elements wit ...
... Sentence: The Lanthanide series is the second row from the bottom. 6. Actinide series- The actinide series is much different. They are all radioactive and some are not found in nature. Sentence: The Actinide series is very reactive. 7. Noble Gas- The noble gases make a group of chemical elements wit ...
Slide 1
... How did chemists begin to organize the known elements? How did Mendeleev organize his periodic table? How is the modern periodic table organized? What are three broad classes of elements? ...
... How did chemists begin to organize the known elements? How did Mendeleev organize his periodic table? How is the modern periodic table organized? What are three broad classes of elements? ...
Unit 4 notes
... xenon, and radon. All the noble gases are found in small amounts in the earth's atmosphere. ...
... xenon, and radon. All the noble gases are found in small amounts in the earth's atmosphere. ...
TOC 9/18 Organization of Periodic Table
... Reactivity is a chemical property that determines how elements will react with others to form compounds. ...
... Reactivity is a chemical property that determines how elements will react with others to form compounds. ...
How the Periodic Table Works
... are nonmetals (poor conductors of heat and electricity). The remaining elements are metalloids, which share properties of both metals and nonmetals. Let's look at some of these element cliques and remember, sometimes group members are spread around the table, not necessarily in one neat column. For ...
... are nonmetals (poor conductors of heat and electricity). The remaining elements are metalloids, which share properties of both metals and nonmetals. Let's look at some of these element cliques and remember, sometimes group members are spread around the table, not necessarily in one neat column. For ...
Periodic Table HW Unit
... Elements can be differentiated by chemical properties. Chemical properties describe how an element behaves during a chemical reaction. Some elements exist in two or more forms in the same phase. These ...
... Elements can be differentiated by chemical properties. Chemical properties describe how an element behaves during a chemical reaction. Some elements exist in two or more forms in the same phase. These ...