The evolution of genomic imprinting and X
... RNAs (snoRNAs). SnoRNAs are best known for their ability to guide posttranscriptional modification of target RNAs, the vast majority of which are non-coding structural RNAs, such as ribosomal RNA. Interestingly, at the PWS-AS domain there are two major arrays of snoRNAs, at least one of which does n ...
... RNAs (snoRNAs). SnoRNAs are best known for their ability to guide posttranscriptional modification of target RNAs, the vast majority of which are non-coding structural RNAs, such as ribosomal RNA. Interestingly, at the PWS-AS domain there are two major arrays of snoRNAs, at least one of which does n ...
Article A Molecular Evolutionary Reference for the Human Variome
... each possible residue state at a given position in a species (species 1 in fig. 1), where the multispecies alignment is modified to replace the residue at the focal position with a missing data symbol (see Materials and Methods). Then, we compute multiple PP values by progressively pruning evolution ...
... each possible residue state at a given position in a species (species 1 in fig. 1), where the multispecies alignment is modified to replace the residue at the focal position with a missing data symbol (see Materials and Methods). Then, we compute multiple PP values by progressively pruning evolution ...
Fifteen years of genomewide scans for selection: trends, lessons
... mutations appear at different rates across the genome and signatures of selection vary among classes of mutational variants. Although it is possible to pinpoint specific mutations targeted by positive selection, most GWSS approaches look for the effects of selection on linked diversity. The length o ...
... mutations appear at different rates across the genome and signatures of selection vary among classes of mutational variants. Although it is possible to pinpoint specific mutations targeted by positive selection, most GWSS approaches look for the effects of selection on linked diversity. The length o ...
Genetic architecture and balancing selection: the life
... selection regimes generates specific population and genomic signatures. Balancing selection usually describes any form of natural selection resulting in the persistence of multiple variants of a given trait at intermediate frequencies within populations. Traits for which the frequency spectrum contr ...
... selection regimes generates specific population and genomic signatures. Balancing selection usually describes any form of natural selection resulting in the persistence of multiple variants of a given trait at intermediate frequencies within populations. Traits for which the frequency spectrum contr ...
Natural selection
... • It is generally impossible to predict the fate of alleles at all the loci ...
... • It is generally impossible to predict the fate of alleles at all the loci ...
slowly switching between environments facilitates reverse evolution
... Natural populations must constantly adapt to ever-changing environmental conditions. A particularly interesting question is whether such adaptations can be reversed by returning the population to an ancestral environment. Such evolutionary reversals have been observed in both natural and laboratory ...
... Natural populations must constantly adapt to ever-changing environmental conditions. A particularly interesting question is whether such adaptations can be reversed by returning the population to an ancestral environment. Such evolutionary reversals have been observed in both natural and laboratory ...
View PDF - Genetics
... ribosomal (Sloan et al. 2014b; Weng et al. 2016) and RNA polymerase complexes (Zhang et al. 2015), providing further evidence for changes in selection pressures. However, these studies could not confidently distinguish between two alternative explanations for increased dN/dS: positive selection an ...
... ribosomal (Sloan et al. 2014b; Weng et al. 2016) and RNA polymerase complexes (Zhang et al. 2015), providing further evidence for changes in selection pressures. However, these studies could not confidently distinguish between two alternative explanations for increased dN/dS: positive selection an ...
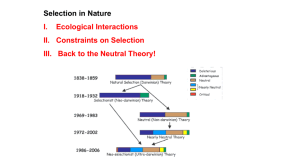
Selection - Integrative Biology
... genetically diverse offspring. There are several reasons for thinking this. One is that sexual reproduction is often associated with stress or environmental change, which is when variability would be most useful. Sexual reproduction is often associated with dispersal, and making it through an unfavo ...
... genetically diverse offspring. There are several reasons for thinking this. One is that sexual reproduction is often associated with stress or environmental change, which is when variability would be most useful. Sexual reproduction is often associated with dispersal, and making it through an unfavo ...
Selection - Integrative Biology
... genetically diverse offspring. There are several reasons for thinking this. One is that sexual reproduction is often associated with stress or environmental change, which is when variability would be most useful. Sexual reproduction is often associated with dispersal, and making it through an unfavo ...
