Cultural Change in the Ancient Mediterranean and Near Eastern
... East. The multitude of cultural artifacts found in the archaeological record from the ancient Near East, from religious relics to everyday items to clay tablets with intercultural correspondences, provide valuable evidence that archaeologists use to both extract and construct the different types of ...
... East. The multitude of cultural artifacts found in the archaeological record from the ancient Near East, from religious relics to everyday items to clay tablets with intercultural correspondences, provide valuable evidence that archaeologists use to both extract and construct the different types of ...
The Heritage of Egypt - Egyptologists` Electronic Forum
... reconstructing them for “real” and thereafter since these varnishes often turned the original apply them on ancient Egyptian pigments white, red and blue pigments in respectively: equally reconstructed - to measure their yellow, dark red or brown, as well as dark blue chemical interactions over a lo ...
... reconstructing them for “real” and thereafter since these varnishes often turned the original apply them on ancient Egyptian pigments white, red and blue pigments in respectively: equally reconstructed - to measure their yellow, dark red or brown, as well as dark blue chemical interactions over a lo ...
Before Recorded History
... the honest, industrious folk found need of living together, that they might protect themselves from all those savage bands that came pillaging out of the desert. Therefore, two or three villages would unite, choosing one of their chieftains as king, and repaying him for his leadership by giving him ...
... the honest, industrious folk found need of living together, that they might protect themselves from all those savage bands that came pillaging out of the desert. Therefore, two or three villages would unite, choosing one of their chieftains as king, and repaying him for his leadership by giving him ...
EGYPT AND EARLY ISRAEL`S CULTURAL SETTING
... Kingdom dates were correct within a century. Middle Kingdom dates were correct within 20 or 30 years, and New Kingdom dates were correct within 10 or 20 years. 4 Controversies over Egyptian chronology have arisen because the ancient Egyptians did not systematize their world view. They saw the world ...
... Kingdom dates were correct within a century. Middle Kingdom dates were correct within 20 or 30 years, and New Kingdom dates were correct within 10 or 20 years. 4 Controversies over Egyptian chronology have arisen because the ancient Egyptians did not systematize their world view. They saw the world ...
Pharaoh Ramses II
... Meanwhile, the reverse could also be said about Muwasallis: he failed to build upon his initial victory and eventually suffered a humiliating loss; nonetheless, he did not lose Syria. After this famous Battle of Kadesh, Ramses II tried for several more times to take down the Hittite Empire to no ava ...
... Meanwhile, the reverse could also be said about Muwasallis: he failed to build upon his initial victory and eventually suffered a humiliating loss; nonetheless, he did not lose Syria. After this famous Battle of Kadesh, Ramses II tried for several more times to take down the Hittite Empire to no ava ...
Egyptian Architecture - worldcultures2-bbs
... Early Kingdom Tomb Pyramid • The pyramids designed as part of a funeral complex for burial of pharaoh • Chefren’s complex is best preserved example • Complex consist of three interconnected units: – A valley temple by the river Nile where the pharaoh’s body was embalmed – A pyramid mortuary temple ...
... Early Kingdom Tomb Pyramid • The pyramids designed as part of a funeral complex for burial of pharaoh • Chefren’s complex is best preserved example • Complex consist of three interconnected units: – A valley temple by the river Nile where the pharaoh’s body was embalmed – A pyramid mortuary temple ...
PDF article
... of narrative literature as experiences over time) or according to movement from place to place, for example through walls, down to the Underworld and eventually to the river lands that represent a sort of paradise after life. In having taken a rite of passage, individuals ‘achieve’ a state of being. ...
... of narrative literature as experiences over time) or according to movement from place to place, for example through walls, down to the Underworld and eventually to the river lands that represent a sort of paradise after life. In having taken a rite of passage, individuals ‘achieve’ a state of being. ...
Pharaoh Poster Project
... Where were the main cities during your pharaohs lifetime? Where were the political boundaries during your pharaoh’s lifetime? Where were other civilizations in relation to Egypt? ...
... Where were the main cities during your pharaohs lifetime? Where were the political boundaries during your pharaoh’s lifetime? Where were other civilizations in relation to Egypt? ...
Religion and the Afterlife Emphasis on the Afterlife Much of Egyptian
... The Egyptians believed that burial sites, especially royal tombs, were very important. For this reason, they built spectacular monuments in which to bury their rulers. The most spectacular were the pyramids—huge, stone tombs with four triangle-shaped sides that met in a point on top. The Egyptians b ...
