The Bedside and Office Neuro-ophthalmology Examination. James J
... a sensitive test of residual visual deficits in patients with optic neuritis in whom high-contrast conventional visual acuity and color vision may be normal. Although ...
... a sensitive test of residual visual deficits in patients with optic neuritis in whom high-contrast conventional visual acuity and color vision may be normal. Although ...
PDF
... Choroid, iris and ciliary body. The choroidal anlage can be observed as early as day 12 in the form of a layer of capillaries developing externally to the outer layer of the optic cup. This vascular network becomes increasingly complex during later prenatal stages and by day 21 large blood vessels a ...
... Choroid, iris and ciliary body. The choroidal anlage can be observed as early as day 12 in the form of a layer of capillaries developing externally to the outer layer of the optic cup. This vascular network becomes increasingly complex during later prenatal stages and by day 21 large blood vessels a ...
View Full Page PDF
... identified that do not conform to this pattern, but they remain in the minority and do not appear to arise from any specific functional class (76). This pattern appears to be present in all of the mammals studied to date. However, depending on the animal type, it can change in the proximal optic ner ...
... identified that do not conform to this pattern, but they remain in the minority and do not appear to arise from any specific functional class (76). This pattern appears to be present in all of the mammals studied to date. However, depending on the animal type, it can change in the proximal optic ner ...
Summer 2012 - Macula Vision Research Foundation
... for initiating additional trials using a larger group of individuals to more fully evaluate plantation as a possible therapeutic treatment for these diseases. In another study ...
... for initiating additional trials using a larger group of individuals to more fully evaluate plantation as a possible therapeutic treatment for these diseases. In another study ...
Structures of the Eye
... • Retina • Sensitive nerve cell layer • Changes the energy of the light rays into nerve impulses • Transmits nerve impulses via optic nerve to brain for interpretation of the image seen by the eye ...
... • Retina • Sensitive nerve cell layer • Changes the energy of the light rays into nerve impulses • Transmits nerve impulses via optic nerve to brain for interpretation of the image seen by the eye ...
Embryological Development of Skeletal Structures of Head and
... cord to form the neural tube. As the folds fuse, the neural tube separates from the overlying ectoderm from which it is derived. A population of ectodermal cells adjacent to the neural fold and not included in the overlying surface (somatic) ectoderm gives rise to the formation of the neural crest. ...
... cord to form the neural tube. As the folds fuse, the neural tube separates from the overlying ectoderm from which it is derived. A population of ectodermal cells adjacent to the neural fold and not included in the overlying surface (somatic) ectoderm gives rise to the formation of the neural crest. ...
Inhibition of dexamethasone-induced cytoskeletal changes in
... humans. In addition, a preliminary experiment suggested that THF was also an effective ocular hypotensive agent in patients with primary open angle glaucoma. The current study was conducted to determine the IOP-lowering mechanism of action of THF. Tetrahydrocortisol was tested in rats for its abilit ...
... humans. In addition, a preliminary experiment suggested that THF was also an effective ocular hypotensive agent in patients with primary open angle glaucoma. The current study was conducted to determine the IOP-lowering mechanism of action of THF. Tetrahydrocortisol was tested in rats for its abilit ...
July 2015 - ModernMedicine.com
... light is shone into one eye, it will cause a direct response in that eye to constrict, and a consensual response in the opposite eye to also constrict. When observing a pupil’s direct and consensual responses to light, the set-up should be normal to dim room illumination with the patient fxating on ...
... light is shone into one eye, it will cause a direct response in that eye to constrict, and a consensual response in the opposite eye to also constrict. When observing a pupil’s direct and consensual responses to light, the set-up should be normal to dim room illumination with the patient fxating on ...
Cha. 9 Autonomic Nervous System
... • enteric nervous system – nervous system in wall of digestive tract – does not arise from the brainstem or spinal cord – innervates smooth muscle and glands ...
... • enteric nervous system – nervous system in wall of digestive tract – does not arise from the brainstem or spinal cord – innervates smooth muscle and glands ...
Structural and Functional Ocular Imaging
... white‑on‑white change. “However, I believe,” Dr Garway‑Heath continued, “that this is not the true picture and actually structure and function damage probably proceeds in tandem; it’s simply the way that we think about it and measure structure and function that gives an apparent picture that structu ...
... white‑on‑white change. “However, I believe,” Dr Garway‑Heath continued, “that this is not the true picture and actually structure and function damage probably proceeds in tandem; it’s simply the way that we think about it and measure structure and function that gives an apparent picture that structu ...
polarization properties of the retinal nerve fiber layer
... anatomy will be discussed in detail later. Beneath the RNFL are the ganglion cell layer, inner plexiform layer, inner nuclear layer, outer plexiform layer, outer nuclear layer, and outer limiting membrane, which together act as a weakly scattering matrix with some laminar structure.29,43 The photore ...
... anatomy will be discussed in detail later. Beneath the RNFL are the ganglion cell layer, inner plexiform layer, inner nuclear layer, outer plexiform layer, outer nuclear layer, and outer limiting membrane, which together act as a weakly scattering matrix with some laminar structure.29,43 The photore ...
