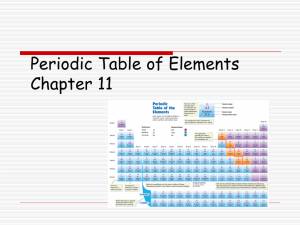
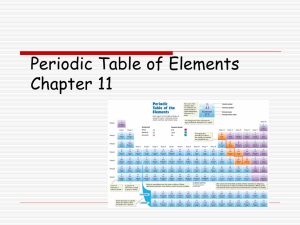
Now
... ‘d block’ elements are called outer transition elements because they contain at most two electrons in their outer shell. The elements for which f sub shells are filling are called the inner transition elements. Based on electronic configuration, all elements are grouped into four categories. They ar ...
... ‘d block’ elements are called outer transition elements because they contain at most two electrons in their outer shell. The elements for which f sub shells are filling are called the inner transition elements. Based on electronic configuration, all elements are grouped into four categories. They ar ...
The Organization of the Elements
... number, and therefore organized the table by nuclear charge (or atomic number) rather than atomic weight. Thus Moseley placed argon (atomic number 18) before potassium (atomic number 19) based on their X-ray wavelengths, despite the fact that argon has a greater atomic weight (39.9) than potassium ( ...
... number, and therefore organized the table by nuclear charge (or atomic number) rather than atomic weight. Thus Moseley placed argon (atomic number 18) before potassium (atomic number 19) based on their X-ray wavelengths, despite the fact that argon has a greater atomic weight (39.9) than potassium ( ...
Periodic Table Notes
... grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families in the periodic table. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, by their properties. Metals are found to the left of the zigzag line. Atoms of mo ...
... grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families in the periodic table. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, by their properties. Metals are found to the left of the zigzag line. Atoms of mo ...
Rem001 - The Vital Chemist
... Members include Lithium Li., Sodium Na, Potassium K, Rubidium Rb, Caesium Cs and Francium Fr. They are not found free in nature due to their high reactivity. They are so easily oxidised. Francium and Caesium are short-lived and radioactive isotopes but the others are common on earth’s crust. Each co ...
... Members include Lithium Li., Sodium Na, Potassium K, Rubidium Rb, Caesium Cs and Francium Fr. They are not found free in nature due to their high reactivity. They are so easily oxidised. Francium and Caesium are short-lived and radioactive isotopes but the others are common on earth’s crust. Each co ...
The d-and f-Block Elements
... ionization energy increases gradually as we move from left to right, and it is due to the increase in nuclear charge. It may be noted that the first ionization energies of 5d elements lie higher than those of 3d and 4d elements because of the weak shielding of the nucleus by 4f electrons. Further th ...
... ionization energy increases gradually as we move from left to right, and it is due to the increase in nuclear charge. It may be noted that the first ionization energies of 5d elements lie higher than those of 3d and 4d elements because of the weak shielding of the nucleus by 4f electrons. Further th ...
2 Atoms, Bonding, and the Periodic Table
... way to depict the number of valence electrons in an element. An electron dot diagram includes the symbol for the element surrounded by dots. Each dot stands for one valence electron. Chemical Bonds and Stability Most atoms are more sta- ...
... way to depict the number of valence electrons in an element. An electron dot diagram includes the symbol for the element surrounded by dots. Each dot stands for one valence electron. Chemical Bonds and Stability Most atoms are more sta- ...
Placing Elements on the Periodic Table
... grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families in the periodic table. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, by their properties. Metals are found to the left of the zigzag line. Atoms of mo ...
... grouped into families based on their chemical properties. Each family has a specific name to differentiate it from the other families in the periodic table. Elements are classified as metals, nonmetals, and metalloids, by their properties. Metals are found to the left of the zigzag line. Atoms of mo ...
The Evolution of the Periodic System - Science
... in London discovered the element argon; over the next few years, Ramsay announced the identification of four other elements—helium, neon, krypton and xenon—known as the noble gases. (The last of the known noble gases, radon, was discovered in 1900 by German physicist Friedrich Ernst Dorn.) The name ...
... in London discovered the element argon; over the next few years, Ramsay announced the identification of four other elements—helium, neon, krypton and xenon—known as the noble gases. (The last of the known noble gases, radon, was discovered in 1900 by German physicist Friedrich Ernst Dorn.) The name ...
The Evolution of the Periodic System
... in London discovered the element argon; over the next few years, Ramsay announced the identification of four other elements—helium, neon, krypton and xenon—known as the noble gases. (The last of the known noble gases, radon, was discovered in 1900 by German physicist Friedrich Ernst Dorn.) The name ...
... in London discovered the element argon; over the next few years, Ramsay announced the identification of four other elements—helium, neon, krypton and xenon—known as the noble gases. (The last of the known noble gases, radon, was discovered in 1900 by German physicist Friedrich Ernst Dorn.) The name ...
Chapter 22 - 2012 Book Archive
... uses. Both indium and thallium oxides are released in flue dust when sulfide ores are converted to metal oxides and SO2. Until relatively recently, these and other toxic elements were allowed to disperse in the air, creating large “dead zones” downwind of a smelter. The flue dusts are now trapped an ...
