10.1 Early Ideas About Evolution
... • KEY CONCEPT: Darwin’s voyage provided insights into evolution • Darwin observed Differences among island species. This is called variation. • Variation is the difference in the physical traits of an individual from those of other individuals in the group to which it belongs. ...
... • KEY CONCEPT: Darwin’s voyage provided insights into evolution • Darwin observed Differences among island species. This is called variation. • Variation is the difference in the physical traits of an individual from those of other individuals in the group to which it belongs. ...
BIO CPE
... New traits may result from new combinations of existing genes or from mutations of genes in reproductive cells within a population. 5.3.12.E.2 Molecular evidence (e.g., DNA, protein structures, etc.) substantiates the anatomical evidence for evolution and provides additional detail about the sequenc ...
... New traits may result from new combinations of existing genes or from mutations of genes in reproductive cells within a population. 5.3.12.E.2 Molecular evidence (e.g., DNA, protein structures, etc.) substantiates the anatomical evidence for evolution and provides additional detail about the sequenc ...
Document
... (1) Part of satellite DNA that forms small peaks during density gradient centrifugation. (2) Constitute small portion of genome. ...
... (1) Part of satellite DNA that forms small peaks during density gradient centrifugation. (2) Constitute small portion of genome. ...
File - Biology by Napier
... 26. Why is it said that natural selection acts on the phenotypes rather than on the genetic material of organisms? Phenotypes are the actual traits being used for survival, genes just code for them Ch 11.3 Other Mechanisms of Evolution (pg 323-325) 27. What is gene flow? Genes and traits moving from ...
... 26. Why is it said that natural selection acts on the phenotypes rather than on the genetic material of organisms? Phenotypes are the actual traits being used for survival, genes just code for them Ch 11.3 Other Mechanisms of Evolution (pg 323-325) 27. What is gene flow? Genes and traits moving from ...
APPENDIX A: FITNESS DERIVATIVES AND BRANCHING CRITERIA
... One of the striking observations from recent whole-genome comparisons is that changes in the number of specialized genes in existing gene families, as opposed to novel taxon-specific gene families, are responsible for the majority of the difference in genome composition between major taxa. Previous ...
... One of the striking observations from recent whole-genome comparisons is that changes in the number of specialized genes in existing gene families, as opposed to novel taxon-specific gene families, are responsible for the majority of the difference in genome composition between major taxa. Previous ...
appendix 2: linear invasion matrix of a novel duplicate
... One of the striking observations from recent whole-genome comparisons is that changes in the number of specialized genes in existing gene families, as opposed to novel taxon-specific gene families, are responsible for the majority of the difference in genome composition between major taxa. Previous ...
... One of the striking observations from recent whole-genome comparisons is that changes in the number of specialized genes in existing gene families, as opposed to novel taxon-specific gene families, are responsible for the majority of the difference in genome composition between major taxa. Previous ...
What should I know about Evolution for the Chapter Test?
... How are epigenetic changes different than Lamarck’s idea of “inheritance of acquired traits”? ...
... How are epigenetic changes different than Lamarck’s idea of “inheritance of acquired traits”? ...
1. Explain the importance of the fossil record to the
... genes for those proteins evolved from a common gene present in a shared ancestor DNA and RNA comparisons a. DNA-DNA hybridization – compares whole genomes by measuring the degree of H bonds between 2 sources b. restriction maps – information about the match-up of specific DNA nucleotide sequences ...
... genes for those proteins evolved from a common gene present in a shared ancestor DNA and RNA comparisons a. DNA-DNA hybridization – compares whole genomes by measuring the degree of H bonds between 2 sources b. restriction maps – information about the match-up of specific DNA nucleotide sequences ...
evolutionary pathways?
... The capacity to produce good solutions via evolution Genome’s ability to produce adaptive variants when acted on by the genetic system (Wagner and Altenberg, 1996) Capacity to generate heritable phenotypic variation (Kirshner and Gerhart, 1998) Capacity to create new adaptations, and especially new ...
... The capacity to produce good solutions via evolution Genome’s ability to produce adaptive variants when acted on by the genetic system (Wagner and Altenberg, 1996) Capacity to generate heritable phenotypic variation (Kirshner and Gerhart, 1998) Capacity to create new adaptations, and especially new ...
Systematic and evolutionary biology
... –Variable, changing!! –iPlant model for information ‘ownership’? http://iplantcollaborative.org/aboutipc/cyberinfrastructure ...
... –Variable, changing!! –iPlant model for information ‘ownership’? http://iplantcollaborative.org/aboutipc/cyberinfrastructure ...
Review Book Topic D: Evolution - wfs
... hunting and agriculture, religion, art, etc.). 22. Cultural evolution is the development of new methods, inventions, or customs. It is distinct from genetic evolution in that it: a. does not involve changes in the allele frequencies in the gene pool; b. can happen during one human lifetime, whereas ...