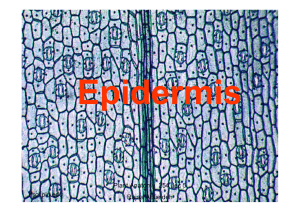
Epidermis
... leaf and on different leaves on same plant. It is affected by environmental conditions • In leaves it may occur on both sides or only on one side which is usually the lower one. • Vary depending on their position relative to epidermis could be : -even with other epidermal cells - raised above - belo ...
... leaf and on different leaves on same plant. It is affected by environmental conditions • In leaves it may occur on both sides or only on one side which is usually the lower one. • Vary depending on their position relative to epidermis could be : -even with other epidermal cells - raised above - belo ...
Vitamin A and Lipid Storage Disease
... In addition to the forms just shown, it must be remembered that the aldehyde form must exist in the 11-cis form (figure shown above) in order to be triggered by light while bound to opsin (as rhodopsin). Note also that the opsin and retinal are bound to each other as a protonated Schiff base . Just ...
... In addition to the forms just shown, it must be remembered that the aldehyde form must exist in the 11-cis form (figure shown above) in order to be triggered by light while bound to opsin (as rhodopsin). Note also that the opsin and retinal are bound to each other as a protonated Schiff base . Just ...
Caldesmon transgene expression disrupts focal adhesions in HTM
... Bahler et al., 2004; Tian et al., 2004). H-7 and latrunculininduced increases in outflow facility result from major morphological and architectural changes in the TM, including apparent cell relaxation, expansion of the juxtacanalicular region, dilation of Schlemm’s canal and luminal protrusion of t ...
... Bahler et al., 2004; Tian et al., 2004). H-7 and latrunculininduced increases in outflow facility result from major morphological and architectural changes in the TM, including apparent cell relaxation, expansion of the juxtacanalicular region, dilation of Schlemm’s canal and luminal protrusion of t ...
Ganglions
... a. stress, such as stretching of capsular and ligamentous supporting joint structures, stimulates the production of mucin, which produces cells that may be modified synovial cells, mesenchymal cells, or fibroblasts, all of which have been shown to produce hyaluronic acid. b. Modified synovial cells ...
... a. stress, such as stretching of capsular and ligamentous supporting joint structures, stimulates the production of mucin, which produces cells that may be modified synovial cells, mesenchymal cells, or fibroblasts, all of which have been shown to produce hyaluronic acid. b. Modified synovial cells ...
“Floaters” are usually normal and harmless
... You may also see flashes of light. These flashes occur more often in older people, and usually are caused by mechanical stimulation of photoreceptors when the gel-like vitreous occasionally tugs on the light-sensitive retina. They may be a warning sign of a detached retina – a very serious problem t ...
... You may also see flashes of light. These flashes occur more often in older people, and usually are caused by mechanical stimulation of photoreceptors when the gel-like vitreous occasionally tugs on the light-sensitive retina. They may be a warning sign of a detached retina – a very serious problem t ...
PDF - British Journal of Ophthalmology
... densely infiltrated throughout with similar cells, almost to the disappearance of normal structures. In the iris traces of the sphincter pupillae can be seen, and in the ciliary body fibres of the ciliary muscle can be detected. The pigment epithelium of the iris is intact, and the epithelium coveri ...
... densely infiltrated throughout with similar cells, almost to the disappearance of normal structures. In the iris traces of the sphincter pupillae can be seen, and in the ciliary body fibres of the ciliary muscle can be detected. The pigment epithelium of the iris is intact, and the epithelium coveri ...
CLINICAL APPROACH TO REFRACTIVE ERRORS
... What determines the type and amount of refractive error? • Refractive power of the cornea and the lens • Length of the eye (1m.m. changes represents about 3 dioptres change in refraction) • Refractive errors of up to 5 D are considered to be biological variation • Higher degrees of refractive error ...
... What determines the type and amount of refractive error? • Refractive power of the cornea and the lens • Length of the eye (1m.m. changes represents about 3 dioptres change in refraction) • Refractive errors of up to 5 D are considered to be biological variation • Higher degrees of refractive error ...
Microscopes
... 6. Clean a slide of the letter “e”. Place the slide onto the stage and secure in place with stage clips (the slide goes between the clips, not under them). Do NOT release the stage clips quickly or they can crack the slide. 7. Rotate the stage knobs so that the specimen to be viewed is directly over ...
... 6. Clean a slide of the letter “e”. Place the slide onto the stage and secure in place with stage clips (the slide goes between the clips, not under them). Do NOT release the stage clips quickly or they can crack the slide. 7. Rotate the stage knobs so that the specimen to be viewed is directly over ...
Chapter 1 The ear: some applied basic science
... The ear: some applied basic science Chapter 1 pneumatization is very variable and is usually reduced in chronic middle-ear disease when the mastoid is often said to be ‘sclerotic’. ...
