The Eyes of Pharaoh Teaching Guide
... 2. A light vehicle, usually on two wheels, drawn by one or more horses, often carrying two standing persons 4. A building devoted to worship 7. Object thought to possess power to protect its owner from danger or harm 8. A girl or young woman, especially an unmarried one 9. The spirit of a soul 11. A ...
... 2. A light vehicle, usually on two wheels, drawn by one or more horses, often carrying two standing persons 4. A building devoted to worship 7. Object thought to possess power to protect its owner from danger or harm 8. A girl or young woman, especially an unmarried one 9. The spirit of a soul 11. A ...
The Gods of Ancient Egypt
... Kingdom he became "The king of the gods". He was said to be able to assume any form he wished, with each of the other gods being one of these forms. From the eighteenth dynasty on he was a national deity. Through political means managed to assimilate many lesser gods. One of chief Theban deities; un ...
... Kingdom he became "The king of the gods". He was said to be able to assume any form he wished, with each of the other gods being one of these forms. From the eighteenth dynasty on he was a national deity. Through political means managed to assimilate many lesser gods. One of chief Theban deities; un ...
Hatshepsut - Ancient History at St Marouns
... Graffito written by Tiy on the island of Sehel – suggests she led campaign Damaged text written by the scribe Djehuty Speos Artemidos text suggest she kept her army in a state of readiness ‘Booties’ from campaigns given to temples ...
... Graffito written by Tiy on the island of Sehel – suggests she led campaign Damaged text written by the scribe Djehuty Speos Artemidos text suggest she kept her army in a state of readiness ‘Booties’ from campaigns given to temples ...
animals - Louvre-Lens
... the Old Kingdom. The animal is most certainly a common reference around which men would gather together over the centuries and through the changing civilisations. However, the Egyptians’ relationship with the representatives of the animal kingdom has not always been properly understood and the asses ...
... the Old Kingdom. The animal is most certainly a common reference around which men would gather together over the centuries and through the changing civilisations. However, the Egyptians’ relationship with the representatives of the animal kingdom has not always been properly understood and the asses ...
No Slide Title
... There is none, and they throw the cultivator full length upon the ground, bind him, drag him to the canal, and fling him in head first; his wife is bound with him, his children are put into chains. The neighbors in the meantime leave him and fly to save their grain. It is a characteristic bit of lit ...
... There is none, and they throw the cultivator full length upon the ground, bind him, drag him to the canal, and fling him in head first; his wife is bound with him, his children are put into chains. The neighbors in the meantime leave him and fly to save their grain. It is a characteristic bit of lit ...
1990 Ph.D. in Egyptology, Oriental Institute, University of Chicago
... 50. “A ‘New’ Slab Stela for Nefer from G 2110? (Giza Archives Project Gleanings: I).” In Egypt and Beyond. Essays Presented to Leonard H. Lesko upon his Retirement from the Wilbour Chair of Egyptology at Brown University, June 2005, pp. 227–36. Edited by Stephen E. Thompson and Peter Der Manuelian. ...
... 50. “A ‘New’ Slab Stela for Nefer from G 2110? (Giza Archives Project Gleanings: I).” In Egypt and Beyond. Essays Presented to Leonard H. Lesko upon his Retirement from the Wilbour Chair of Egyptology at Brown University, June 2005, pp. 227–36. Edited by Stephen E. Thompson and Peter Der Manuelian. ...
Document Word
... the pharaon was honoured ; mastaba tombs for relatives of the pharaon and important officials ; funerary pits for lesser officials ; and an enclosure wall . The bestexample of a pyramid complex is that at Giza where boat pits also formed part of the complex . Building a Pyramide The pyramids were bu ...
... the pharaon was honoured ; mastaba tombs for relatives of the pharaon and important officials ; funerary pits for lesser officials ; and an enclosure wall . The bestexample of a pyramid complex is that at Giza where boat pits also formed part of the complex . Building a Pyramide The pyramids were bu ...
The Ancient Egyptians were credited with discovery. Do you think
... In ancient Egypt, Anubis was the jackal-headed god of embalming who guided the souls of the dead through the underworld kingdom of his father, Osiris. Considered benevolent and good, Anubis was present at the weighing of the dead person's soul, and was also at home in the heavenly sky realms of Ra. ...
... In ancient Egypt, Anubis was the jackal-headed god of embalming who guided the souls of the dead through the underworld kingdom of his father, Osiris. Considered benevolent and good, Anubis was present at the weighing of the dead person's soul, and was also at home in the heavenly sky realms of Ra. ...