... hunting and agriculture, religion, art, etc.). 22. Cultural evolution is the development of new methods, inventions, or customs. It is distinct from genetic evolution in that it: a. does not involve changes in the allele frequencies in the gene pool; b. can happen during one human lifetime, whereas ...
UNIT 5: EVOLUTION
... 22. The supposed ancestor of the genus Homo, “Lucy” is the most-common fossil of this type, which follows the out-of-Africa hypothesis. 23. An organism (such as a primate) that can walk on two legs is called this. 24. The diversity of a species into a number of different species, often over a relati ...
... 22. The supposed ancestor of the genus Homo, “Lucy” is the most-common fossil of this type, which follows the out-of-Africa hypothesis. 23. An organism (such as a primate) that can walk on two legs is called this. 24. The diversity of a species into a number of different species, often over a relati ...
HealthGrid Conference
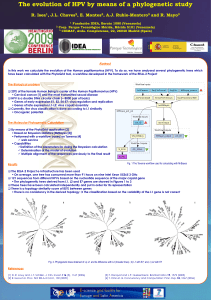
... Definition of the parameters for doing the Bayesian calculation Determination of the model of evolution Multiple alignment of the sequences previously to the final result Fig. 1 The Taverna workflow used for calculating with MrBayes ...
... Definition of the parameters for doing the Bayesian calculation Determination of the model of evolution Multiple alignment of the sequences previously to the final result Fig. 1 The Taverna workflow used for calculating with MrBayes ...
Chapter 1 Exam Review
... 8. ______ Cells working together to carry out a common function is called an organ. 9. ______ An adaptation is a variation that can help an organism reproduce or survive in its environment. 10. ______ Theories help scientists explain large bodies of data. 11. ______ DNA is the smallest unit capable ...
... 8. ______ Cells working together to carry out a common function is called an organ. 9. ______ An adaptation is a variation that can help an organism reproduce or survive in its environment. 10. ______ Theories help scientists explain large bodies of data. 11. ______ DNA is the smallest unit capable ...
Lecture 2
... Is a 4-chambered heart an homologous or analogous character between mammals & birds? Homologous ...
... Is a 4-chambered heart an homologous or analogous character between mammals & birds? Homologous ...
THEME 1: EVOLUTION OF CHEMOTAXIS
... To determine how selection changes the response of single-cells to spatially defined chemical gradients, students will perform single-cell chemotactic response measurements using an optical trapping-based ‘bacterial-treadmill’ assay. Techniques include optical trapping and data analysis with Matlab. ...
... To determine how selection changes the response of single-cells to spatially defined chemical gradients, students will perform single-cell chemotactic response measurements using an optical trapping-based ‘bacterial-treadmill’ assay. Techniques include optical trapping and data analysis with Matlab. ...
Charles Darwin
... CAUSES OF MACROEVOLUTION • Convergent Evolution • Unrelated species evolve similar traits due to similar environments even though they live in different parts of the world ...
... CAUSES OF MACROEVOLUTION • Convergent Evolution • Unrelated species evolve similar traits due to similar environments even though they live in different parts of the world ...
Chapter 23 outline
... to maintain stable frequencies of two or more phenotypic forms in a population. Two mechanisms: Heterozygote Advantage – If individuals who are heterozygous at a particular locus have greater survivorship and reproductive success than any type of homozygote, then two or more alleles will be maintain ...
... to maintain stable frequencies of two or more phenotypic forms in a population. Two mechanisms: Heterozygote Advantage – If individuals who are heterozygous at a particular locus have greater survivorship and reproductive success than any type of homozygote, then two or more alleles will be maintain ...
Phenotype Genotype and the Environment
... Bell Curve: It is a graph of normal-distribution. In any normal population this would be the distribution of traits that you would expect ...
... Bell Curve: It is a graph of normal-distribution. In any normal population this would be the distribution of traits that you would expect ...
Evolution Review Guide
... 4) Darwin proposed that natural selection takes place as individuals best suited / adapted to the survive and reproduce. 5) A sunflower produces many seeds. Will all of the seeds grow into mature plants? Explain. ...
... 4) Darwin proposed that natural selection takes place as individuals best suited / adapted to the survive and reproduce. 5) A sunflower produces many seeds. Will all of the seeds grow into mature plants? Explain. ...
ZO317 - NUI Galway
... This module is focused on key concepts in evolutionary biology including the mechanisms operating on molecules, on populations and those involved in the formation of new species. It will also include topics such as evolutioary repatterning of development, evolutionary constraint and bias and evoluti ...
... This module is focused on key concepts in evolutionary biology including the mechanisms operating on molecules, on populations and those involved in the formation of new species. It will also include topics such as evolutioary repatterning of development, evolutionary constraint and bias and evoluti ...