... genetically diverse offspring. There are several reasons for thinking this. One is that sexual reproduction is often associated with stress or environmental change, which is when variability would be most useful. Sexual reproduction is often associated with dispersal, and making it through an unfavo ...
W = 1
... that were not killed by predators), estimating the mean shell thickness of these selected parents as xS 12mm . In a previous study, the same group of scientists had estimated that the slope of a regression of mid-parent shell thickness on offspring shell thickness was 0.50. Use this information to ...
... that were not killed by predators), estimating the mean shell thickness of these selected parents as xS 12mm . In a previous study, the same group of scientists had estimated that the slope of a regression of mid-parent shell thickness on offspring shell thickness was 0.50. Use this information to ...
Evolution of the Y Sex Chromosome in AnimalsY chromosomes
... The sexually antagonistic genes to accumulate on a primitive Y chrohypothesis was motivated by early mosome. To see why, consider a genetic mapping studies of the guppy, male-benefit sexually antagonistic a common aquarium fish with genic allele introduced by mutation just sex determination (or an u ...
... The sexually antagonistic genes to accumulate on a primitive Y chrohypothesis was motivated by early mosome. To see why, consider a genetic mapping studies of the guppy, male-benefit sexually antagonistic a common aquarium fish with genic allele introduced by mutation just sex determination (or an u ...
CHILL COMA ASSAY AND EVOLUTION INVESTIGATION
... melanogaster recover more rapidly from exposure to cold events than others. Considering what you learned about climate change and “whiplash weather” events it appears that it would be advantageous to be a fly from one of the strains that recovers most rapidly. Let’s explore how populations of organi ...
... melanogaster recover more rapidly from exposure to cold events than others. Considering what you learned about climate change and “whiplash weather” events it appears that it would be advantageous to be a fly from one of the strains that recovers most rapidly. Let’s explore how populations of organi ...
RidgeRace: ridge regression for continuous ancestral character
... the least-squares optimization technique of Cavalli-Sforza and Edwards (1967) for the inference of branch weights in a phylogeny via pairwise distances. RidgeRace does not assume certain rates at certain regions of the phylogeny or a particular model of rate change over time. It treats phenotypic me ...
... the least-squares optimization technique of Cavalli-Sforza and Edwards (1967) for the inference of branch weights in a phylogeny via pairwise distances. RidgeRace does not assume certain rates at certain regions of the phylogeny or a particular model of rate change over time. It treats phenotypic me ...
CHARACTERS AS THE UNITS OF EVOLUTIONARY CHANGE
... probabilities can accurately capture the fate of individuals. For example, transition probabilities may depend not just on the current state ofan individual in the model, but also on that individual's history, which would be expected to affect the state of variables, such as energy reserves, which a ...
... probabilities can accurately capture the fate of individuals. For example, transition probabilities may depend not just on the current state ofan individual in the model, but also on that individual's history, which would be expected to affect the state of variables, such as energy reserves, which a ...
Comparative genomics of the Brassicaceae
... Retention of duplicate genes is biased in favor of transcription factors, signal transducers, and developmental genes The divergence of these genes could have contributed to the increase in plant complexity seen in the origin of Angiosperm evolution and in the specialization of floral morphology to ...
... Retention of duplicate genes is biased in favor of transcription factors, signal transducers, and developmental genes The divergence of these genes could have contributed to the increase in plant complexity seen in the origin of Angiosperm evolution and in the specialization of floral morphology to ...
Evolutionary Biology www.AssignmentPoint.com Evolutionary
... genes are involved, how large are the effects of each gene, to what extent are the effects of different genes interdependent, what sort of function do the genes involved tend to have, and what sort of changes tend to happen to them (e.g., point mutations vs. gene duplication or even genome duplicati ...
... genes are involved, how large are the effects of each gene, to what extent are the effects of different genes interdependent, what sort of function do the genes involved tend to have, and what sort of changes tend to happen to them (e.g., point mutations vs. gene duplication or even genome duplicati ...