... The Egyptians believed that burial sites, especially royal tombs, were very important. For this reason, they built spectacular monuments in which to bury their rulers. The most spectacular were the pyramids—huge, stone tombs with four triangle-shaped sides that met in a point on top. The Egyptians b ...
Genesis 41:25-57 • From Degradation to Exultation
... of a woman’s lies, forgotten for 2 years by a man he helped, and yet all these circumstances are used by God to elevate him to become the ruler of all Egypt and to be in the position to best carry out God’s will and help his family. Application: Do you think because “bad things” happen that God has ...
... of a woman’s lies, forgotten for 2 years by a man he helped, and yet all these circumstances are used by God to elevate him to become the ruler of all Egypt and to be in the position to best carry out God’s will and help his family. Application: Do you think because “bad things” happen that God has ...
1. Mesopotamia
... (Old Testament references to Cyrus, the threat of Croesus, Cyrus’s westward campaign, the ambiguous oracle to Croesus, battle with Croesus, fall of Sardis, sparing the life of Croesus, attack on Babylon, Belshazzar’s feast and Daniel’s prophecy, Daniel in the lion’s den, Daniel’s prayer and the visi ...
... (Old Testament references to Cyrus, the threat of Croesus, Cyrus’s westward campaign, the ambiguous oracle to Croesus, battle with Croesus, fall of Sardis, sparing the life of Croesus, attack on Babylon, Belshazzar’s feast and Daniel’s prophecy, Daniel in the lion’s den, Daniel’s prayer and the visi ...
Bell Ringer
... • he wisely took all the laws of the region’s city-states and unified them into one code. This helped unify the region. • Engraved in stone, erected all over the empire. • Strict in nature – “the punishment fits the crime” / “eye for an eye” Such laws were adopted by neighbors – many similar found i ...
... • he wisely took all the laws of the region’s city-states and unified them into one code. This helped unify the region. • Engraved in stone, erected all over the empire. • Strict in nature – “the punishment fits the crime” / “eye for an eye” Such laws were adopted by neighbors – many similar found i ...
Presentation Plus! - Central Dauphin School District
... The Middle Kingdom • About 2300 B.C., government officials, jealous of the pharaoh’s power, took control of Egypt. • Almost 200 years of confusion followed. • Finally, new pharaohs brought peace and a new period called the Middle Kingdom. • Pharaohs had less power in the Middle Kingdom. • ...
... The Middle Kingdom • About 2300 B.C., government officials, jealous of the pharaoh’s power, took control of Egypt. • Almost 200 years of confusion followed. • Finally, new pharaohs brought peace and a new period called the Middle Kingdom. • Pharaohs had less power in the Middle Kingdom. • ...
History - Ancient Egypt
... cult of the goddess Isis spread throughout the Roman Empire. But Egyptians were also open to foreign religious ideas. The Persians did little to impose their gods on the country when they sacked Thebes in the 6th century BC and made Egypt part of their empire. Two centuries later, Alexander the Grea ...
... cult of the goddess Isis spread throughout the Roman Empire. But Egyptians were also open to foreign religious ideas. The Persians did little to impose their gods on the country when they sacked Thebes in the 6th century BC and made Egypt part of their empire. Two centuries later, Alexander the Grea ...
1 - LaCourART
... The dominating feature of the statuary-lined approach to a New Kingdom temple was the monumental façade of the pylon, with was routinely covered with reliefs glorifying Egypt's rulers. Inside, was an open court with columns on two or more sides, followed by a hall between the court and sanctuary, it ...
... The dominating feature of the statuary-lined approach to a New Kingdom temple was the monumental façade of the pylon, with was routinely covered with reliefs glorifying Egypt's rulers. Inside, was an open court with columns on two or more sides, followed by a hall between the court and sanctuary, it ...
Ancient Egyptians
... Akhenaten changed the religion. Because many people did not agree, his monuments were destroyed and his name was scratched off of statues shortly after his death. 1479- Hatshepsut began rule after she was widowed by Thutmose II. ...
... Akhenaten changed the religion. Because many people did not agree, his monuments were destroyed and his name was scratched off of statues shortly after his death. 1479- Hatshepsut began rule after she was widowed by Thutmose II. ...
Egyptian Art - WordPress.com
... ended in 332 BC) This image records the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt into the “Kingdom of Two Lands” at the very end of the Predynastic period. ...
... ended in 332 BC) This image records the unification of Upper and Lower Egypt into the “Kingdom of Two Lands” at the very end of the Predynastic period. ...