Genesis Bible Study, Lesson #20
... you wouldn’t listen! Now we must give an accounting for his blood.” 23 They did not realize that Joseph could understand them, since he was using an interpreter. 24 He turned away from them and began to weep, but then turned back and spoke to them again. He had Simeon taken from them and bound befor ...
... you wouldn’t listen! Now we must give an accounting for his blood.” 23 They did not realize that Joseph could understand them, since he was using an interpreter. 24 He turned away from them and began to weep, but then turned back and spoke to them again. He had Simeon taken from them and bound befor ...
Many details of Moses` birth, childhood, and coming of age are not
... parents to hide his birth from the Egyptian bailiffs; he was able to walk and speak when only one day old; he was placed in the Nile, in a basket which floated; he was found by the Pharaoh’s daughter, who admired him immediately; and he was raised as a member of the royal family. In addition to prov ...
... parents to hide his birth from the Egyptian bailiffs; he was able to walk and speak when only one day old; he was placed in the Nile, in a basket which floated; he was found by the Pharaoh’s daughter, who admired him immediately; and he was raised as a member of the royal family. In addition to prov ...
Yosef ha-Tzaddik
... that the Egyptians brought this on themselves by not maintaining private stores for the coming famine, let me cite a stunning midrash from Bereishit Rabbah 91. That midrash asserts that Joseph forced all Egyptian males to circumcise themselves before allowing them to buy grain. Reasonably, they prot ...
... that the Egyptians brought this on themselves by not maintaining private stores for the coming famine, let me cite a stunning midrash from Bereishit Rabbah 91. That midrash asserts that Joseph forced all Egyptian males to circumcise themselves before allowing them to buy grain. Reasonably, they prot ...
Moses First Chapter
... began what historians call the New Kingdom period of Egyptian history. Ahmose I may have been the “new king to whom Joseph meant nothing” who “came to power in Egypt.” It would appear that the Israelites were not forced to leave Egypt with the Hyksos but allowed to remain. But the Egyptians had some ...
... began what historians call the New Kingdom period of Egyptian history. Ahmose I may have been the “new king to whom Joseph meant nothing” who “came to power in Egypt.” It would appear that the Israelites were not forced to leave Egypt with the Hyksos but allowed to remain. But the Egyptians had some ...
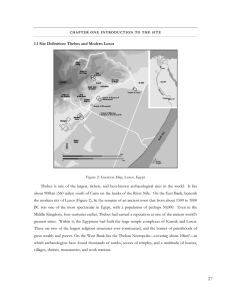
1.1 Site Definition: Thebes and Modern Luxor Thebes is one of the
... C H A P T E R O N E I N T RO D U C T I O N TO T H E S I T E ...
... C H A P T E R O N E I N T RO D U C T I O N TO T H E S I T E ...
Tomb 100, Tomb UJ and Maadi South
... By examining the evidence, it can be confirmed that themes of kingship, religion, and order versus chaos, as found throughout later ancient Egyptian history, are represented at Predynastic seats of authority. However, due to its egalitarian nature, evidence of kingship was not evident at Maadi South ...
... By examining the evidence, it can be confirmed that themes of kingship, religion, and order versus chaos, as found throughout later ancient Egyptian history, are represented at Predynastic seats of authority. However, due to its egalitarian nature, evidence of kingship was not evident at Maadi South ...
Ancient RiverValley Civilizations
... B. each city had its own government / rulers, warriors, it’s own patron god, and functioned like an independent country C. includes within the city walls and also the surrounding farm land D. Examples include Sumerian cities of Ur, Uruk, Kish, Lagesh E. At center of each city was the walled temple w ...
... B. each city had its own government / rulers, warriors, it’s own patron god, and functioned like an independent country C. includes within the city walls and also the surrounding farm land D. Examples include Sumerian cities of Ur, Uruk, Kish, Lagesh E. At center of each city was the walled temple w ...
Egyptian Reading Packet
... sands and scorching heat). Another name for ancient Egypt is Tamera, “the land of the inundation.” From earliest times Ancient Egyptians unified neighboring villages into districts called hesep, or in Greek, nome. Each nome had its own government, capital city, protective god or gods, and temple. Th ...
... sands and scorching heat). Another name for ancient Egypt is Tamera, “the land of the inundation.” From earliest times Ancient Egyptians unified neighboring villages into districts called hesep, or in Greek, nome. Each nome had its own government, capital city, protective god or gods, and temple. Th ...
Exodus - Chapter 09
... uniqueness would not only be demonstrated to Pharaoh and Egypt, but also to the Hebrews. They had to be educated in the Truth, weaned from every element of idolatry, and made to realise that the God they were called upon to worship is the one, living, true God, and that they must not have "any gods ...