1 Rapid evolution of phenotypic plasticity and shifting thresholds of
... complex trait that can be heritable, subject to selection, and evolve. However, the rate and genetic basis of plasticity evolution remain largely unknown. We experimentally evolved outbred populations of the nematode Caenorhabditis remanei under an acute heat shock during early larval development. W ...
... complex trait that can be heritable, subject to selection, and evolve. However, the rate and genetic basis of plasticity evolution remain largely unknown. We experimentally evolved outbred populations of the nematode Caenorhabditis remanei under an acute heat shock during early larval development. W ...
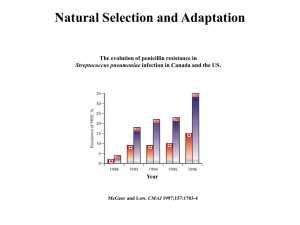
Natural Selection and Adaptation
... that were not killed by predators), estimating the mean shell thickness of these selected parents as xS 12mm . In a previous study, the same group of scientists had estimated that the slope of a regression of mid-parent shell thickness on offspring shell thickness was 0.50. Use this information to ...
... that were not killed by predators), estimating the mean shell thickness of these selected parents as xS 12mm . In a previous study, the same group of scientists had estimated that the slope of a regression of mid-parent shell thickness on offspring shell thickness was 0.50. Use this information to ...
(QTL) mapping for adaptive traits of tree growth in forests
... – Need constant supply – Optimal land use – Efficiency of scale for timber operations ...
... – Need constant supply – Optimal land use – Efficiency of scale for timber operations ...
Prokaryotic Evolution in Light of Gene Transfer
... of success for all recombinant cells. That is, the evolutionary importance of recombinatorial events will depend on the probability that the products of gene exchange offer selective advantages. If recombination has introduced maladaptive changes, eliminated niche-specific information, or disrupted ...
... of success for all recombinant cells. That is, the evolutionary importance of recombinatorial events will depend on the probability that the products of gene exchange offer selective advantages. If recombination has introduced maladaptive changes, eliminated niche-specific information, or disrupted ...
neutphylo
... - "Living Fossils" show extreme genetic change and variation, yet have remained morphologically unchanged for millennia. And, their rate of genetic change in this morphologically constant species is the same as in hominids, which have changed dramatically in morphology over a short period. PATTERN C ...
... - "Living Fossils" show extreme genetic change and variation, yet have remained morphologically unchanged for millennia. And, their rate of genetic change in this morphologically constant species is the same as in hominids, which have changed dramatically in morphology over a short period. PATTERN C ...
What is Situated Evolution?
... follow up –if sometimes only notionally– on Embodied Evolution, which was introduced by Watson, Ficici and Pollack [11], [28]. This introduces a truly autonomous scheme where agents broadcast (mutated) genes at a rate proportional to their fitness (Probabilistic Gene Transfer Algorithm, PGTA). This d ...
... follow up –if sometimes only notionally– on Embodied Evolution, which was introduced by Watson, Ficici and Pollack [11], [28]. This introduces a truly autonomous scheme where agents broadcast (mutated) genes at a rate proportional to their fitness (Probabilistic Gene Transfer Algorithm, PGTA). This d ...
Functional constraints and frequency of deleterious mutations in
... Previous attempts to quantify the fraction of conserved nucleotides have relied on searching for blocks of DNA sequences that are conserved between distantly related taxa (15–18). However, there are at least two difficulties with this approach. First, estimation of noncoding DNA sequence alignment b ...
... Previous attempts to quantify the fraction of conserved nucleotides have relied on searching for blocks of DNA sequences that are conserved between distantly related taxa (15–18). However, there are at least two difficulties with this approach. First, estimation of noncoding DNA sequence alignment b ...
Genetic consequences of directional selection in
... natural selection can be studied, random processes have to be well understood. At the level of an individual neutral locus genetic drift results in random fluctuations of allele frequencies in each generation (binomial variance of allele frequency change/generation σp² = p(1-p)/2N, where p is a fre ...
... natural selection can be studied, random processes have to be well understood. At the level of an individual neutral locus genetic drift results in random fluctuations of allele frequencies in each generation (binomial variance of allele frequency change/generation σp² = p(1-p)/2N, where p is a fre ...