... The ear: some applied basic science Chapter 1 pneumatization is very variable and is usually reduced in chronic middle-ear disease when the mastoid is often said to be ‘sclerotic’. ...
The Oculomotorl Nerve HO
... ciliary nerves that, branch a few times and pierce the sclera in a circle around the optic nerve. Here they are accompanied with the short posterior ciliary arteries. The short ciliary nerves then run forward deep to the sclera to reach the ciliary muscle and constrictor pupillae, which ...
... ciliary nerves that, branch a few times and pierce the sclera in a circle around the optic nerve. Here they are accompanied with the short posterior ciliary arteries. The short ciliary nerves then run forward deep to the sclera to reach the ciliary muscle and constrictor pupillae, which ...
Differential Effects of Early Monocular Deprivation on Binocular and
... segment. The nondeprived monocular segment was easily found. Tt contained simple and complex cells (10 and 7, respectively) in apparently normal numbers, and their receptive fields were comparable to those found in monocular segments of normal cats (26). Responses of two of these cells are illustrat ...
... segment. The nondeprived monocular segment was easily found. Tt contained simple and complex cells (10 and 7, respectively) in apparently normal numbers, and their receptive fields were comparable to those found in monocular segments of normal cats (26). Responses of two of these cells are illustrat ...
Dr Ziai chronic visual loss_compressed
... profound loss of vision RAPD is present orange reflex from the choroid stands out at the fovea, and contrasts with the surrounding pale retina (cherry-red ...
... profound loss of vision RAPD is present orange reflex from the choroid stands out at the fovea, and contrasts with the surrounding pale retina (cherry-red ...
Evaluating and Treating Vision for Neurological Patients in Acute Care
... • Head tilt, shutting one eye, squinting, headaches, muscle aches, increased spasticity, nausea, BP/HR with movement, decreased cooperation, increased agitation ...
... • Head tilt, shutting one eye, squinting, headaches, muscle aches, increased spasticity, nausea, BP/HR with movement, decreased cooperation, increased agitation ...
牂楡獮整m
... perforated substance to the medial surface of the frontal lobe under the genu of the corpus callosum. The olfactory epithelium occupies an area of about 2 cm2 in the roof of each nasal cavity, overlying portions of the superior nasal concha and of the nasal septum. It contains receptor cells, suppor ...
... perforated substance to the medial surface of the frontal lobe under the genu of the corpus callosum. The olfactory epithelium occupies an area of about 2 cm2 in the roof of each nasal cavity, overlying portions of the superior nasal concha and of the nasal septum. It contains receptor cells, suppor ...
Photoreceptor cell

A photoreceptor cell is a specialized type of neuron found in the retina that is capable of phototransduction. The great biological importance of photoreceptors is that they convert light (visible electromagnetic radiation) into signals that can stimulate biological processes. To be more specific, photoreceptor proteins in the cell absorb photons, triggering a change in the cell's membrane potential.The two classic photoreceptor cells are rods and cones, each contributing information used by the visual system to form a representation of the visual world, sight. The rods are narrower than the cones and distributed differently across the retina, but the chemical process in each that supports phototransduction is similar. A third class of photoreceptor cells was discovered during the 1990s: the photosensitive ganglion cells. These cells do not contribute to sight directly, but are thought to support circadian rhythms and pupillary reflex.There are major functional differences between the rods and cones. Rods are extremely sensitive, and can be triggered by a single photon. At very low light levels, visual experience is based solely on the rod signal. This explains why colors cannot be seen at low light levels: only one type of photoreceptor cell is active.Cones require significantly brighter light (i.e., a larger numbers of photons) in order to produce a signal. In humans, there are three different types of cone cell, distinguished by their pattern of response to different wavelengths of light. Color experience is calculated from these three distinct signals, perhaps via an opponent process. The three types of cone cell respond (roughly) to light of short, medium, and long wavelengths. Note that, due to the principle of univariance, the firing of the cell depends upon only the number of photons absorbed. The different responses of the three types of cone cells are determined by the likelihoods that their respective photoreceptor proteins will absorb photons of different wavelengths. So, for example, an L cone cell contains a photoreceptor protein that more readily absorbs long wavelengths of light (i.e., more ""red""). Light of a shorter wavelength can also produce the same response, but it must be much brighter to do so.The human retina contains about 120 million rod cells and 6 million cone cells. The number and ratio of rods to cones varies among species, dependent on whether an animal is primarily diurnal or nocturnal. Certain owls, such as the tawny owl, have a tremendous number of rods in their retinae. In addition, there are about 2.4 million to 3 million ganglion cells in the human visual system, the axons of these cells form the 2 optic nerves, 1 to 2% of them photosensitive.The pineal and parapineal glands are photoreceptive in non-mammalian vertebrates, but not in mammals. Birds have photoactive cerebrospinal fluid (CSF)-contacting neurons within the paraventricular organ that respond to light in the absence of input from the eyes or neurotransmitters. Invertebrate photoreceptors in organisms such as insects and molluscs are different in both their morphological organization and their underlying biochemical pathways. Described here are human photoreceptors.