... uniqueness would not only be demonstrated to Pharaoh and Egypt, but also to the Hebrews. They had to be educated in the Truth, weaned from every element of idolatry, and made to realise that the God they were called upon to worship is the one, living, true God, and that they must not have "any gods ...
Assessing Summaries of Texts
... many things. It also told how the pharaohs had scribes that wrote down everything they said or did. Which were later put o n their tombs or grave. There were explanations about the celebrations that went on at royal court. Of the music and the games The temples in the article were made for worship o ...
... many things. It also told how the pharaohs had scribes that wrote down everything they said or did. Which were later put o n their tombs or grave. There were explanations about the celebrations that went on at royal court. Of the music and the games The temples in the article were made for worship o ...
Egyptian Architecture
... • After the Mykerinus period, the era of pyramid construction ended • More pyramids were built later but they were smaller and less complex • Later pharaohs could not afford the cost of huge pyramid construction • Grave robbers learned how to break into and steal the goods buried with pharaohs • End ...
... • After the Mykerinus period, the era of pyramid construction ended • More pyramids were built later but they were smaller and less complex • Later pharaohs could not afford the cost of huge pyramid construction • Grave robbers learned how to break into and steal the goods buried with pharaohs • End ...
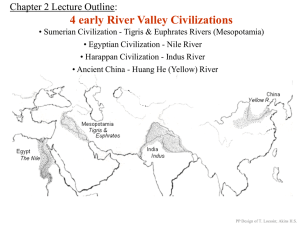
Four early river valley civilizations
... B. each city had its own government / rulers, warriors, it’s own patron god, and functioned like an independent country C. includes within the city walls and also the surrounding farm land D. Examples include Sumerian cities of Ur, Uruk, Kish, Lagesh E. At center of each city was the walled temple w ...
... B. each city had its own government / rulers, warriors, it’s own patron god, and functioned like an independent country C. includes within the city walls and also the surrounding farm land D. Examples include Sumerian cities of Ur, Uruk, Kish, Lagesh E. At center of each city was the walled temple w ...
Four Early River Valley Civilizations
... B. each city had its own government / rulers, warriors, it’s own patron god, and functioned like an independent country C. includes within the city walls and also the surrounding farm land D. Examples include Sumerian cities of Ur, Uruk, Kish, Lagesh E. At center of each city was the walled temple w ...
... B. each city had its own government / rulers, warriors, it’s own patron god, and functioned like an independent country C. includes within the city walls and also the surrounding farm land D. Examples include Sumerian cities of Ur, Uruk, Kish, Lagesh E. At center of each city was the walled temple w ...
1 Ancient Civilizations
... • Women could have the same jobs as men and could join the priesthood but could not be educated • Culturally the greatest epic written during this time was the story of Gilgamesh ...
... • Women could have the same jobs as men and could join the priesthood but could not be educated • Culturally the greatest epic written during this time was the story of Gilgamesh ...
Document
... 1. were considered gods; served both political and religious roles Define Type of government where the political rulers are thought to be type of divinely-guided, or even divine themselves is a theocracy. government 2. Believed each pharaoh ruled even after death, because they all possessed the same ...
... 1. were considered gods; served both political and religious roles Define Type of government where the political rulers are thought to be type of divinely-guided, or even divine themselves is a theocracy. government 2. Believed each pharaoh ruled even after death, because they all possessed the same ...
Resurrection Machines - ScholarWorks@GVSU
... their religion place far more emphasis on the next life than the present one? Most significantly, why did the Egyptians believe they had the power to produce resurrection? For the answer to these questions, we will focus on the Egyptians‟ tombs and the contents within them, utilizing the approaches ...
... their religion place far more emphasis on the next life than the present one? Most significantly, why did the Egyptians believe they had the power to produce resurrection? For the answer to these questions, we will focus on the Egyptians‟ tombs and the contents within them, utilizing the approaches ...
Complete mapping of 4 River Civilizations
... B. each city had its own government / rulers, warriors, it’s own patron god, and functioned like an independent country C. includes within the city walls and also the surrounding farm land D. Examples include Sumerian cities of Ur, Uruk, Kish, Lagesh E. At center of each city was the walled temple w ...
... B. each city had its own government / rulers, warriors, it’s own patron god, and functioned like an independent country C. includes within the city walls and also the surrounding farm land D. Examples include Sumerian cities of Ur, Uruk, Kish, Lagesh E. At center of each city was the walled temple w ...