... uses. Both indium and thallium oxides are released in flue dust when sulfide ores are converted to metal oxides and SO2. Until relatively recently, these and other toxic elements were allowed to disperse in the air, creating large “dead zones” downwind of a smelter. The flue dusts are now trapped an ...
Electrons in Atoms - Effingham County Schools
... Hydrogen has an electron configuration of 1s1, but despite the ns1 configuration, it does not share the same properties as the elements of Group 1 ...
... Hydrogen has an electron configuration of 1s1, but despite the ns1 configuration, it does not share the same properties as the elements of Group 1 ...
Document
... Development of the Periodic Table (cont.) • Meyer and Mendeleev both demonstrated a connection between atomic mass and elemental properties. • Moseley rearranged the table by increasing atomic number, and resulted in a clear periodic pattern. • Periodic repetition of chemical and physical propertie ...
... Development of the Periodic Table (cont.) • Meyer and Mendeleev both demonstrated a connection between atomic mass and elemental properties. • Moseley rearranged the table by increasing atomic number, and resulted in a clear periodic pattern. • Periodic repetition of chemical and physical propertie ...
File
... linear accelerator at the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy Ion Research in Germany. It created the calcium-ions used in new tests that produced element 117. For now, number 117 is the most massive element confirmed to exist! Success Criteria: Can I recognize that all matter consists of atoms? (SPI0807 ...
... linear accelerator at the GSI Helmholtz Center for Heavy Ion Research in Germany. It created the calcium-ions used in new tests that produced element 117. For now, number 117 is the most massive element confirmed to exist! Success Criteria: Can I recognize that all matter consists of atoms? (SPI0807 ...
Periodic Table
... between Groups 3 and 4 in the sixth and seventh periods. Their position reflects the fact that they involve the filling of the 4f sublevel. The first row of the f block, the lanthanides, are shiny metals similar in reactivity to the Group 2 alkaline metals. The second row of the f block, the actinid ...
... between Groups 3 and 4 in the sixth and seventh periods. Their position reflects the fact that they involve the filling of the 4f sublevel. The first row of the f block, the lanthanides, are shiny metals similar in reactivity to the Group 2 alkaline metals. The second row of the f block, the actinid ...
xi_chem_ch3_classification of elements
... 21. Fourth and fifth period contains 18 elements 22. Sixth period contains 32 elements 23. In the modern periodic table, 14 elements of both sixth and seventh periods i.e. lanthanoids and actinoids respectively are placed separately at the bottom of the periodic table. 24. Elements with atomic numbe ...
... 21. Fourth and fifth period contains 18 elements 22. Sixth period contains 32 elements 23. In the modern periodic table, 14 elements of both sixth and seventh periods i.e. lanthanoids and actinoids respectively are placed separately at the bottom of the periodic table. 24. Elements with atomic numbe ...
The Upper Limit of the Periodic Table of Elements Points out to the
... table consisting of cells (each single cell manifests a single element). The cells are joined into periods along the horizontal axis (each row represents a single period), while the cells are joined into groups along the vertical axis (each column represents a single group). The resulting system is ...
... table consisting of cells (each single cell manifests a single element). The cells are joined into periods along the horizontal axis (each row represents a single period), while the cells are joined into groups along the vertical axis (each column represents a single group). The resulting system is ...
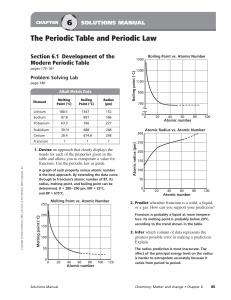
The Periodic Table and Periodic Law
... groups and periods that the elements are in. Without this information, you cannot apply the periodic trends in atomic size to determine which element has the larger radius. ...
... groups and periods that the elements are in. Without this information, you cannot apply the periodic trends in atomic size to determine which element has the larger radius. ...
Unit 3.pmd
... same principal quantum level, the shielding effect of inner core of electrons does not increase very much to compensate for the increased attraction of the electron to the nucleus. ...
... same principal quantum level, the shielding effect of inner core of electrons does not increase very much to compensate for the increased attraction of the electron to the nucleus. ...
Record: 1 THE EVOLUTION OF THE PERIODIC SYSTEM Page 1 of
... in London discovered the element argon; over the next few years, Ramsay announced the identification of four other elements--helium, neon, krypton and xenon--known as the noble gases. (The last of the known noble gases, radon, was discovered in 1900 by German physicist Friedrich Ernst Dorn.) The nam ...
... in London discovered the element argon; over the next few years, Ramsay announced the identification of four other elements--helium, neon, krypton and xenon--known as the noble gases. (The last of the known noble gases, radon, was discovered in 1900 by German physicist Friedrich Ernst Dorn.) The nam ...
D. - Telluride Middle/High School
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
ch 6 ppt - Madison County Schools
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
Chapter 6 PP
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
Document
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
... • Ionization energies generally increase from left to right across a period, and decrease as you move down a group. • The octet rule states that atoms gain, lose, or share electrons to acquire a full set of eight valence electrons. • Electronegativity generally increases from left to right across a ...
File
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
H Unit 4: Periodic Table
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...
... The table is also arranged in vertical columns called “groups” or “families” and horizontal rows called “periods.” Each arrangement is significant. The elements in each vertical column or group have similar properties. There are a number of major groups with similar properties. They are as follows: ...