An introduction to the scientific study of mummies - Beck-Shop
... Historical background Mummification (the artificial preservation of the body after death) may have been practised in Egypt for more than 4,000 years, and perhaps developed as early as c. 4500 b.c., when Neolithic communities lived in scattered settlements in the Egyptian Delta and along the banks of t ...
... Historical background Mummification (the artificial preservation of the body after death) may have been practised in Egypt for more than 4,000 years, and perhaps developed as early as c. 4500 b.c., when Neolithic communities lived in scattered settlements in the Egyptian Delta and along the banks of t ...
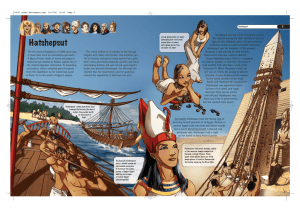
the story of Ancient Egyptian leader, Queen
... For the ancient Egyptians of 3,500 years ago, it must have been an astonishing spectacle. A fleet of boats made of wood and papyrus reeds had just docked at Thebes, capital city of the mighty Egyptian civilization. To mounting excitement, sailors unloaded great treasures from the expedition to the m ...
... For the ancient Egyptians of 3,500 years ago, it must have been an astonishing spectacle. A fleet of boats made of wood and papyrus reeds had just docked at Thebes, capital city of the mighty Egyptian civilization. To mounting excitement, sailors unloaded great treasures from the expedition to the m ...
EgyptandNubia
... Egyptinnpolicy'in l{ubin in, the Old a,ndMi,ddlelQngdorn The E,gyptianNew Kingdom presencein Nubia cannot be consideredi,n vacwo, but hasto be seenasthe third phaseof a complex relationship that stretched back for some 2000-plusyears. Pending the publication of the material from the Old I(ngdom Town ...
... Egyptinnpolicy'in l{ubin in, the Old a,ndMi,ddlelQngdorn The E,gyptianNew Kingdom presencein Nubia cannot be consideredi,n vacwo, but hasto be seenasthe third phaseof a complex relationship that stretched back for some 2000-plusyears. Pending the publication of the material from the Old I(ngdom Town ...
TEACHER`S MANUAL
... Who was Howard Carter? He was born on May 9, 1874 in Kensington, a district of London. He grew up outside the city of London in the countryside of north Norfolk. His father Samuel worked as a painter. During his childhood Carter came into contact with the rich and famous Amherst family, which posses ...
... Who was Howard Carter? He was born on May 9, 1874 in Kensington, a district of London. He grew up outside the city of London in the countryside of north Norfolk. His father Samuel worked as a painter. During his childhood Carter came into contact with the rich and famous Amherst family, which posses ...
Masterpieces of the past: Egyptian pyramids Who Built the Pyramids?
... Although there are no depictions of women labourers, some female skeletons which have been found show signs of wear due to working with heavy stone over a long period of time. Some of the builders were permanently employed by the pharaoh while others were taken on just for a limited period of time a ...
... Although there are no depictions of women labourers, some female skeletons which have been found show signs of wear due to working with heavy stone over a long period of time. Some of the builders were permanently employed by the pharaoh while others were taken on just for a limited period of time a ...
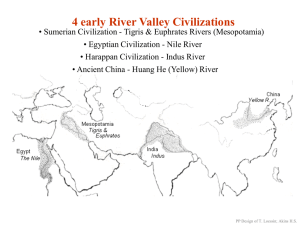
The Four Early River Valley Civilizations
... “The Four Early River Valley Civilizations” City-States in Mesopotamia II. The City-State Structure of Government A. Although all the cities shared the same culture … B. each city had its own government / rulers, warriors, it’s own patron god, and functioned like an independent country C. includes ...
... “The Four Early River Valley Civilizations” City-States in Mesopotamia II. The City-State Structure of Government A. Although all the cities shared the same culture … B. each city had its own government / rulers, warriors, it’s own patron god, and functioned like an independent country C. includes ...
IMPORTANT PHARAOHS Netjerykhet (Djoser) 2630
... first thirteen of his heirs. Ramesses was named co-ruler with his father, Seti I, early in his life. He accompanied his father on numerous campaigns in Libya and Nubia. At the age of 22 Ramesses went on a campaign in Nubia with two of his own sons. Seti I and Ramesses built a palace in Avaris where ...
... first thirteen of his heirs. Ramesses was named co-ruler with his father, Seti I, early in his life. He accompanied his father on numerous campaigns in Libya and Nubia. At the age of 22 Ramesses went on a campaign in Nubia with two of his own sons. Seti I and Ramesses built a palace in Avaris where ...